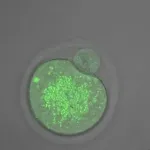
(Press-News.org) A hormone commonly associated with sleep-wake regulation has been found to reduce cysts in fruit flies, according to Concordia researchers. It's a finding that may affect the way we treat some kidney diseases and reduce the need for kidney transplants.
In a new paper published in the journal END
Concordia researchers find melatonin is effective against polycystic kidney disease
Hormone treatment can help reduce cysts in fruit fly renal tubules, according to Cassandra Millet-Boureima and Chiara Gamberi
2021-01-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Story tips from Johns Hopkins experts on Covid-19
2021-01-26
STUDY PROFILES IMMUNE CELLS FIGHTING COVID-19, MAY HELP GUIDE NEXT-GEN VACCINE DEVELOPMENT
Media Contact: Michael E. Newman, mnewma25@jhmi.edu
Even as the first vaccines for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, are being distributed, scientists and clinicians around the world have remained steadfast in their efforts to better understand how the human immune system responds to the virus and protects people against it. Now, a research team -- led by Johns Hopkins Medicine and in collaboration with ImmunoScape, a U.S.-Singapore biotechnology company -- has published one of the most comprehensive characterizations to date of a critical contributor to that protection: ...
When push comes to shove, what counts as a fight?
2021-01-26
Biologists often study animal sociality by collecting observations about several types of behavioral interactions. These interactions can be things like severe fights, minor fights, cooperative food sharing, or grooming each other.
But to analyze animal behavior, researchers need to make decisions about how to categorize these interactions and how to code these behaviors during data collection. Turns out, this question can be complicated.
Researchers at the University of Cincinnati dug into this tricky question while studying monk parakeets. In new research, published in the journal Current Zoology, the team asked: How do you properly categorize two seemingly similar behaviors? The study was led by UC ...
AI used to predict early symptoms of schizophrenia in relatives of patients
2021-01-26
University of Alberta researchers have taken another step forward in developing an artificial intelligence tool to predict schizophrenia by analyzing brain scans.
In recently published research, the tool was used to analyze functional magnetic resonance images of 57 healthy first-degree relatives (siblings or children) of schizophrenia patients. It accurately identified the 14 individuals who scored highest on a self-reported schizotypal personality trait scale.
Schizophrenia, which affects 300,000 Canadians, can cause delusions, hallucinations, disorganized ...
Strokes after TIAs have declined over time, study shows
2021-01-26
SAN ANTONIO and BOSTON - Study findings released Tuesday in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) hold both good news and bad news about transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), which are harbingers of subsequent strokes.
Sudha Seshadri, MD, professor of neurology at The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio and director of the university's Glenn Biggs Institute for Alzheimer's and Neurodegenerative Diseases, is senior author of the study and senior investigator of the Framingham Heart Study, from which the findings are derived. She said the extensive follow-up of Framingham participants over more than six decades enabled the study to present a more-complete picture of the risk of stroke to patients after a TIA.
The study points to the need for ...
Mouse study identifies novel compound that may help develop diabetes drugs
2021-01-26
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Research led by The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and College of Medicine identified a new compound that might serve as a basis for developing a new class of drugs for diabetes.
Study findings are published online in the journal Nature Chemical Biology.
The adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (Ampk) is a crucial enzyme involved in sensing the body's energy stores in cells. Impaired energy metabolism is seen in obesity, which is a risk factor for diabetes. Some medications used to treat diabetes, such as metformin, work by increasing the activity of Ampk.
"In ...
Drug to treat rare genetic disease may help control transmission of African Trypanosomiasis
2021-01-26
African trypanosomiasis (also known as sleeping sickness) is a disease transmitted by tsetse flies and is fatal to humans and other animals; however, there is currently no vaccine, this disease is mainly controlled by reducing insect populations and patient treatment. A study published in the open access journal PLOS Biology by Alvaro Acosta-Serrano at Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine and an international team of researchers suggests that the approved drug nitisinone could be repurposed to kill tsetse flies without harming important pollinator insects.
Currently, the most effective method of controlling the transmission of African trypanosomiasis is by employing insecticide-based vector control campaigns (traps, targets, ...
Compelling evidence of neutrino process opens physics possibilities
2021-01-26
The COHERENT particle physics experiment at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory has firmly established the existence of a new kind of neutrino interaction. Because neutrinos are electrically neutral and interact only weakly with matter, the quest to observe this interaction drove advances in detector technology and has added new information to theories aiming to explain mysteries of the cosmos.
"The neutrino is thought to be at the heart of many open questions about the nature of the universe," said Indiana University physics professor Rex Tayloe. He led the installation, operation and data analysis of a cryogenic liquid argon ...
Study helps understand why kids of obese mothers may be susceptible to metabolic diseases
2021-01-26
A Brazilian study published in the journal Molecular Human Reproduction helps understand why obese mothers tend to have children with a propensity to develop metabolic disease during their lifetime, as suggested by previous research.
According to the authors, "transgenerational transmission of metabolic diseases" may be associated with Mfn2 deficiency in the mother's oocytes (immature eggs). Mfn2 refers to mitofusin-2, a protein involved in the regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. It is normally found in the outer membrane of mitochondria, ...
Rates of skin cancer have increased dramatically over recent decades
2021-01-26
Incidence rates of skin cancer (cutaneous malignant melanoma) have increased more than 550% in males and 250% in females since the early 1980s in England - according to a new study by Brighton and Sussex Medical School (BSMS).
Published in the new Lancet journal, The Lancet Regional Health - Europe, the study analysed data on more than 265,000 individuals diagnosed with skin cancer in England over the 38-year period, 1981-2018.
Skin cancer is the fifth most common cancer in the UK, with about 16,200 new cases each year.
Excessive exposure to UV radiation from the sun (or sunlight) is the main environmental risk factor for developing skin cancer. It is estimated that about 86% of all skin cancers in the UK are ...
Avoid repeating old mistakes
2021-01-26
Since the founding of the United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) in Rio de Janeiro in 1992, member states have regularly agreed on global strategies to bring the increasingly rapid loss of biodiversity to a halt. In 2002, the heads of state adopted the so-called 2010 biodiversity targets. Eight years later, little progress had been made and 20 new, even more ambitious goals were set for the next ten years. Last year, it became clear that this target had been missed, too. The loss of biodiversity continues unabated.
This year, new targets are being negotiated again - this time for 2030. The decisions are to be made at the Conference of the Parties (COP15) in Kunming, China. To ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
UCLA researchers engineer CAR-T cells to target hard-to-treat solid tumors
New study reveals asynchronous land–ocean responses to ancient ocean anoxia
Ctenophore research points to earlier origins of brain-like structures
[Press-News.org] Concordia researchers find melatonin is effective against polycystic kidney diseaseHormone treatment can help reduce cysts in fruit fly renal tubules, according to Cassandra Millet-Boureima and Chiara Gamberi