(Press-News.org) New Rochelle, NY, January 19, 2021--Gene editing therapies, including CRISPR-Cas systems, offer the potential to correct mutations causing inherited retinal degenerations, a leading cause of blindness. Technological advances in gene editing, continuing safety concerns, and strategies to overcome these challenges are highlighted in the peer-reviewed journal Human Gene Therapy. Click here to read the full-text article free on the Human Gene Therapy website.
"Currently, the field is undergoing rapid development with a number of competing gene editing strategies, including allele-specific knock-down, base editing, prime editing, and RNA editing, are under investigation. Each offers a different balance of on-target editing efficiency versus off-target risks," state Kanmin Xue, University of Oxford, and coauthors. "Testing these newly-developed CRISPR technologies in human retinal tissue, organoids and in vivo will help to highlight the most-viable therapeutic approaches for treating inherited retinal diseases in the future."
Characterizing the rapidly evolving field of CRISPR-Cas based genome editing and current strategies for extending the capabilities of CRISPR-Cas9, the article also features epigenetic editing, the risks of retinal gene editing, and approaches in development to control Cas9 activity and improve safety.
"The eye is an ideal target for in vivo gene editing. Dr. Xue's review provides an excellent overview of the current state of the art," says Editor-in-Chief of Human Gene Therapy Terence R. Flotte, MD, Celia and Isaac Haidak Professor of Medical Education and Dean, Provost, and Executive Dep
uty Chancellor, University of Massachusetts Medical School.
INFORMATION:
About the Journal
Human Gene Therapy, the Official Journal of the European Society of Gene and Cell Therapy and eight other international gene therapy societies, was the first peer-reviewed journal in the field and provides all-inclusive access to the critical pillars of Human Gene Therapy: research, methods, and clinical applications. The Journal is led by Editor-in-Chief Terence R. Flotte, MD, Celia and Isaac Haidak Professor of Medical Education and Dean, Provost, and Executive Deputy Chancellor, University of Massachusetts Medical School, and an esteemed international editorial board. Human Gene Therapy is available in print and online. Complete tables of contents and a sample issue are available on the Human Gene Therapy website.
About the Publisher
Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers is known for establishing authoritative peer-reviewed journals in many promising areas of science and biomedical research. Its biotechnology trade magazine, GEN (Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News), was the first in its field and is today the industry's most widely read publication worldwide. A complete list of the firm's 90 journals, books, and newsmagazines is available on the Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers website.
ITHACA, N.Y. - When the semester shifted online amid the COVID-19 pandemic last spring, Cornell University instructor Mark Sarvary, and his teaching staff decided to encourage - but not require - students to switch on their cameras.
It didn't turn out as they'd hoped.
"Most of our students had their cameras off," said Sarvary, director of the Investigative Biology Teaching Laboratories in the College of Agriculture and Life Sciences (CALS).
"Students enjoy seeing each other when they work in groups. And instructors like seeing students, because it's a way to assess whether or not they understand the material," Sarvary said. "When we switched to online learning, that component got lost. We wanted to investigate the reasons ...
Scientists have combined NASA data and cutting-edge image processing to gain new insight into the solar structures that create the Sun's flow of high-speed solar wind, detailed in new research published today in The Astrophysical Journal. This first look at relatively small features, dubbed "plumelets," could help scientists understand how and why disturbances form in the solar wind.
The Sun's magnetic influence stretches billions of miles, far past the orbit of Pluto and the planets, defined by a driving force: the solar wind. This constant outflow of solar material carries the Sun's magnetic field out into space, where it shapes the environments around Earth, other worlds, and in the reaches of deep space. Changes in the solar wind ...
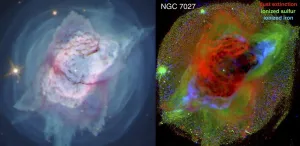
Images of two iconic planetary nebulae taken by the Hubble Space Telescope are revealing new information about how they develop their dramatic features. Researchers from Rochester Institute of Technology and Green Bank Observatory presented new findings about the Butterfly Nebula (NGC 6302) and the Jewel Bug Nebula (NGC 7027) at the 237th meeting of the American Astronomical Society on Friday, Jan. 15.
Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3 observed the nebulae in 2019 and early 2020 using its full, panchromatic capabilities, and the astronomers involved in the project ...
New high-resolution structures of the bacterial ribosome determined by researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago show that a single water molecule may be the cause -- and possible solution -- of antibiotic resistance.
The findings of the new UIC study are published in the journal Nature Chemical Biology.
Pathogenic germs become resistant to antibiotics when they develop the ability to defeat the drugs designed to kill them. Each year in the U.S., millions of people suffer from antibiotic-resistant infections, and thousands of people die as a result.
Developing new drugs is a key way the scientific community is trying to reduce the impact of antibiotic resistance.
"The first thing we need to do to make improved drugs is to better understand how antibiotics work and how 'bad ...
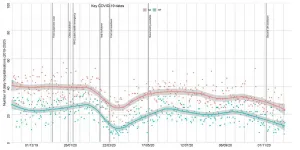
Data analysis is revealing a second sharp drop in the number of people admitted to hospital in England with acute heart failure or a heart attack.
The decline began in October as the numbers of COVID-19 infections began to surge ahead of the second lockdown, which came into force in early November.
The findings, from a research group led by the University of Leeds, have been revealed in a letter to the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The decline - 41 percent fewer people attending with heart failure and 34 percent with a heart attack compared to pre-pandemic levels ...
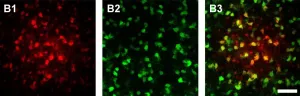
The human brain has about as many neurons as glial cells. These are divided into four major groups: the microglia, the astrocytes, the NG2 glial cells, and the oligodendrocytes. Oligodendrocytes function primarily as a type of cellular insulating tape: They form long tendrils, which consist largely of fat-like substances and do not conduct electricity. These wrap around the axons, which are the extensions through which the nerve cells send their electrical impulses. This prevents short circuits and accelerates signal forwarding.
Astrocytes, on the other hand, supply the nerve cells with energy: Through their appendages they come into contact with blood vessels and absorb glucose from these. ...
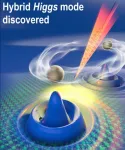
AMES, Iowa - Even if you weren't a physics major, you've probably heard something about the Higgs boson.
There was the title of a 1993 book by Nobel laureate Leon Lederman that dubbed the Higgs "The God Particle." There was the search for the Higgs particle that launched after 2009's first collisions inside the Large Hadron Collider in Europe. There was the 2013 announcement that Peter Higgs and Francois Englert won the Nobel Prize in Physics for independently theorizing in 1964 that a fundamental particle - the Higgs - is the source of mass in subatomic ...
BROOKLYN, New York, Tuesday, January 19, 2021 - The World Health Organization END ...
WASHINGTON, January 19, 2021 -- A Velcro-like fastener with a microscopic design that looks like tiny mushrooms could mean advances for everyday consumers and scientific fields like robotics.
In Biointerphases, published by AIP Publishing, researchers from Wageningen University in the Netherlands show how the design can use softer materials and still be strong enough to work.
Probabilistic fasteners work, because they are designed with a tiny pattern on one surface that interlocks with features on the other surface. Currently available fasteners, like Velcro and 3M, are called hook and loop fasteners. That design requires harder, stiff material, which ...
Even prior to the pandemic, burnout among health care professionals was a pervasive public health concern, with END ...