(Press-News.org) A group of KAIST researchers and collaborators have engineered a tiny brain implant that can be wirelessly recharged from outside the body to control brain circuits for long periods of time without battery replacement. The device is constructed of ultra-soft and bio-compliant polymers to help provide long-term compatibility with tissue. Geared with micrometer-sized LEDs (equivalent to the size of a grain of salt) mounted on ultrathin probes (the thickness of a human hair), it can wirelessly manipulate target neurons in the deep brain using light.
This study, led by Professor Jae-Woong Jeong, is a step forward from the wireless head-mounted implant neural device he developed in 2019. That previous version could indefinitely deliver multiple drugs and light stimulation treatment wirelessly by using a smartphone.
For the new upgraded version, the research team came up with a fully implantable, soft optoelectronic system that can be remotely and selectively controlled by a smartphone. This research was published on January 22, 2021 in Nature Communications.
The new wireless charging technology addresses the limitations of current brain implants. Wireless implantable device technologies have recently become popular as alternatives to conventional tethered implants, because they help minimize stress and inflammation in freely-moving animals during brain studies, which in turn enhance the lifetime of the devices. However, such devices require either intermittent surgeries to replace discharged batteries, or special and bulky wireless power setups, which limit experimental options as well as the scalability of animal experiments.
"This powerful device eliminates the need for additional painful surgeries to replace an exhausted battery in the implant, allowing seamless chronic neuromodulation," said Professor Jeong. "We believe that the same basic technology can be applied to various types of implants, including deep brain stimulators, and cardiac and gastric pacemakers, to reduce the burden on patients for long-term use within the body."
To enable wireless battery charging and controls, researchers developed a tiny circuit that integrates a wireless energy harvester with a coil antenna and a Bluetooth low-energy chip. An alternating magnetic field can harmlessly penetrate through tissue, and generate electricity inside the device to charge the battery. Then the battery-powered Bluetooth implant delivers programmable patterns of light to brain cells using an "easy-to-use" smartphone app for real-time brain control.
"This device can be operated anywhere and anytime to manipulate neural circuits, which makes it a highly versatile tool for investigating brain functions," said lead author Choong Yeon Kim, a researcher at KAIST.
Neuroscientists successfully tested these implants in rats and demonstrated their ability to suppress cocaine-induced behaviour after the rats were injected with cocaine. This was achieved by precise light stimulation of relevant target neurons in their brains using the smartphone-controlled LEDs. Furthermore, the battery in the implants could be repeatedly recharged while the rats were behaving freely, thus minimizing any physical interruption to the experiments.
"Wireless battery re-charging makes experimental procedures much less complicated," said the co-lead author Min Jeong Ku, a researcher at Yonsei University's College of Medicine.
"The fact that we can control a specific behaviour of animals, by delivering light stimulation into the brain just with a simple manipulation of smartphone app, watching freely moving animals nearby, is very interesting and stimulates a lot of imagination," said Jeong-Hoon Kim, a professor of physiology at Yonsei University's College of Medicine. "This technology will facilitate various avenues of brain research."
The researchers believe this brain implant technology may lead to new opportunities for brain research and therapeutic intervention to treat diseases in the brain and other organs.
INFORMATION:
This work was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea and the KAIST Global Singularity Research Program.
-About KAIST
KAIST is the first and top science and technology university in Korea. KAIST was established in 1971 by the Korean government to educate scientists and engineers committed to the industrialization and economic growth of Korea.
Since then, KAIST and its 64,739 graduates have been the gateway to advanced science and technology, innovation, and entrepreneurship. KAIST has emerged as one of the most innovative universities with more than 10,000 students enrolled in five colleges and seven schools including 1,039 international students from 90 countries.
On the precipice of its semi-centennial anniversary in 2021, KAIST continues to strive to make the world better through the pursuit in education, research, entrepreneurship, and globalization.
The prevalence of inflammatory bowel diseases has significantly increased both in Finland and globally. These disorders cannot be entirely cured. Instead, they are treated with anti-inflammatory drugs and, at times, through surgery.
If conventional drug therapies based on anti-inflammatory drugs are ineffective, the diseases can be treated using infliximab, a biological TNF-α blocker that is administered intravenously. Infliximab is an antibody that prevents TNF-α, a pro-inflammatory factor, from binding with inflammatory cells in the intestine. It is effective in reducing inflammation and improving the patient's condition, while also controlling the disease well.
Although infliximab therapy is often effective, roughly 30-40% of patients either do not respond ...
An international research team succeeded in gaining new insights into the artificially produced superheavy element flerovium, element 114, at the accelerator facilities of the GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung in Darmstadt, Germany. Under the leadership of Lund University in Sweden and with significant participation of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) as well as the Helmholtz Institute Mainz (HIM) in Germany and other partners, flerovium was produced and investigated to determine whether it has a closed proton shell. The results suggest that, contrary to expectations, flerovium is not a so-called "magic nucleus". The results were published in ...
Two family members test positive for COVID-19 -- how do we know who infected whom? In a perfect world, network science could provide a probable answer to such questions. It could also tell archaeologists how a shard of Greek pottery came to be found in Egypt, or help evolutionary biologists understand how a long-extinct ancestor metabolized proteins.
As the world is, scientists rarely have the historical data they need to see exactly how nodes in a network became connected. But a new paper published in Physical Review Letters offers hope for reconstructing the missing information, using a new method to evaluate the rules that generate network models.
"Network models are like impressionistic ...
A new paper from UC Santa Cruz researchers, published in END ...
Overview:
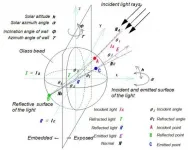
Jihui Yuan (Assistant Professor, Department of Architecture and Civil Engineering, Toyohashi University of Technology) proposed a numerical bead model to predict the upward-to-downward reflection ratio of glass bead retro-reflective (RR) material purposed for urban heat island (UHI) mitigation and reducing energy consumption. It revealed that the retro-reflectivity of glass bead RR material gradually increases from morning to noon, at which time it begins to gradually decrease. These results will contribute to existing research on the absorption or reflection of solar radiation to improve urban thermal and lighting ...
WASHINGTON--Poor social conditions caused by systemic racism contribute to health disparities in people with diabetes, according to a paper published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Minorities are disproportionately affected by diabetes because of poor social conditions that contribute to negative health outcomes such as poverty, unsafe housing, lack of access to healthy food and safe physical activity, and inadequate employment and educational opportunities. These are known as the social determinants of health and are the result of residential ...
PITTSBURGH, 26 January 2021 - A vaginal ring containing the antiretroviral drug dapivirine and the contraceptive hormone levonorgestrel delivered sustained levels of each drug when used continuously for 90 days - levels likely sufficient to serve its dual purpose for protecting against both HIV and unwanted pregnancy, according to findings of a new study.
Results of the Phase I study of the 90-day dual-purpose ring are being presented at the HIV Research for Prevention (HIVR4P) Virtual Conference, or HIVR4P // Virtual, which is taking place over the course of ...
"Shell-crushing" - exactly what it sounds like - is a predatory mode used by numerous marine life from crabs to octopuses to large fishes and mammals when they eat hard-shelled mollusks like clams, oysters and conchs. These predators have to break apart the shell using robust claws or fortified jaws to access the prey's soft tissues.
Despite its prevalence in the marine environment, this feeding behavior has remained elusive to study remotely, particularly for larger marine animals that destroy shells almost completely, leaving behind little trace. Moreover, because they are highly mobile, scientists have difficulty in directly observing their foraging habits, which is why the ecology of shell-crushing (durophagy) remains ...
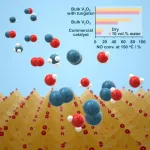
Tokyo, Japan - Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have created a new tungsten-substituted vanadium oxide catalyst for breaking down harmful nitrogen oxides in industrial exhaust. Their new catalyst material works at lower temperatures and does not suffer major drops in performance when processing "wet" exhaust, resolving a major drawback in conventional vanadium oxide catalysts. They found that the unaggregated dispersal of atomic tungsten in the original crystal structure plays a key role in how it functions.
Selective catalytic reduction (SCR) is an essential technology for keeping air clean. Industrial exhaust is passed through catalytic units and reacted with ...
If we are to prevent the impending environmental crisis, it is imperative that we find efficient and sustainable ways to avoid being wasteful. One area with much room for improvement is the recycling of waste heat from industrial processes and technological devices into electricity. Thermoelectric materials are at the core of research in this field because they allow for clean power generation at little cost.
For thermoelectric materials to be used in vastly different fields such as steel works and transportation, they need to be able to operate in both high and low temperature regimes. In this regard, "half-Heusler Ni-based ...