INFORMATION:
In addition to Kastner, Moraga, and Bublitz, the research team involved in the HST imaging work includes Rodolfo Montez Jr. '10 Ph.D. (astrophysical sciences and technology) from Harvard-Smithsonian CfA; Bruce Balick from University of Washington; as well as Adam Frank and Eric Blackman from University of Rochester. Bublitz's international team of collaborators on radio molecular line imaging of NGC 7027 includes Kastner, Montez Jr., and astrophysicists from Spain, France, and Brazil.
For more information, contact Luke Auburn at 585-490-3198, luke.auburn@rit.edu, or on Twitter: @lukeauburn.
Astronomers dissect the anatomy of planetary nebulae using Hubble Space Telescope images
Researchers from RIT and Green Bank Observatory shed new light on nebula formation processes
2021-01-19
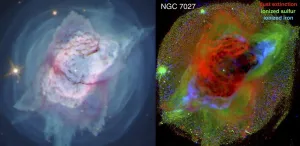
(Press-News.org) Images of two iconic planetary nebulae taken by the Hubble Space Telescope are revealing new information about how they develop their dramatic features. Researchers from Rochester Institute of Technology and Green Bank Observatory presented new findings about the Butterfly Nebula (NGC 6302) and the Jewel Bug Nebula (NGC 7027) at the 237th meeting of the American Astronomical Society on Friday, Jan. 15.
Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3 observed the nebulae in 2019 and early 2020 using its full, panchromatic capabilities, and the astronomers involved in the project have been using emission line images from near-ultraviolet to near-infrared light to learn more about their properties. The studies were first-of-their-kind panchromatic imaging surveys designed to understand the formation process and test models of binary-star-driven planetary nebula shaping.
"We're dissecting them," said Joel Kastner, a professor in RIT's Chester F. Carlson Center for Imaging Science and School of Physics and Astronomy. "We're able to see the effect of the dying central star in how it's shedding and shredding its ejected material. We're able to see that material that the central star has tossed away is being dominated by ionized gas, where it's dominated by cooler dust, and even how the hot gas is being ionized, whether by the star's UV or by collisions caused by its present, fast winds."
Kastner said analysis of the new HST images of the Butterfly Nebula is confirming that the nebula was ejected only about 2,000 years ago--an eyeblink by the standards of astronomy - and that the S-shaped iron emission that helps give it the "wings" of gas may be even younger. Surprisingly, they found that while astronomers previously believed they had located the nebula's central star, it was actually a star not associated with the nebula that is much closer to Earth than the nebula. Kastner said he hopes that future studies with the James Webb Space Telescope could help locate the actual central star.
The team's ongoing analysis of the Jewel Bug Nebula is built on a 25-year baseline of measurements dating back to early Hubble imaging. Paula Moraga Baez, an astrophysical sciences and technology Ph.D. student from DeKalb, Ill., called the nebula "remarkable for its unusual juxtaposition of circularly symmetric, axisymmetric, and point-symmetric (bipolar) structures." Moraga noted, "The nebula also retains large masses of molecular gas and dust despite harboring a hot central star and displaying high excitation states."
Jesse Bublitz '20 Ph.D. (astrophysical sciences and technology), now a postdoctoral researcher at Green Bank Observatory, has continued analysis of NGC 7027 with radio images from the Northern Extended Millimeter Array (NOEMA) Telescope, where he identified molecular tracers of ultraviolet and X-ray light that continue to shape the nebula. The combined observations from telescopes at other wavelengths, like Hubble, and bright molecules CO+ and HCO+ from NOEMA indicate how different regions of NGC 7027 are affected by the irradiation of its central star.
"We're very excited about these findings," said Bublitz. "We had hoped to find structure that clearly showed CO+ and HCO+ spatially coincident or entirely in distinctive regions, which we did. This is the first map of NGC 7027, or any planetary nebula, in the molecule CO+, and only the second CO+ map of any astronomical source."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Unlocking 'the shape of water' in mechanisms of antibiotic resistance
2021-01-19
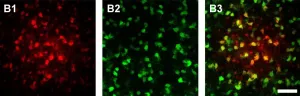
New high-resolution structures of the bacterial ribosome determined by researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago show that a single water molecule may be the cause -- and possible solution -- of antibiotic resistance.
The findings of the new UIC study are published in the journal Nature Chemical Biology.
Pathogenic germs become resistant to antibiotics when they develop the ability to defeat the drugs designed to kill them. Each year in the U.S., millions of people suffer from antibiotic-resistant infections, and thousands of people die as a result.
Developing new drugs is a key way the scientific community is trying to reduce the impact of antibiotic resistance.
"The first thing we need to do to make improved drugs is to better understand how antibiotics work and how 'bad ...
Heart attack patients in England 'fearful' of seeking medical help amid COVID crisis
2021-01-19
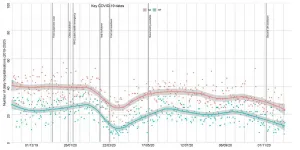
Data analysis is revealing a second sharp drop in the number of people admitted to hospital in England with acute heart failure or a heart attack.
The decline began in October as the numbers of COVID-19 infections began to surge ahead of the second lockdown, which came into force in early November.
The findings, from a research group led by the University of Leeds, have been revealed in a letter to the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The decline - 41 percent fewer people attending with heart failure and 34 percent with a heart attack compared to pre-pandemic levels ...
Brain cell network supplies neurons with energy
2021-01-19
The human brain has about as many neurons as glial cells. These are divided into four major groups: the microglia, the astrocytes, the NG2 glial cells, and the oligodendrocytes. Oligodendrocytes function primarily as a type of cellular insulating tape: They form long tendrils, which consist largely of fat-like substances and do not conduct electricity. These wrap around the axons, which are the extensions through which the nerve cells send their electrical impulses. This prevents short circuits and accelerates signal forwarding.
Astrocytes, on the other hand, supply the nerve cells with energy: Through their appendages they come into contact with blood vessels and absorb glucose from these. ...
Light-controlled Higgs modes found in superconductors; potential sensor, computing uses
2021-01-19
AMES, Iowa - Even if you weren't a physics major, you've probably heard something about the Higgs boson.
There was the title of a 1993 book by Nobel laureate Leon Lederman that dubbed the Higgs "The God Particle." There was the search for the Higgs particle that launched after 2009's first collisions inside the Large Hadron Collider in Europe. There was the 2013 announcement that Peter Higgs and Francois Englert won the Nobel Prize in Physics for independently theorizing in 1964 that a fundamental particle - the Higgs - is the source of mass in subatomic ...
New COVID-19 model shows little benefit in vaccinating high-risk individuals first
2021-01-19
BROOKLYN, New York, Tuesday, January 19, 2021 - The World Health Organization END ...
Fastener with microscopic mushroom design holds promise
2021-01-19
WASHINGTON, January 19, 2021 -- A Velcro-like fastener with a microscopic design that looks like tiny mushrooms could mean advances for everyday consumers and scientific fields like robotics.
In Biointerphases, published by AIP Publishing, researchers from Wageningen University in the Netherlands show how the design can use softer materials and still be strong enough to work.
Probabilistic fasteners work, because they are designed with a tiny pattern on one surface that interlocks with features on the other surface. Currently available fasteners, like Velcro and 3M, are called hook and loop fasteners. That design requires harder, stiff material, which ...
Individual and organizational capacity to change can reduce health care workforce burnout
2021-01-19
Even prior to the pandemic, burnout among health care professionals was a pervasive public health concern, with END ...
Land deals meant to improve food security may have hurt
2021-01-19
Large-scale land acquisitions by foreign investors, intended to improve global food security, had little to no benefit, increasing crop production in some areas while simultaneously threatening local food security in others, according to researchers who studied their effects.
The END ...
Even a small amount of gender bias in hiring can be costly to employers
2021-01-19
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Tiny amounts of gender bias in employee hiring decisions contribute to concerning rates of discrimination and productivity losses that together represent significant costs, financial and otherwise, for employers, a new study from Oregon State University has found.
Gender bias is a subtle, unintentional preference for one gender over the other. Despite significant efforts to reduce bias in hiring over the last several decades, it continues to persist and pose potential problems for companies, said Jay Hardy, an assistant professor of management in OSU's College ...
Disease threatens to decimate western bats
2021-01-19
BOZEMAN, Montana (January 19, 2021) - A four-year study recently published in Ecology and Evolution concludes that the fungal disease, white-nose syndrome, poses a severe threat to many western North American bats.
Since it was first detected in 2006, white-nose syndrome has killed millions of bats in eastern and central North America. The spread of the fungal pathogen that causes white-nose syndrome in hibernating bats has reached several western U.S. states, mostly likely through bat-to-bat spread, and is presently threatening western species.
Bats with white-nose syndrome have fungus growing on their nose and wings, as the name implies, but the fungal infection also triggers a higher frequency of arousals from hibernation. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
[Press-News.org] Astronomers dissect the anatomy of planetary nebulae using Hubble Space Telescope imagesResearchers from RIT and Green Bank Observatory shed new light on nebula formation processes