New study points to better diagnostics for cancer
CHALM method helps researchers identify more reliable cancer biomarkers
2021-01-27
(Press-News.org) Irvine, CA - January 27, 2021 - A new University of California, Irvine-led study finds a new method for identifying biomarkers may aid in early cancer diagnosis. The study focused on lung cancer, however the Cell Heterogeneity-Adjusted cLonal Methylation (CHALM) method has been tested on aging and Alzheimer's diseases as well and is expected to be effective for studying other diseases.
"We found the CHALM method may be a valuable tool in helping researchers to identify more reliable differentially methylated genes from sequence-based methylation data," said Wei Li, PhD, the Grace B. Bell chair and professor of bioinformatics in the Department of Biological Chemistry at the UCI School of Medicine. "For clinicians, this method may aid in cancer diagnosis by helping them identify more useful biomarkers, which are overlooked by the traditional method."
Published in Nature Communications, the study, titled, "Cellular Heterogeneity-Adjusted cLonal Methylation (CHALM) improves prediction of gene expression," illustrates the importance of considering cell heterogeneity when calculating the DNA methylation level from sequencing data.
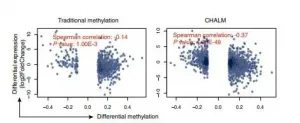
"After applying our CHALM method to a lung cancer dataset, we were able to identify more reliable and biological functions-related differentially methylated genes. Applying our CHALM method may lead to better early cancer detection," said Li.
Using traditional methods for identifying cancer biomarkers, researchers have consistently found the correlation between gene expression and promoter methylation to be weak, especially for low methylated genes. This new study found the CHALM method allowed for more reliable identification of methylated markers that cannot be detected by traditional methods.
INFORMATION:
This study was funded in part by the National Institutes of Health.
About the UCI School of Medicine
Each year, the UCI School of Medicine educates more than 400 medical students, and nearly 150 doctoral and master's students. More than 700 residents and fellows are trained at UCI Medical Center and affiliated institutions. The School of Medicine offers an MD; a dual MD/PhD medical scientist training program; and PhDs and master's degrees in anatomy and neurobiology, biomedical sciences, genetic counseling, epidemiology, environmental health sciences, pathology, pharmacology, physiology and biophysics, and translational sciences. Medical students also may pursue an MD/MBA, an MD/master's in public health, or an MD/master's degree through one of three mission-based programs: the Health Education to Advance Leaders in Integrative Medicine (HEAL-IM), the Leadership Education to Advance Diversity-African, Black and Caribbean (LEAD-ABC), and the Program in Medical Education for the Latino Community (PRIME-LC). The UCI School of Medicine is accredited by the Liaison Committee on Medical Accreditation and ranks among the top 50 nationwide for research. For more information, visit som.uci.edu.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-27
Doctors are increasingly using genetic signatures to diagnose diseases and determine the best course of care, but using DNA sequencing and other techniques to detect genomic rearrangements remains costly or limited in capabilities. However, an innovative breakthrough developed by researchers at Virginia Commonwealth University Massey Cancer Center and the VCU Department of Physics promises to diagnose DNA rearrangement mutations at a fraction of the cost with improved accuracy.
Led by VCU physicist Jason Reed, Ph.D., the team developed a technique that combines a process called digital polymerase chain reaction (dPCR) with high-speed atomic force microscopy (HSAFM) to create an image with such nanoscale resolution that users can measure differences in ...
2021-01-27
Historically redlined neighborhoods are more likely to have a paucity of greenspace today compared to other neighborhoods. The study by researchers at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health and the University of California, Berkeley and San Francisco, demonstrates the lasting effects of redlining, a racist mortgage appraisal practice of the 1930s that established and exacerbated racial residential segregation in the United States. Results appear in Environmental Health Perspectives.
In the 1930s, the Home Owners' Loan Corporation (HOLC) assigned risk grades to neighborhoods across the country based on racial demographics and other factors. "Hazardous" areas--often those whose residents included people ...
2021-01-27
LAWRENCE -- For at least a century, ecologists have wondered at the tendency for populations of different species to cycle up and down in steady, rhythmic patterns.
"These cycles can be really exaggerated -- really huge booms and huge busts -- and quite regular," said Daniel Reuman, professor of ecology & evolutionary biology at the University of Kansas and senior scientist at the Kansas Biological Survey. "It attracted people's attention because it was kind of mysterious. Why would such a big thing be happening?"
A second observation in animal populations ...
2021-01-27
(Boston)--Researchers from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) have identified proteins that are essential for the viability of whole genome doubled tumor cells, yet non-essential to normal cells that comprise the majority of human tissue.
"Exploiting these vulnerabilities represents a highly significant and currently untapped opportunity for therapeutic intervention, particularly because whole genome doubling is a distinguishing characteristic of many tumor types," said corresponding author Neil J. Ganem, PhD, associate professor of pharmacology and medicine, section of hematology and medical oncology, at Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM).
The vast majority of human cells are diploid, meaning that they possess two copies of each ...
2021-01-27
The Asia Pacific Consortium on Osteoporosis (APCO) has today launched the first pan-Asia Pacific clinical practice standards for the screening, diagnosis, and management of osteoporosis, targeting a broad range of high-risk groups.
Published in Osteoporosis International today, 'The APCO Framework' comprises 16 minimum clinical standards set to serve as a benchmark for the provision of optimal osteoporosis care in the region.
Developed by APCO members representing key osteoporosis stakeholders, and multiple medical and surgical specialities, this set of clear, concise, relevant and pragmatic clinical standards aims to support national societies, guidelines development authorities, and health care policy makers with ...
2021-01-27
People who take opioid medications for chronic pain may have a hard time finding a new primary care clinic that will take them on as a patient if they need one, according to a new "secret shopper" study of hundreds of clinics in states across the country.
Stigma against long-term users of prescription opioids, likely related to the prospect of taking on a patient who might have an opioid use disorder or addiction, appears to play a role, the University of Michigan research suggests.
Simulated patients who said their doctor or other primary care provider had retired were more likely to be told they could be accepted as new patients, compared with those who said their provider had stopped prescribing opioids to them for an unknown reason.
The U-M primary care provider ...
2021-01-27
Neurons, the fundamental units of the brain, are complex computers by themselves. They receive input signals on a tree-like structure - the dendrite. This structure does more than simply collect the input signals: it integrates and compares them to find those special combinations that are important for the neurons' role in the brain. Moreover, the dendrites of neurons come in a variety of shapes and forms, indicating that distinct neurons may have separate roles in the brain.
A simple yet faithful model
In neuroscience, there has historically been a tradeoff between a model's faithfulness to the underlying biological neuron and its complexity. Neuroscientists have constructed ...
2021-01-27
Being constantly flooded by a mass of stimuli, it is impossible for us to react to all of them. The same holds true for a little fish. Which stimuli should it pay attention to and which not? Scientists at the Max Planck Institute of Neurobiology have now deciphered the neuronal circuit that zebrafish use to prioritize visual stimuli. Surrounded by predators, a fish can thus choose its escape route from this predicament.
Even though we are not exposed to predators, we still have to decide which stimuli we pay attention to - for example, when crossing a street. Which cars should we avoid, which ones can we ignore?
"The ...
2021-01-27
A massive simulation of the cosmos and a nod to the next generation of computing
A team of physicists and computer scientists from the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory performed one of the five largest cosmological simulations ever. Data from the simulation will inform sky maps to aid leading large-scale cosmological experiments.
The simulation, called the Last Journey, follows the distribution of mass across the universe over time -- in other words, how gravity causes a mysterious invisible substance called "dark matter" to clump ...
2021-01-27
Many genetic mutations have been found to be associated with a person's risk of developing Parkinson's disease. Yet for most of these variants, the mechanism through which they act remains unclear.
Now a new study in Nature led by a team from the University of Pennsylvania has revealed how two different variations--one that increases disease risk and leads to more severe disease in people who develop Parkinson's and another that reduces risk--manifest in the body.
The work, led by Dejian Ren, a professor in the School of Arts & Sciences' Department of Biology, showed that the variation that raises disease risk, which about 17% of people possess, causes a reduction in function of an ion channel ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New study points to better diagnostics for cancer
CHALM method helps researchers identify more reliable cancer biomarkers