INFORMATION:
This research was conducted with the support from the Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center for Future Technology.
A display that completely blocks off counterfeits
2021-01-21
(Press-News.org) Despite the anticounterfeiting devices attached to luxury handbags, marketable securities, and identification cards, counterfeit goods are on the rise. There is a demand for the next-generation anticounterfeiting technology - that surpasses the traditional ones - that are not easily forgeable and can hold various data.
A POSTECH research team, led by Professor Junsuk Rho of the departments of mechanical engineering and chemical engineering, Ph.D. candidates Chunghwan Jung of the Department of Chemical Engineering and Younghwan Yang of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, have together succeeded in making a switchable display device using nanostructures that is capable of encrypting full-color images depending on the polarization of light. These findings were recently published in Nanophotonics.
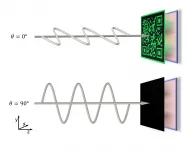
The new device developed by the research team was produced with a microstructure about one thousand times thinner than a strand of hair which is called a metasurface. It is known that various colors can be expressed through a uniformly arranged microstructures within the metasurface. Because the microstructures produced this time have very small pixels, they boast high resolution (approximately 40,000 dpi) and wide viewing angle while being thin, which allows it to be produced in the form of stickers.
In addition, unlike previous studies that focused on the expression of various colors, in this study, the on and off states can be adjusted according to the polarization of the incident light. This new device displays full-color images during the on state and shows no images in the off state.
Besides having the ability to turn on and turn off an image, the device can switch between different images. Specifically, by arranging three consecutive nanostructures, it achieves higher colorization rate than the previous studies. The researchers properly configured a total of 125 types of structures to encode a full-color image and proved through experiments that it completely turns off according to the polarization.
This feature can be utilized in real life as an anti-forgery device. For example, it can be designed into a security label that appears to be a simple color image to the naked eye, but reveals the serial number when a special filter is used. Moreover, by utilizing its ultrahigh resolution feature and inserting high-capacity data security algorithm, it can be used as a new security device that can replace the traditional labeling method.
Chunghwan Jung, the first author of the paper, commented, "This new device is practically impossible to forge because it requires an electron microscope with magnification capacity of several thousand and a nanometer-scale production equipment."
"This device is an ultra-high-resolution device-type display that can turn on and turn off full-color images according to the polarization component of the incident light," remarked the corresponding author Professor Junsuk Rho who led the study. "These displays can store multiple images simultaneously and can be applied to in optical cryptography."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The interconnection of global pandemics -- Obesity, impaired metabolic health and COVID-19
2021-01-21
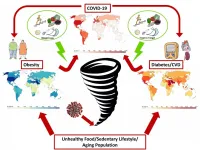
In a Nature Reviews Endocrinology article authors from the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD) highlight the interconnection of obesity and impaired metabolic health with the severity of COVID-19. First, they provide information about the independent relationships of obesity, disproportionate fat distribution and impaired metabolic health with the severity of COVID-19. Then they discuss mechanisms for a complicated course of COVID-19 and how this disease may impact on the global obesity and cardiometabolic pandemics. Finally, they provide recommendations for prevention and treatment in clinical practice and in the public health sector to combat these global pandemics.
Norbert Stefan, Andreas Birkenfeld and Matthias Schulze summarize ...
Neuronal recycling: This is how our brain allows us to read
2021-01-21
Letters, syllables, words and sentences--spatially arranged sets of symbols that acquire meaning when we read them. But is there an area and cognitive mechanism in our brain that is specifically devoted to reading? Probably not; written language is too much of a recent invention for the brain to have developed structures specifically dedicated to it.
According to this novel paper published in Current Biology, underlying reading there is evolutionarily ancient function that is more generally used to process many other visual stimuli. To prove it, SISSA ...
Fans of less successful football clubs are more loyal to one another
2021-01-21
Research led by the universities of Kent and Oxford has found that fans of the least successful Premier League football teams have a stronger bond with fellow fans and are more 'fused' with their club than supporters of the most successful teams.
The study, which was carried out in 2014, found that fans of Crystal Palace, Hull, Norwich, Sunderland, and West Bromwich Albion were found to have higher loyalty towards one another and even expressed greater willingness to sacrifice their own lives to save the lives of other fans of their club. This willingness was much higher than that of Manchester United, Arsenal, Chelsea, Liverpool or Manchester City fans. A decade of club statistics from 2003-2013 was used to identify the ...
Randomized trials could help to return children safely to schools - study
2021-01-21
Schools are closing again in response to surging levels of COVID-19 infection, but staging randomised trials when students eventually return could help to clarify uncertainties around when we should send children back to the classroom, according to a new study.
Experts say that school reopening policies currently lack a rigorous evidence base - leading to wide variation in policies around the world, but staging cluster randomized trials (CRT) would create a body of evidence to help policy makers take the right decisions.
The pandemic's rapid ...
Important cause of preeclampsia discovered
2021-01-21
Despite being the subject of increasing interest for a whole century, how preeclampsia develops has been unclear - until now.
Researchers believe that they have now found a primary cause of preeclampsia.
"We've found a missing piece to the puzzle. Cholesterol crystals are the key and we're the first to bring this to light," says researcher Gabriela Silva.
Silva works at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology's (NTNU) Centre of Molecular Inflammation Research (CEMIR), a Centre of Excellence, where she is part of a research group for inflammation in pregnancy led by Professor Ann-Charlotte Iversen.
The findings are good news for the approximately three per cent of pregnant ...
Study suggests that gut fungi are not associated with Parkinson's disease
2021-01-21
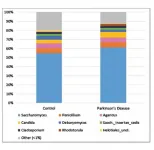
Amsterdam, NL, January 21, 2021 - The bacterial gut microbiome is strongly associated with Parkinson's disease (PD), but no studies had previously investigated he role of fungi in the gut. In this novel study published in the Journal of Parkinson's Disease, a team of investigators at the University of British Columbia examined whether the fungal constituents of the gut microbiome are associated with PD. Their research indicated that gut fungi are not a contributing factor, thereby refuting the need for any potential anti-fungal treatments of the gut in PD patients.
"Several studies conducted since 2014 have characterized changes in the gut microbiome," explained lead investigator Silke Appel-Cresswell, MD, Pacific Parkinson's Research Centre and Djavad ...
New study on the role of monocytes in sarcoidosis
2021-01-21
The cause of the inflammatory lung disease sarcoidosis is unknown. In a new study, researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have investigated whether a type of immune cell called a monocyte could be a key player in sarcoidosis pathogenesis and explain why some patients develop more severe and chronic disease than others. The study, which is published in The European Respiratory Journal, opens new possibilities for future diagnostic and therapeutic methods.
Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory disease that in 90 percent of cases affects the lungs, but can also attack the heart, skin and lymph system. The cause of the disease is not yet established, and there is currently ...
Pioneering new technique could revolutionise super-resolution imaging systems
2021-01-21
Scientists have developed a pioneering new technique that could revolutionise the accuracy, precision and clarity of super-resolution imaging systems.
A team of scientists, led by Dr Christian Soeller from the University of Exeter's Living Systems Institute, which champions interdisciplinary research and is a hub for new high-resolution measurement techniques, has developed a new way to improve the very fine, molecular imaging of biological samples.
The new method builds upon the success of an existing super-resolution imaging technique called DNA-PAINT ...
Seeds transfer their microbes to the next generation
2021-01-21
Scientists have been pondering if the microbiome of plants is due to nature or nurture. Research at Stockholm University, published in Environmental Microbiology, showed that oak acorns contain a large diversity of microbes, and that oak seedlings inherit their microbiome from these acorns.
"The idea that seeds can be the link between the microbes in the mother tree and its offspring has frequently been discussed, but this is the first time someone proves the transmission route from the seed to the leaves and roots of emerging plants", says Ahmed Abdelfattah, researcher at the Department of Ecology Environment and Plant ...
Turbulence model could help design aircraft capable of handling extreme scenarios
2021-01-21
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. -- In 2018, passengers onboard a flight to Australia experienced a terrifying 10-second nosedive when a vortex trailing their plane crossed into the wake of another flight. The collision of these vortices, the airline suspected, created violent turbulence that led to a free fall.
To help design aircraft that can better maneuver in extreme situations, Purdue University researchers have developed a modeling approach that simulates the entire process of a vortex collision at a reduced computational time. This physics knowledge could then be incorporated into engineering design codes so that the aircraft ...