Set clear rules for vaccinating health care workers against SARS-CoV-2
2021-01-19
(Press-News.org) Provincial and territorial governments should set clear rules for vaccinating health care workers against SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, in public and private settings, and should not leave this task to employers, according to an analysis in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
"An effective vaccine provided to health care workers will protect both the health workforce and patients, reducing the overall burden of COVID-19 on services and ensuring adequate personnel to administer to people's health needs through the pandemic," writes Dr. Colleen M. Flood, University of Ottawa Research Chair in Health Law & Policy and a professor at the university, with coauthors.
The analysis, authored by legal scholars and a physician-researcher, describes legal precedents from attempts to mandate influenza vaccines for health care workers and how those precedents might apply to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination. It also describes the legal justification for mandating SARS-CoV-2 vaccination for health care workers and other legal considerations.
When creating policy for mandatory vaccination of health care workers, it will be important to include exemptions for people who cannot receive a vaccine because of underlying health issues or other reasons. These exemptions will help protect government mandates if there is a challenge under the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms. Based on current evidence, these challenges would likely be unsuccessful if there are exemptions in place for employees. It is important to note that any vaccinate or stay at home order would not force a health care worker to be vaccinated.
"What is less clear is whether or not a health care worker could argue that they should be able, in lieu of vaccination, to wear personal protective equipment," says Dr. Flood. "Initially, even those vaccinated will continue to wear PPE, but we think courts should accept the application of the precautionary principle so as to require vaccination in most circumstances. It will, however, be essential to collect and weigh real-world evidence of the benefits of both vaccines and PPE."
The authors distinguish between overall mandated government actions that might qualify under the Charter and actions from nongovernmental organizations, such as a private long-term care home requiring its own health care workers to be vaccinated, in which case the Charter would not apply.
"This is an important issue to address with science and law working together," says Dr. Kumanan Wilson, senior scientist, The Ottawa Hospital, and Clinical Research Chair in Digital Health Innovation, University of Ottawa. "Given the rapid development of various COVID-19 vaccines and emerging evidence, new data will determine whether these policies will stay in effect or will be modified."
Support for people who may experience a rare adverse event from mandatory vaccination is important. "We applaud the recent announcement of a no-fault vaccine compensation scheme and await the implementation of the program. Although not a cure all, it does provide some security for health care workers obligated to vaccinate pursuant to carrying out their vital work," the authors write.
Listen to a podcast with Dr. Colleen M. Flood on the legal aspect of mandatory vaccination of health care workers
https://soundcloud.com/cmajpodcasts/202755-ana
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-19
HAMILTON, ON, Jan. 19, 2021 -- McMaster researchers have developed a new form of cultivated meat using a method that promises more natural flavour and texture than other alternatives to traditional meat from animals.
Researchers Ravi Selvaganapathy and Alireza Shahin-Shamsabadi, both of the university's School of Biomedical Engineering, have devised a way to make meat by stacking thin sheets of cultivated muscle and fat cells grown together in a lab setting. The technique is adapted from a method used to grow tissue for human transplants.
The sheets of living cells, each about the thickness of a sheet of printer paper, are first grown in culture and then concentrated on growth plates before being peeled ...
2021-01-19
NANOTECHNOLOGY PREVENTS PREMATURE BIRTH IN MOUSE STUDIES
Media Contact: Rachel Butch, rbutch1@jhmi.edu
In a study in mice and human cells, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers say that they have developed a tiny, yet effective method for preventing premature birth. The vaginally delivered treatment contains nanosized (billionth of a meter) particles of drugs that easily penetrate the vaginal wall to reach the uterine muscles and prevent them from contracting. If proven effective in humans, the treatment could be one of the only clinical options available to prevent ...
2021-01-19
From a pair of simple principles of evolution--chance mutation and natural selection--nature has constructed an almost unfathomable richness of life around us. Despite our scientific sophistication, human design and engineering have struggled to emulate nature's techniques and her inexhaustible inventiveness. But that may be changing.
In a new perspective article, Stephanie Forrest and Risto Miikkulainen explore a domain known as evolutionary computation (EC), in which aspects of Darwinian evolution are simulated in computer systems.
The study highlights the progress our machines have made in replicating evolutionary processes and what this could mean for engineering design, software refinement, gaming strategy, robotics and even medicine, while fostering a deeper insight ...
2021-01-19
Using cutting-edge DNA sequencing technologies, a group of laboratories in Konstanz, Würzburg, Hamburg and Vienna, led by evolutionary biologist Professor Axel Meyer from the University of Konstanz, succeeded in fully sequencing the genome of the Australian lungfish. The genome, with a total size of more than 43 billion DNA building blocks, is nearly 14 times larger than that of humans and the largest animal genome sequenced to date. Its analysis provides valuable insights into the genetic and developmental evolutionary innovations that made it possible for fish to colonize land. The findings, published online in the journal Nature, expand our understanding of this major evolutionary ...
2021-01-19
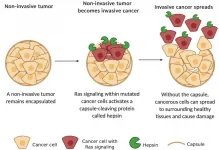
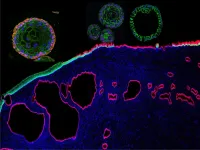
Researchers at the University of Helsinki have defined a cancer invasion machinery, which is orchestrated by a frequently mutated cancer gene called Ras. When signaling from Ras protein becomes abnormally high, like it does in many cancers, this switches on the cellular machinery that helps the cancer cells to depart from the tissue from which the cells have developed.
It has been unclear how the cancer invasion machinery works exactly, until now, as the study finds Ras in the role of Friar Lawrence in Shakespeare's famous play, "Get me an iron crow and bring it straight unto my cell (Romeo and Juliet, 5.2.21-23)." ...
2021-01-19
Climate change is more pronounced in the Arctic than anywhere else on the planet, raising concerns about the ability of wildlife to cope with the new conditions. A new study shows that rare insects are declining, suggesting that climatic changes may favour common species.
As part of a new volume of studies on the global insect decline, researchers are presenting the first Arctic insect population trends from a 24-year monitoring record of standardized insect abundance data from North-East Greenland.
The work took place during 1996-2018 as part of the ecosystem-based monitoring program Greenland Ecosystem Monitoring at the field station Zackenberg, located in the world's largest national ...
2021-01-19
Organoids are increasingly being used in biomedical research. These are organ-like structures created in the laboratory that are only a few millimetres in size. Organoids can be used to study life processes and the effect of drugs. Because they closely resemble real organs, they offer several advantages over other cell cultures.
Now there are also organoid models developed for the cervix. This part of the female body is particularly at risk to develop cancers. By creating novel organoid models, a group led by Cindrilla Chumduri (Würzburg), Rajendra Kumar Gurumurthy (Berlin) and Thomas F. Meyer ...
2021-01-19
WHAT:
Healthcare providers must be able to explain the latest data supporting the safety and efficacy of vaccines for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) so they can strongly encourage vaccination when appropriate while acknowledging that uncertainty and unknowns remain. This message comes from a new commentary co-authored by Anthony S. Fauci, M.D., director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, and other leading NIAID scientists in the journal Annals of Internal Medicine.
The commentary provides an overview of the seven COVID-19 vaccines furthest along in development in the United States. For each vaccine candidate, the authors describe ...
2021-01-19
Understanding how the natural world works enables us to mimic it for the benefit of humankind. Think of how much we rely on batteries. At the core is understanding molecular structures and the behavior of electrons within them. Calculating the energy differences between a molecule's electronic ground and excited spin states helps us understand how to better use that molecule in a variety of chemical, biomedical and industrial applications. We have made much progress in molecules with closed-shell systems, in which electrons are paired up and stable. Open-shell systems, on the ...
2021-01-19
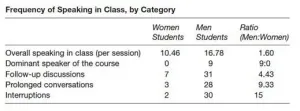
Men speak 1.6 times more often than women in college classrooms, revealing how gender inequities regarding classroom participation still exist, according to a Dartmouth study. By comparison, women are more hesitant to speak and are more apt to use apologetic language. The findings are published in Gender & Society.
When students didn't have to raise their hands to participate in class, men spoke three times more often than women. "You would think that it would be more equitable for students to not have to raise their hands to speak in class because then anyone could talk ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Set clear rules for vaccinating health care workers against SARS-CoV-2