(Press-News.org) Two giant radio galaxies have been discovered with South Africa's powerful MeerKAT telescope. These galaxies are thought to be amongst the largest single objects in the Universe. The discovery has been published today in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
Whereas normal radio galaxies are fairly common, only a few hundred of these have radio jets exceeding 700 kilo-parsecs in size, or around 22 times the size of the Milky Way. These truly enormous systems are dubbed 'giant radio galaxies'.
Despite the scarcity of giant radio galaxies, the authors found two of these cosmic beasts in a remarkably small patch of sky.
Dr Jacinta Delhaize, a Research Fellow at the University of Cape Town and lead author of the work, said: "We found these giant radio galaxies in a region of sky which is only about 4 times the area of the full Moon. Based on our current knowledge of the density of giant radio galaxies in the sky, the probability of finding two of them in this region is less than 0.0003 per cent."
"This means that giant radio galaxies are probably far more common than we thought!"
Dr Matthew Prescott, a Research Fellow at the University of the Western Cape and co-author of the work, said, "These two galaxies are special because they are amongst the largest giants known, and in the top 10 per cent of all giant radio galaxies. They are more than 2 Mega-parsecs across, which is around 6.5 million light years or about 62 times the size of the Milky Way. Yet they are fainter than others of the same size."
"We suspect that many more galaxies like these should exist, because of the way we think galaxies grow and change over their lifetimes."
Why so few radio galaxies have such gigantic sizes remains something of a mystery. It is thought that the giants are the oldest radio galaxies, which have existed for long enough (several hundred million years) for their radio jets to grow outwards to these enormous sizes. If this is true, then many more giant radio galaxies should exist than are currently known.
The giant radio galaxies were spotted in new radio maps of the sky created by the MeerKAT International Gigahertz Tiered Extragalactic Exploration (MIGHTEE) survey. It is one of the large survey projects underway with South Africa's impressive MeerKAT radio telescope, a precursor to the Square Kilometre Array (SKA), which is due to become fully operational in the mid-2020s.
Dr Ian Heywood, a co-author at the University of Oxford, said "The MeerKAT telescope is the best of its kind in the world. We have managed to identify these giant radio galaxies for the first time because of MeerKAT's unprecedented sensitivity to faint and diffuse radio light."
Dr Delhaize adds, "In the past, this population of galaxies has been hidden from our 'sight' by the technical limitations of radio telescopes. However, it is now being revealed thanks to the impressive capabilities of the new generation of telescopes."
Construction of the highly anticipated trans-continental SKA telescope is due to commence in South Africa and Australia in 2021, and continue until 2027. Science commissioning observations could begin as early as 2023, and it is hoped that the telescope will reveal larger populations of radio galaxies than ever before and revolutionise our understanding of galaxy evolution.
INFORMATION:
Scientists from the Leibniz Institute for Zoo and Wildlife Research (Leibniz-IZW) have found that interacting with other males is more "stressful" for low-ranking than for high-ranking male spotted hyenas. This restricts the time and energy low-ranking males can invest in courting the most desirable females and is therefore a key factor for their lower reproductive success than their high-ranking rivals. This mechanism seems to be more important in determining the number and quality of offspring than physical traits such as attractiveness and fighting ability. These insights were possible owing to a combination of extensive field and lab work - over 20 years of searching and identifying thousands ...
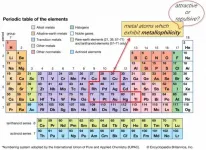
A research team led by Professor Chi-Ming CHE and Dr Jun YANG, from the Research Division for Chemistry and Department of Chemistry at the Faculty of Science of the University of Hong Kong, has resolved a long-standing fundamental problem in the field of metal-metal closed-shell interaction. This work has been published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
Metal-Metal closed-shell interaction, also known as metallophilicity, has a huge impact in diverse fields of chemistry, such as supramolecular chemistry and organometallic chemistry. Early reports on metallophilicity could be traced back to the 1970s. Many leading theoretical chemists ...
According to current studies, the COVID-19 disease which is caused by the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus comprises at least five different variants. These differ in how the immune system responds to the infection. Researchers from the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE) and the University of Bonn, together with other experts from Germany, Greece and the Netherlands, present these findings in the scientific journal "Genome Medicine". Their results may help to improve the treatment of the disease.
Infection with SARS-CoV-2 can manifest in different ways: Many of those affected do not even seem to notice the presence of the virus in their bodies. In other ...
In order to achieve the goals of the Paris Agreement, the world must reach net-zero carbon emissions by 2050. Carbon pricing is viewed by many governments and experts as the most important climate policy instrument. However, a new study shows that carbon pricing has been less effective as a driver of technological change than was previously anticipated.
While the introduction of carbon pricing systems has led to emissions reductions in some countries, they have not significantly stimulated technological change. Bringing about the necessary transformation will require sector-specific promotion of climate-friendly technologies, for example ...
For this specific method of cryopreservation, oocytes are collected directly after an animal is castrated or deceased and immediately frozen at -196°C in liquid nitrogen. This technique allows the storage of oocytes of valuable animals for an unlimited time, so that they can be used to produce offspring with the help of assisted reproduction techniques. The aim is to further improve and apply these methods to save highly endangered species such as the Asiatic lion from extinction. The current research on African lions as a model species is an important step in this direction. The results are reported in the scientific journal Cryobiology.
Lion oocytes are presumed to be very sensitive to chilling due to their high lipid content, resulting ...
Acetals are important chemical compounds that are used, for example, in the production of certain medical agents. A new method now makes their synthesis easier and more environmentally friendly. Chemists at the University of Bonn have developed and optimized the sustainable catalytic process. State-of-the-art computer simulations were also used. The reaction is based on a mechanism that frequently occurs in nature, but has rarely been used in chemical synthesis up to now. The results are published in the journal Angewandte Chemie.
The key step in the production of acetals is the bonding of two oxygen ...
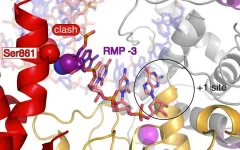
Remdesivir is the first drug against Covid-19 to be conditionally approved in Europe and the United States. The drug is designed to suppress the rapid replication of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in human cells by blocking the viral copying machine, called RNA polymerase. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute (MPI) for Biophysical Chemistry in Göttingen and the University of Würzburg have now elucidated how remdesivir interferes with the viral polymerase during copying and why it does not inhibit it completely.
"After complicated studies, we come to a simple conclusion," Max Planck Director Patrick ...
UPTON, NY--Marking a major achievement in the field of spintronics, researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory and Yale University have demonstrated the ability to control spin dynamics in magnetic materials by altering their thickness. The study, published today in Nature Materials, could lead to smaller, more energy-efficient electronic devices.
"Instead of searching for different materials that share the right frequencies, we can now alter the thickness of a single material--iron, in this case--to find a magnetic medium that will enable the transfer of information across a device," said Brookhaven physicist and principal investigator Valentina ...
Scientists have discovered a molecule that can selectively kill cells of a hard-to-treat subtype of breast cancer, which could lead to a new therapy.
The study, led by researchers at RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences, is published in the current edition of Science Advances.
Triple negative breast cancer is a subtype of breast cancer which is mainly treated with chemotherapy. Unfortunately, up to 70% of patients with this form of breast cancer develop resistance to treatment.
The researchers tested different molecules to see if they could selectively kill the cells of this type of breast cancer while sparing normal ...
As hemp begins to reemerge as an important crop in the United States, scientists are beginning research into the diseases that might prevent the crop from flourishing. A study published in the December issue of Plant Health Progress is one of the first to study the potential disease and disorder limitations for hemp production in the southeastern United States.
Lindsey Thiessen, a plant pathologist at North Carolina State University, worked with colleagues to evaluate hemp samples from North Carolina and observed 16 different diseases. They found Fusarium flower blight most consistently followed by Helminthosporium ...