As the American hemp industry grows, so does our understanding of hemp diseases
2021-01-19
(Press-News.org) As hemp begins to reemerge as an important crop in the United States, scientists are beginning research into the diseases that might prevent the crop from flourishing. A study published in the December issue of Plant Health Progress is one of the first to study the potential disease and disorder limitations for hemp production in the southeastern United States.
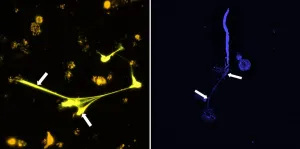
Lindsey Thiessen, a plant pathologist at North Carolina State University, worked with colleagues to evaluate hemp samples from North Carolina and observed 16 different diseases. They found Fusarium flower blight most consistently followed by Helminthosporium leaf spot. They also surveyed hemp producers who self-identified Fusarium species as the most common issue in their fields.
"Interestingly, diseases that are frequently reported in other hemp-producing regions in the western U.S. or worldwide, such as gray mold or powdery mildew, were not prominent diseases in our study," said Thiessen.
The study also found nutritional deficiencies and toxicities in more than 58 percent of samples evaluated and identified issues with excess water, root binding, and herbicide injuries. All these issues may complicate production for growers in the southeastern United States and similar regions. This study also underscores regional variability of important diseases and disorders, showing that best production practices will vary by region.
"Little research on hemp has been recently conducted in the U.S., and this study identifies pathogens with molecular tools and morphology using more recent taxonomic classifications," Thiessen said when asked what made this research unique. "This work also identifies the ranges of nutritional content in soil and foliar tissues of currently available hemp strains."
Thiessen points out that while hemp used to be grown in the United States, many of the diseases have been understudied. This research, summarized in "Surveying for Potential Diseases and Abiotic Disorders of Industrial Hemp (Cannabis sativa) Production," begins to build a new and important body of knowledge for this growing industry.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-19
A new study published in PNAS finds that aid provided by the United Nations (UN) in the aftermath of climate-related disasters is driven by humanitarian need rather than by strategic donor interests. The results underline the importance of climate-related hazards for understanding aid disbursements.
The study 'Humanitarian need drives multilateral disaster aid' provides the first estimation of UN climate-related disaster aid worldwide. Although it cannot be entirely ruled out that powerful donor states' interests shape UN aid flows, the UN seems able to fend off donor states' strategic ...
2021-01-19
Filariae, slender but sometimes up to 70 centimeters long nematodes, can set up residence in their host quite tenaciously and cause serious infectious diseases in the tropics. The tiny larvae of the worms are usually transmitted from person to person by mosquitoes, which pick up the larvae from the blood or subcutaneous tissue when they bite and deposit them in the vessels or tissues of their next victim. Researchers led by the University of Bonn (Germany) have now investigated a mechanism by which the immune system attacks the filariae. Certain immune cells, the eosinophil granulocytes, release DNA that forms a kind of web around the larvae and traps them. The researchers ...
2021-01-19
Our brains experience significant changes in blood flow and neural activity during sleep, according to Penn State researchers. Such changes may help to clean out metabolic brain waste that builds up during the day.
"We studied the sleep patterns of mice during both rapid eye movement and non-rapid eye movement sleep stages, as well as in different alertness states," said Patrick Drew, Huck Distinguished Associate Professor of Engineering Science and Mechanics, Neurosurgery and Biomedical Engineering.
Mice were chosen for the study because of their brains' remarkable similarity with human brains, said the researchers.
In both mice and humans, non-REM sleep ...
2021-01-19
A team of researchers from RUDN University and RLT suggested restoring normal levels of lymphocytes in patients with COVID-19 and other viral diseases by subjecting them to the combined influence of light, magnetic field, and ultrasound. The results of the study were published in the Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology.
Some COVID-19 patients are asymptomatic, while others suffer from complications. To effectively fight coronavirus with drugs and therapeutic methods, scientists and medics have to find out what causes these differences in the course of the disease. A team of scientists from RUDN University together with their colleagues from the international company Radiant Life Technologies (RLT) suggested that the reason might ...
2021-01-19
A scientific study carried out by the Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (UC3M) and the Universidad Complutense de Madrid (UCM) has produced a mathematical description of the way in which a tumor invades the epithelial cells and automatically quantifies the progression of the tumor and the remaining cell islands after its progression. The model developed by these researchers could be used to better understand the biophysical characteristics of the cells involved when developing new treatments for wound healing, organ regeneration, or cancer progression.
This research analyses the collective ...
2021-01-19
An Academic Analytics Research Center (AARC) study has found greater rates of authorship of open access (OA) research articles among scholars at more prestigious institutions with greater access to resources and job security. "The open access publishing model is growing, and open access successfully democratizes the results of research projects, but it's clear now that some scholars are more likely to be represented in the open access literature" said AARC director and lead author of the study Anthony Olejniczak, Ph.D.
The researchers analyzed characteristics of 182,320 open access authors at American research universities from 2014 through 2018. The study ...
2021-01-19
In a series of experiments with laboratory-cultured bacteria, Johns Hopkins scientists have found evidence that there is a second role for the widely used gene-cutting system CRISPR-Cas9 -- as a genetic dimmer switch for CRISPR-Cas9 genes. Its role of dialing down or dimming CRISPR-Cas9 activity may help scientists develop new ways to genetically engineer cells for research purposes.
A summary of the findings was published Jan. 8 in Cell.
First identified in the genome of gut bacteria in 1987, CRISPR-Cas9 is a naturally occurring but unusual group of genes with a potential for cutting DNA sequences in ...
2021-01-19
Cerebral infarction, commonly known as ischemic stroke, has a high mortality rate and causes severe damage to nervous cells in the brain owing to the loss of oxygen, which results in limiting body movements. Several technologies, including physiotherapy and brain stimulation techniques, are being developed and tested for the rehabilitation of brain nervous cells damaged by a stroke. In particular, low-intensity focused ultrasound is expected to be effective for rehabilitating neurological diseases such as stroke, as it can excite or inhibit nerve cells by delivering mechanical energy with high precision at the desired position, while ultrasound is penetrating the cranium without requiring a surgical operation.
Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) announced that the research ...
2021-01-19
Why is studying spin properties of one-dimensional quantum nanowires important?
Quantum nanowires-which have length but no width or height-provide a unique environment for the formation and detection of a quasiparticle known as a Majorana zero mode.
A new UNSW-led study overcomes previous difficulty detecting the Majorana zero mode, and produces a significant improvement in device reproducibility.
Potential applications for Majorana zero modes include fault-resistant topological quantum computers, and topological superconductivity.
MAJORANA FERMIONS IN 1D WIRES
A Majorana fermion is a composite particle that is its own antiparticle.
Antimatter explainer: Every fundamental particle has a corresponding antimatter particle, with ...
2021-01-19
A KAIST team's mathematical modelling shows that the topographic tiling of cortical maps originates from bottom-up projections from the periphery.
Researchers have explained how the regularly structured topographic maps in the visual cortex of the brain could arise spontaneously to efficiently process visual information. This research provides a new framework for understanding functional architectures in the visual cortex during early developmental stages.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Se-Bum Paik from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has demonstrated that the orthogonal organization of retinal mosaics in the periphery is mirrored onto the primary visual cortex and initiates ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] As the American hemp industry grows, so does our understanding of hemp diseases