(Press-News.org) Just like us, many insects need a decent night's sleep to function properly, but this might not be possible if they have been exposed to neonicotinoid insecticides, the most common form of insecticide used worldwide, suggests research by academics at the University of Bristol.
Two studies by scientists at Bristol's Schools of Physiology, Pharmacology and Neuroscience and Biological Sciences have shown these insecticides affect the amount of sleep taken by both bumblebees and fruit flies, which may help us understand why insect pollinators are vanishing from the wild.
Dr Kiah Tasman, Teaching Associate in the School of Physiology, Pharmacology and Neuroscience and lead author of the studies, said: "The neonicotinoids we tested had a big effect on the amount of sleep taken by both flies and bees. If an insect was exposed to a similar amount as it might experience on a farm where the pesticide had been applied, it slept less, and its daily behavioural rhythms were knocked out of synch with the normal 24-hour cycle of day and night."
The fruit fly study published today [21 January] in Scientific Reports, allowed the researchers to study the impact of the pesticides on the insect brain.
As well as finding that typical agricultural concentrations of neonicotinoids ruined the flies' ability to remember, the researchers also saw changes in the clock in the fly brain which controls its 24-hour cycle of day and night.
Dr James Hodge, Associate Professor in Neuroscience in the School of Physiology, Pharmacology and Neuroscience and senior author for the study, added: "Being able to tell time is important for knowing when to be awake and forage, and it looked like these drugged insects were unable to sleep. We know quality sleep is important for insects, just as it is for humans, for their health and forming lasting memories."
Dr Sean Rands, Senior Lecturer in the School of Biological Sciences and co-author, explained: "Bees and flies have similar structures in their brains, and this suggests one reason why these drugs are so bad for bees is they stop the bees from sleeping properly and then being able to learn where food is in their environment.
"Neonicotinoids are currently banned in the EU, and we hope that this continues in the UK as we leave EU legislation."
INFORMATION:
Papers
'Neonicotinoids disrupt memory, circadian behaviour and sleep' by Tasman K, Hidalgo S, Zhu B, Rands SA & Hodge JJL in Scientific Reports
'The neonicotinoid insecticide imidacloprid disrupts bumblebee circadian rhythms and sleep' by Tasman K, Rands SA & Hodge JJL in iScience [open access]
Just over 200,000 Americans suffer from systemic lupus erythematosus, or SLE, a condition in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own healthy tissues, especially joints and skin, a new study shows.
Led by a researcher at NYU Grossman School of the Medicine, the study provides the first national estimate of how widespread the autoimmune disease is since the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) set up a half dozen state registries to track the illness more than a decade ago. SLE affects mostly women, can be fatal, and often involves debilitating flare-ups of fatigue and pain that keep nearly ...
PHILADELPHIA--Patients with inactive cancer and not currently undergoing treatments also face a significantly higher risk of severe illness from COVID-19, a new study from Penn Medicine published online today in JNCI Cancer Spectrum shows. Past reports have established an increased risk of severe disease and death for sick or hospitalized cancer patients with COVID-19 compared to patients without cancer, but less is known about patients in the general population.
The findings underscore the importance of COVID-19 mitigation, like social distancing and mask wearing, and vaccinations for all patients, not just those recently diagnosed or with active disease.
"Patients who have cancer need to be careful ...
New research has shown that people are more likely to follow Covid-19 restrictions based on what their friends do, rather than their own principles.
Research led by the University of Nottingham carried out in partnership with experts in collective behaviour from British, French, German and American universities shows how social influence affects people's adherance to government restrictions. The researchers found that the best predictor of people's compliance to the rules was how much their close circle complied with the rules, which had an even stronger effect than people's own approval of the rules.
The research published in British Journal of Psychology highlights a blindspot in policy responses ...
The US prevalence of the autoimmune disease lupus is 72.8 cases per 100,000 individuals, according to an analysis of population-based registries. The analysis, which is published in END ...
Where people die can affect the quality of their deaths and the end-of-life care that they receive. A study published in the END ...
Pharmacists play an important role in managing medication-based therapies for older community-dwelling patients, according to a study published in the END ...
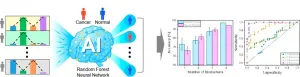
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers among men. Patients are determined to have prostate cancer primarily based on *PSA, a cancer factor in blood. However, as diagnostic accuracy is as low as 30%, a considerable number of patients undergo additional invasive biopsy and thus suffer from resultant side effects, such as bleeding and pains.
*Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA): a prostate-specific antigen (a cancer factor) used as an index for the screening of prostate cancer.
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) announced that the collaborative research team led by Dr. Kwan Hyi Lee from the Biomaterials Research Center and Professor In Gab Jeong from Asan Medical Center developed a technique ...
Pathogenic bacteria in humans are developing resistance to antibiotics much faster than expected. Now, computational research at Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, shows that one reason could be significant genetic transfer between bacteria in our ecosystems and to humans. This work has also led to new tools for resistance researchers.
According to the World Health Organisation, antibiotic resistance is one of the greatest threats to global health, food safety and development. It already causes over 33,000 deaths a year in Europe alone.
Completely ...
Since 1997 (Reno vs. American Civil Liberties Union), the Supreme Court has used the metaphor of the free market of ideas to define the Internet, thus addressing the regulation of the net as a matter of freedom of speech. In law, metaphors have a constitutive value and, once established, affect the debate and the decisions of the Courts for a long time. In the paper 'Judicial Frames and Fundamental Right in Cyberspace', published in the American Journal of Comparative Law, Oreste Pollicino (Bocconi University) and Alessandro Morelli (Università Magna Graecia, Catanzaro) apply to judicial reasoning reflections on metaphors and go so far as to criticize, on the one hand, the US Supreme Court's orientations on (non-)regulation of the Internet and, on the other, to invoke changes ...
In the first systematic large-scale evaluation of the UK National Early Warning Risk Score (NEWS) 2 as a scoring system for predicting severe COVID-19 outcomes in patients, researchers at King's College London have found poor-to-moderate accuracy for identifying patients at risk of being transferred to intensive care units (ICUs) or dying after 14 days of hospitalisation. Accuracy of predictions in short term (three days) showed moderate success.
For people who are hospitalised with severe COVID-19, it is vital to quickly identify which patients may deteriorate and require transfer to an intensive care unit (ICU) for organ support or may die. NEWS2 is an ...