NUS scientists discover a new pathway essential for blood formation
This cellular mechanism is important for the function of normal blood stem cells
2021-01-28
(Press-News.org) Blood is vital to life, and a healthy body replenishes worn-out blood cells with new ones throughout one's lifetime. If something goes wrong with this process, serious illness will result.
Researchers from the National University of Singapore (NUS) have now discovered a mechanism controlling the replenishment of blood cells, which could have relevance for new treatments for blood cancers and other blood-related diseases.
The international research team, helmed by Dr Akihiko Numata while he was a Postdoctoral Fellow in the laboratory of Professor Daniel Tenen of the Cancer Science Institute of Singapore and Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine at NUS, focused their investigations on a protein called Tip60, which catalyzes important biological processes in many living organisms. In particular, Tip60 controls hematopoietic stem cells, the source of new blood cells.
In a 10-year-long study, the scientists developed sophisticated molecular tools and experiments to understand the role Tip60 plays in hematopoietic stem cells. They knocked out the protein by modifying its genetic code, thereby deleting certain parts of the protein and preventing it from binding to other biological molecules. The scientists then compared the malfunctioning Tip60 with the normal version.
"We discovered that Tip60 plays a crucial role, activating genes that are in turn responsible for maintaining the hematopoietic stem cells and their DNA. In fact, when completely deprived of Tip60, many of the cells suffered 'catastrophic' DNA damage and died. On the other hand, some of the genes that Tip60 affects can lead to leukemia, and understanding this pathway may lead to novel therapeutic approaches," explained Prof Tenen.
INFORMATION:
The team's findings were published in the prestigious scientific journal Blood in October 2020.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-28
Countries around the world are seeing a surge in the number of computer science students. Enrolment in related university programs in the U.S. and Canada tripled between 2006-2016 and Europe too has seen rising numbers. At the same time, the age to start coding is becoming younger and younger because governments in many different countries are pushing K-12 computer science education. Despite the increasing popularity of computer programming, little is known about how our brains adapt to this relatively new activity. A new study by researchers in Japan has examined the brain activity ...
2021-01-28
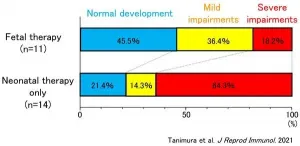
A cross-institutional research group has revealed for the first time in the world that infants with symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection who were treated with a combination of immunoglobulin fetal therapy and neonatal therapy with antiviral drugs were less likely to experience the severe aftereffects associated with the infection than those who only received the neonatal therapy.
It is hoped that the number of children suffering severe aftereffects resulting from congenital CMV infection will decrease in the future.
The research group included the following members:
Doctor YAMADA Hideto ...
2021-01-28
Tokyo, Japan -- In the marchland of Japan's Oze National Park, keeping track of the deer population has been a difficult and time-consuming task for the park rangers. Now their lives could get much easier, thanks to a novel technique for tracking deer movements using unmanned listening devices developed by researchers at the Institute of Industrial Science, a part of The University of Tokyo.
Monitoring deer numbers is important in Oze and other national parks in Japan because deer are not native to the ecosystem and can have damaging effects on it. Current methods of monitoring deer populations range from traditional techniques such as counting droppings to photographing deer at night using automated cameras or from above during the day using unmanned aerial vehicles ...
2021-01-28
Air pollution is a key risk factor for cardiovascular disease, and a major contributor to the global burden of disease. Long-term exposure to air pollution has also been linked to an increased risk of death from COVID-19. This dangerous "triple threat" of air pollution, COVID-19 and cardiovascular disease should be taken seriously, warn major health authorities.
Four leading cardiovascular organizations - the World Heart Federation (WHF), American College of Cardiology (ACC), American Heart Association (AHA) and European Society of Cardiology (ESC) - today released a joint statement urging the medical community and health authorities to mitigate the impact of air pollution on people's ...
2021-01-28
A Quebec research team has discovered two early plasma markers to detect Alzheimer's disease five years before its onset. The results of this recent study led by the doctoral student Mohamed Raâfet Ben Khedher and postdoctoral student Mohamed Haddad, directed by Professor Charles Ramassamy of the Institut national de la recherche scientifique (INRS), have been published in the prestigious scientific journal Alzheimer's & Dementia: Translational Research & Clinical Interventions (TRCI).
The diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease is usually based on a series of psychometric ...
2021-01-28
Support for policies prohibiting smoking and the use of tobacco products on Oregon State University's Corvallis campus grew substantially over a five-year span, especially among tobacco users, a recent OSU study found.
The study, published earlier this month in the journal Preventive Medicine, is unique in its analysis of support for smoke- and tobacco-free campus policies over a long period of time. Most other studies of attitudes toward smoking policies only assess a single point in time.
"Tobacco-free policies are one of the most effective things we can do to reduce the burden of tobacco use, and they are highly supported ...
2021-01-28
Navigating, exploring and thinking about space are part of daily life, whether it's carving a path through a crowd, hiking a backcountry trail or maneuvering into a parking spot.
For most of human history, the driving force for day-to-day wayfinding and movement across the landscape was a need for food. And unlike other primates, our species has consistently divided this labor along gender lines.
In new research published in Nature Human Behaviour, scientists including James Holland Jones of Stanford and lead author Brian Wood of University of California, Los Angeles, argue that the increasingly gendered division of labor in human societies during the past 2.5 million years dramatically shaped how our species uses space, and possibly ...
2021-01-28
A research team from HSE University and SkolTech, together with experts from the Smorodintsev Research Institute of Influenza in St. Petersburg and the RAS Kharkevich Institute for Information Transmission Problems (IITP), discovered that the SARS-CoV-2 virus independently entered Russia at least 67 times, mostly at the end of February and beginning of March 2020. The vast majority of introductions came from European countries. No cases of introduction from China were registered, which is likely due to the timely closure of borders with the country. Currently, nine local virus lineages are circulating in Russia, which are not present elsewhere in the world. Given that Russia was actively 'importing' the virus from abroad, the researchers have not detected any cases of 'exporting' ...
2021-01-28
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- In a new study published in Circulation, Mayo Clinic researchers provide the first preclinical, proof-of-concept study for hybrid gene therapy in long QT syndrome, a potentially lethal heart rhythm condition.
Researchers demonstrated its potential therapeutic efficacy in two in vitro model systems using beating heart cells reengineered from the blood samples of patients with 1 long QT syndrome. They targeted the whole KCNQ1 gene rather than specific LQT1-causative mutations, making this study applicable to all patients with long QT ...
2021-01-28
When you think of fungi, what comes to mind may be a crucial ingredient in a recipe or their amazing ability to break down dead organic matter into vital nutrients. But new research by Shuhai Xiao, a professor of geosciences with the Virginia Tech College of Science, and Tian Gan, a visiting Ph.D. student in the Xiao lab, highlights yet another important role that fungi have played throughout the Earth's history: helping the planet recover from an ice age.
A team of scientists from Virginia Tech, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guizhou Education University, and University of Cincinnati has discovered the remains of a fungi-like microfossil that ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] NUS scientists discover a new pathway essential for blood formation
This cellular mechanism is important for the function of normal blood stem cells