INFORMATION:
Scientists use a novel ink to 3D print 'bone' with living cells
2021-01-25
(Press-News.org) Scientists from UNSW Sydney have developed a ceramic-based ink that may allow surgeons in the future to 3D-print bone parts complete with living cells that could be used to repair damaged bone tissue.
Using a 3D-printer that deploys a special ink made up of calcium phosphate, the scientists developed a new technique, known as ceramic omnidirectional bioprinting in cell-suspensions (COBICS), enabling them to print bone-like structures that harden in a matter of minutes when placed in water.
While the idea of 3D-printing bone-mimicking structures is not new, this is the first time such material can be created at room temperature - complete with living cells - and without harsh chemicals or radiation, says Dr Iman Roohani from UNSW's School of Chemistry.
"This is a unique technology that can produce structures that closely mimic bone tissue," he says.
"It could be used in clinical applications where there is a large demand for in situ repair of bone defects such as those caused by trauma, cancer, or where a big chunk of tissue is resected."
Associate Professor Kristopher Kilian who co-developed the breakthrough technology with Dr Roohani says the fact that living cells can be part of the 3D-printed structure, together with its portability, make it a big advance on current state-of-the-art technology.
Up until now, he says, making a piece of bone-like material to repair bone tissue of a patient involves first going into a laboratory to fabricate the structures using high-temperature furnaces and toxic chemicals.
"This produces a dry material that is then brought into a clinical setting or in a laboratory, where they wash it profusely and then add living cells to it," Professor Kilian says.
"The cool thing about our technique is you can just extrude it directly into a place where there are cells, like a cavity in a patient's bone. We can go directly into the bone where there are cells, blood vessels and fat, and print a bone-like structure that already contains living cells, right in that area."
"There are currently no technologies that can do that directly."
In a research paper published recently in Advanced Functional Materials, the authors describe how they developed the special ink in a microgel matrix with living cells.
"The ink takes advantage of a setting mechanism through the local nanocrystallisation of its components in aqueous environments, converting the inorganic ink to mechanically interlocked bone apatite nanocrystals," Dr Roohani says.
"In other words, it forms a structure that is chemically similar to bone-building blocks. The ink is formulated in such a way that the conversion is quick, non-toxic in a biological environment and it only initiates when ink is exposed to the body fluids, providing an ample working time for the end-user, for example, surgeons."
He says when the ink is combined with a collagenous substance containing living cells, it enables in-situ fabrication of bone-like tissues which may be suitable for bone tissue engineering applications, disease modelling, drug screening, and in-situ reconstruction of bone and osteochondral defects.
Already there has been keen interest from surgeons and medical technology manufacturers. A/Prof. Kilian thinks while it's early days, this new bone-printing process could open up a whole new way of treating and repairing bone tissue.
"This advance really paves the way for numerous opportunities that we believe could prove transformational - from using the ink to create bone in the lab for disease modelling, as a bioactive material for dental restoration, to direct bone reconstruction in a patient," says A/Prof. Kilian.
"I imagine a day where a patient needing a bone graft can walk into a clinic where the anatomical structure of their bone is imaged, translated to a 3D printer, and directly printed into the cavity with their own cells.
"This has the potential to radically change current practice, reducing patient suffering and ultimately saving lives."
Next up the duo will be performing in vivo tests in animal models to see if the living cells in the bone-like constructs continue to grow after being implanted in existing bone tissue.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
First comprehensive LCA shows reprocessed medical devices cut GHG emissions in half
2021-01-25
The carbon footprint of plastic production for initial use is greater than the global warming impact of the entire process used for medical device reprocessing Use of reprocessed devices is environmentally superior to use of original products in 13 of 16 categories evaluatedReprocessing found to advance "circular economy," a key strategy for reaching the UN Sustainability GoalsLCA offers evidence showing that in order to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and honor the Paris Climate Agreement, EU Member States must opt-in to EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR)'s reprocessing/remanufacturing provisions
[Berlin / Washington, ...
Dramatic increase in microplastics in seagrass soil since the 1970s
2021-01-25
Large-scale production of vegetables and fruit in Spain with intensive plastic consumption in its greenhouse industry is believed to have leaked microplastic contaminants since the 1970s into the surrounding Mediterranean seagrass beds. This is shown in a new study where researchers have succeeded in tracing plastic pollution since the 1930s and 1940s by analyzing seagrass sediments.
About half of Sweden's cucumbers and a fifth of the tomatoes in Sweden are currently imported from Spain according to the Swedish Board of Agriculture. A special area in Spain where large-scale vegetable cultivation ...
Titanium oxide nanotubes facilitate low-cost laser-assisted photoporation
2021-01-25
Overview:
A research team at the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Toyohashi University of Technology developed a nanosecond pulse laser-assisted photoporation method using titanium-oxide nanotubes (TNTs) for highly efficient and low-cost intracellular delivery. The proof of concept for the possibility of intracellular delivery after irradiation with nanosecond pulse laser on TNTs was validated. TNTs were formed on titanium sheets using the electrochemical anodization technique at different voltages and times. HeLa - human cervical cancer cells were cultured in the nanotubes and submerged in a solution of biomolecules. After cells were exposed to nanosecond pulse laser, we successfully delivered ...
There's lots of water in the world's most explosive volcano
2021-01-25
There isn't much in Kamchatka, a remote peninsula in northeastern Russia just across the Bering Sea from Alaska, besides an impressive population of brown bears and the most explosive volcano in the world.
Kamchatka's Shiveluch volcano has had more than 40 violent eruptions over the last 10,000 years. The last gigantic blast occurred in 1964, creating a new crater and covering an area of nearly 100 square kilometers with pyroclastic flows. But Shiveluch is actually currently erupting, as it has been for over 20 years. So why would anyone risk venturing too close?
Researchers from Washington University in St. Louis, including Michael Krawczynski, assistant professor of earth and planetary sciences in Arts & Sciences and graduate student ...
Abusive bosses 'fake nice' instead of 'make nice'
2021-01-25
Abusive bosses may retain their positions by taking superficial steps to repair their social images following outbursts, without acting meaningfully to change their behaviors, according to research led by a University of Wyoming business management expert.
Shawn McClean, an assistant professor in UW's College of Business, joined colleagues from the University of Iowa, the University of Nebraska-Lincoln and Texas A&M University in conducting the research, which appears in the journal Personnel Psychology. Their study also was featured in Harvard Business Review, a preeminent business magazine.
"Our study shows that supervisors are often driven by simply repairing their social image rather than ...
Male breast cancer patients face high prevalence of heart disease risk factors
2021-01-25
Male breast cancer patients were found to have a high prevalence of cardiovascular conditions, in a small study of this rare patient population presented at the American College of Cardiology's Advancing the Cardiovascular Care of the Oncology Patient Virtual course.
"Due to the rarity of male breast cancer, there is no cardiovascular data from larger clinical trials or population studies. The lack of large data makes it even more important to individualize cardiovascular assessment and management based on each patient's unique oncologic, therapeutic and pre-existing cardiovascular risk profile to support them through cancer treatment into survivorship," said Michael Ibrahim, fourth year ...
Opertech Bio's pioneering approach to taste testing and measurement published in JPET
2021-01-25
PHILADELPHIA, PA - January 25, 2021 - Opertech Bio, Inc., today announced the publication of a seminal research article describing the application of its pioneering TāStation® technology to the pharmacological characterization of human taste discrimination. The findings are published in the peer-reviewed Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, JPET.
The paper, entitled "Rapid throughput concentration-response analysis of human taste discrimination," is the first to quantitatively define the concentration-response function for human taste discrimination, a crucial step in understanding ...
Litter provides habitat for diverse animal communities in rivers, study finds
2021-01-25
In a study of local rivers, experts at the University of Nottingham in the UK have discovered more invertebrates - animals without a backbone, such as insects and snails - living on litter than on rocks.
In urban rivers where there are no better alternatives, litter provided the largest, most stable and complex habitat available for invertebrates to live on.
The findings could have important implications for the management of urban rivers, including how river clean-up events are conducted.
The research team, in the School of Geography, studied three local rivers; the River Leen, Black Brook, and Saffron Brook, in ...
New skull of tube-crested dinosaur reveals evolution of bizarre crest
2021-01-25
DISCOVERY BRIEF:
The first new skull of a rare species of the dinosaur Parasaurolophus (recognized by the large hollow tube that grows on its head) discovered in 97 years.
Exquisite preservation of the new skull gives paleontologists their first opportunity to definitively identify how such a bizarre structure grew on this dinosaur.
For the first time, this study found characteristics to link tube-crested dinosaur species found in southern North America (New Mexico, Utah), distinct from the only northern species (Alberta).
The locality, in northwestern New Mexico, is dated to about 75 million years ago, a time when North America was divided by a shallow sea and teemed with duckbilled dinosaurs, horned dinosaurs and early tyrannosaurs.
Fossils from ...
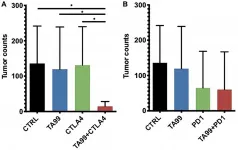
Oncotarget: Improved therapeutic efficacy of unmodified anti-tumor antibodies
2021-01-25
The cover for issue 2 of Oncotarget features Figure 4, "Combination therapy TA99/ICB reduced the lung tumor burden in the B16 model of metastases," published in "Improved therapeutic efficacy of unmodified anti-tumor antibodies by immune checkpoint blockade and kinase targeted therapy in mouse models of melanoma" by Pérez-Lorenzo, et al. which reported that here, the authors showed that removing immune suppression and enhancing stimulatory signals increased the anti-tumor activity of unmodified TA99 antibodies with a significant reduction of ...