(Press-News.org) In order to achieve the goals of the Paris Agreement, the world must reach net-zero carbon emissions by 2050. Carbon pricing is viewed by many governments and experts as the most important climate policy instrument. However, a new study shows that carbon pricing has been less effective as a driver of technological change than was previously anticipated.
While the introduction of carbon pricing systems has led to emissions reductions in some countries, they have not significantly stimulated technological change. Bringing about the necessary transformation will require sector-specific promotion of climate-friendly technologies, for example changes in electricity market design and a better charging network for electric cars. These changes require significant investment. Carbon pricing has a disappointing track record in this respect, as shown in a new study by scientists Johan Lilliestam (IASS/University of Potsdam), Anthony Patt (ETH Zurich) and Germán Bersalli (IASS Potsdam). They examined empirical studies on the effects of carbon pricing systems in the European Union, New Zealand, the Canadian province of British Columbia, and the Nordic countries.
"The significant reductions in emissions that we are seeing are being driven not by urgently needed investment in zero-carbon technologies but by operational shifts towards less carbon-intensive applications. But the effect of switching from gasoline to diesel or from coal to gas-fired power generation is practically irrelevant when it comes to achieving climate neutrality", says lead author Johan Lilliestam. Achieving net zero emissions will require more sweeping, systemic changes
Higher carbon prices fail to boost investment in zero emissions technologies
Most of the research examined in this study identify an overallocation of emission certificates, leading to low carbon prices, as a key factor in the failure of carbon pricing to drive change. But according to Lilliestam, Patt and Bersalli, this explanation does not tell the whole story. In the Nordic countries, for example, where carbon prices are relatively high, carbon pricing schemes have had little noticeable effect on the pace of technological change.
Instead, the authors suggest, it is other other policy measures - in particular programmes to promote renewable energy generation - that have driven the energy transition in this region. These targeted measures offered investors stronger investment incentives than the carbon pricing systems introduced concurrently, and the growth of renewables triggered by these measures in turn resulted in significant reductions in the cost of wind and solar power. In addition, fluctuations in the price of fossil fuels often exceed the cost of carbon surcharges. Such fluctuations, for example in the price of petrol, undermine the steering effects of carbon pricing schemes
Carbon pricing has its place in the policy toolbox
Despite this disappointing track record, the authors identify two use cases for carbon pricing. "On the one hand, carbon pricing can be used to generate revenue for urgently needed support measures and public investment. On the other hand, in certain sectors, such as coal-fired power generation, it could be used to diminish the competitive advantage of carbon intensive technologies as emerging technologies reach market maturity," explains Lilliestam. While carbon pricing is not suitable as a central policy solution, the authors conclude, it could contribute to efforts to achieve climate goals as one part of a broad package of measures.
INFORMATION:
For this specific method of cryopreservation, oocytes are collected directly after an animal is castrated or deceased and immediately frozen at -196°C in liquid nitrogen. This technique allows the storage of oocytes of valuable animals for an unlimited time, so that they can be used to produce offspring with the help of assisted reproduction techniques. The aim is to further improve and apply these methods to save highly endangered species such as the Asiatic lion from extinction. The current research on African lions as a model species is an important step in this direction. The results are reported in the scientific journal Cryobiology.
Lion oocytes are presumed to be very sensitive to chilling due to their high lipid content, resulting ...
Acetals are important chemical compounds that are used, for example, in the production of certain medical agents. A new method now makes their synthesis easier and more environmentally friendly. Chemists at the University of Bonn have developed and optimized the sustainable catalytic process. State-of-the-art computer simulations were also used. The reaction is based on a mechanism that frequently occurs in nature, but has rarely been used in chemical synthesis up to now. The results are published in the journal Angewandte Chemie.
The key step in the production of acetals is the bonding of two oxygen ...
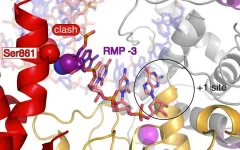
Remdesivir is the first drug against Covid-19 to be conditionally approved in Europe and the United States. The drug is designed to suppress the rapid replication of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in human cells by blocking the viral copying machine, called RNA polymerase. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute (MPI) for Biophysical Chemistry in Göttingen and the University of Würzburg have now elucidated how remdesivir interferes with the viral polymerase during copying and why it does not inhibit it completely.
"After complicated studies, we come to a simple conclusion," Max Planck Director Patrick ...
UPTON, NY--Marking a major achievement in the field of spintronics, researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory and Yale University have demonstrated the ability to control spin dynamics in magnetic materials by altering their thickness. The study, published today in Nature Materials, could lead to smaller, more energy-efficient electronic devices.
"Instead of searching for different materials that share the right frequencies, we can now alter the thickness of a single material--iron, in this case--to find a magnetic medium that will enable the transfer of information across a device," said Brookhaven physicist and principal investigator Valentina ...
Scientists have discovered a molecule that can selectively kill cells of a hard-to-treat subtype of breast cancer, which could lead to a new therapy.
The study, led by researchers at RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences, is published in the current edition of Science Advances.
Triple negative breast cancer is a subtype of breast cancer which is mainly treated with chemotherapy. Unfortunately, up to 70% of patients with this form of breast cancer develop resistance to treatment.
The researchers tested different molecules to see if they could selectively kill the cells of this type of breast cancer while sparing normal ...
As hemp begins to reemerge as an important crop in the United States, scientists are beginning research into the diseases that might prevent the crop from flourishing. A study published in the December issue of Plant Health Progress is one of the first to study the potential disease and disorder limitations for hemp production in the southeastern United States.
Lindsey Thiessen, a plant pathologist at North Carolina State University, worked with colleagues to evaluate hemp samples from North Carolina and observed 16 different diseases. They found Fusarium flower blight most consistently followed by Helminthosporium ...
A new study published in PNAS finds that aid provided by the United Nations (UN) in the aftermath of climate-related disasters is driven by humanitarian need rather than by strategic donor interests. The results underline the importance of climate-related hazards for understanding aid disbursements.
The study 'Humanitarian need drives multilateral disaster aid' provides the first estimation of UN climate-related disaster aid worldwide. Although it cannot be entirely ruled out that powerful donor states' interests shape UN aid flows, the UN seems able to fend off donor states' strategic ...
Filariae, slender but sometimes up to 70 centimeters long nematodes, can set up residence in their host quite tenaciously and cause serious infectious diseases in the tropics. The tiny larvae of the worms are usually transmitted from person to person by mosquitoes, which pick up the larvae from the blood or subcutaneous tissue when they bite and deposit them in the vessels or tissues of their next victim. Researchers led by the University of Bonn (Germany) have now investigated a mechanism by which the immune system attacks the filariae. Certain immune cells, the eosinophil granulocytes, release DNA that forms a kind of web around the larvae and traps them. The researchers ...
Our brains experience significant changes in blood flow and neural activity during sleep, according to Penn State researchers. Such changes may help to clean out metabolic brain waste that builds up during the day.
"We studied the sleep patterns of mice during both rapid eye movement and non-rapid eye movement sleep stages, as well as in different alertness states," said Patrick Drew, Huck Distinguished Associate Professor of Engineering Science and Mechanics, Neurosurgery and Biomedical Engineering.
Mice were chosen for the study because of their brains' remarkable similarity with human brains, said the researchers.
In both mice and humans, non-REM sleep ...
A team of researchers from RUDN University and RLT suggested restoring normal levels of lymphocytes in patients with COVID-19 and other viral diseases by subjecting them to the combined influence of light, magnetic field, and ultrasound. The results of the study were published in the Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology.
Some COVID-19 patients are asymptomatic, while others suffer from complications. To effectively fight coronavirus with drugs and therapeutic methods, scientists and medics have to find out what causes these differences in the course of the disease. A team of scientists from RUDN University together with their colleagues from the international company Radiant Life Technologies (RLT) suggested that the reason might ...