INFORMATION:
New catalyst moves seawater desalination, hydrogen production closer to commercialization
Fast, one-step assembly at room temperature yields high efficiency at low cost
2021-01-28
(Press-News.org) Seawater makes up about 96% of all water on earth, making it a tempting resource to meet the world's growing need for clean drinking water and carbon-free energy. And scientists already have the technical ability to both desalinate seawater and split it to produce hydrogen, which is in demand as a source of clean energy.
But existing methods require multiple steps performed at high temperatures over a lengthy period of time in order to produce a catalyst with the needed efficiency. That requires substantial amounts of energy and drives up the cost.
Researchers from the University of Houston have reported an oxygen evolving catalyst that takes just minutes to grow at room temperature on commercially available nickel foam. Paired with a previously reported hydrogen evolution reaction catalyst, it can achieve industrially required current density for overall seawater splitting at low voltage. The work is described in a paper published in Energy & Environmental Science.
Zhifeng Ren, director of the Texas Center for Superconductivity at UH (TcSUH) and corresponding author for the paper, said speedy, low-cost production is critical to commercialization.
"Any discovery, any technology development, no matter how good it is, the end cost is going to play the most important role," he said. "If the cost is prohibitive, it will not make it to market. In this paper, we found a way to reduce the cost so commercialization will be easier and more acceptable to customers."
Ren's research group and others have previously reported a nickel-iron-(oxy)hydroxide compound as a catalyst to split seawater, but producing the material required a lengthy process conducted at temperatures between 300 Celsius and 600 Celsius, or as high as 1,100 degrees Fahrenheit. The high energy cost made it impractical for commercial use, and the high temperatures degraded the structural and mechanical integrity of the nickel foam, making long-term stability a concern, said Ren, who also is M.D. Anderson Professor of physics at UH.
To address both cost and stability, the researchers discovered a process to use nickel-iron-(oxy)hydroxide on nickel foam, doped with a small amount of sulfur to produce an effective catalyst at room temperature within five minutes. Working at room temperature both reduced the cost and improved mechanical stability, they said.
"To boost the hydrogen economy, it is imperative to develop cost-effective and facile methodologies to synthesize NiFe-based (oxy)hydroxide catalysts for high-performance seawater electrolysis," they wrote. "In this work, we developed a one-step surface engineering approach to fabricate highly porous self-supported S-doped Ni/Fe (oxy)hydroxide catalysts from commercial Ni foam in 1 to 5 minutes at room temperature."
In addition to Ren, co-authors include first author Luo Yu and Libo Wu, Brian McElhenny, Shaowei Song, Dan Luo, Fanghao Zhang and Shuo Chen, all with the UH Department of Physics and TcSUH; and Ying Yu from the College of Physical Science and Technology at Central China Normal University.
Ren said one key to the researchers' approach was the decision to use a chemical reaction to produce the desired material, rather than the energy-consuming traditional focus on a physical transformation.
"That led us to the right structure, the right composition for the oxygen evolving catalyst," he said.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
George Mason University expands testing and tracking behind faculty research
2021-01-28
Mason scientists employ a rapid-result, saliva-based test that significantly expands testing capacity, and an antibody test that can track vaccine response.
George Mason University announces it is introducing a rapid-result, saliva-based COVID-19 test that will greatly expand testing capabilities on its campuses this spring. The effort, led by Mason's faculty, is part of a comprehensive program to better track and control the virus on campus.
Mason scientists, who are pushing the boundaries of technologies that are keeping Mason's campuses safe, are ...
How a cancer drug carrier's structure can help selectively target cancer cells
2021-01-28
The main culprit in cancer is healthy cells that have gone rogue and acquire the ability to divide uncontrollably. These cells acquire growth advantages over normal cells and manipulate their environment by altering the cellular pathways involved in growth and metabolism. Over the past few decades, various altered pathways and proteins have been identified as targets for therapeutic interventions. However, what remains challenging is selectively targeting cancer cells and ensuring that the drug reaches the tumor in adequate amounts, without severely affecting normal cells. And in this regard, biocompatible delivery vehicles (which are non-toxic to normal cells) can be useful.
One such potential candidate is "porphyrins," a group of organic cyclic compounds that form the ...
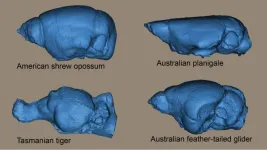
Squeeze it like toothpaste: The flexible brain of marsupial mammals
2021-01-28
Being stretchy and squeezable may be the key to finding space for the brain in mammals, including humans.
An international study, co-led by Flinders University's Vera Weisbecker, has revealed that marsupial mammals like possums, kangaroos, and wombats appear to have a lot of flexibility when it comes to accommodating their brains into their skulls.
"The brain is one of the heaviest parts of the head, particularly in smaller mammals. But it needs to be placed in a way that doesn't interfere with the many vital functions of the head, such as seeing, hearing, smelling and of course feeding," says Dr. Weisbecker.
"Stowing" a large brain ...
Improvements to holographic displays poised to enhance virtual and augmented reality
2021-01-28
WASHINGTON -- Researchers have developed a new approach that improves the image quality and contrast for holographic displays. The new technology could help improve near-eye displays used for virtual and augmented reality applications.
"Augmented and virtual reality systems are poised to have a transformative impact on our society by providing a seamless interface between a user and the digital world," said research team member Jonghyun Kim from technology company NVIDIA and Stanford University. "Holographic displays could overcome some of the biggest ...
Press briefing highlights disparities among key groups
2021-01-28
(Singapore--January 28, 2021 11:00 p.m. SPT/10:00 a.m. EST)----Several leading international lung cancer researchers at a press briefing held by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer today, presented compelling new data revealing that factors of race, gender, sexual orientation and income continue to be significant barriers to those living with lung cancer. The press briefing is part of the IASLC's World Conference on Lung Cancer 2020 Singapore.
The press briefing is moderated by IASLC Communications Committee Chair Dr. Anne-Marie Baird, senior research fellow at Trinity College in ...
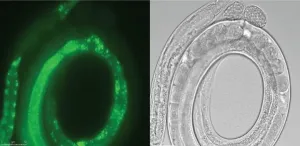
Rules of resistance against transgene silencing
2021-01-28
Clear rules for engineering transgenes that can be inserted and propagated over multiple generations of nematodes include ways to protect inserted genes from the organism's natural defenses against foreign DNA. Developed by KAUST researchers, the rules have implications for many research fields, including gene therapy development.
Scientists often study biological processes, such as normal and mutant gene functions, in the worm Caenorhabditis elegans because it has many genes and molecular pathways in common with humans. Specific gene functions can be investigated by injecting DNA into the worm's reproductive organs, where it links into what is known as an extra-chromosomal array. This array is eventually incorporated into the nucleus, where it is duplicated ...
Brain 3D genome study uncovers human-specific regulatory changes during development
2021-01-28
A team led by Prof. SU Bing from the Kunming Institute of Zoology (KIZ) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), Prof. LI Cheng from Peking University, and Prof. ZHANG Shihua from the Academy of Mathematics and Systems Science of CAS has reported the highest resolution by far of the 3D genome of the primate brain, and demonstrated the molecular regulatory mechanisms of human brain evolution through cross-species multi-omics analysis and experimental validation. The study was published in Cell.
The unique pattern of human brain development stems from accumulated genetic changes during human evolution. Among the huge number of diverging genetic changes, only a small portion of the between-species ...
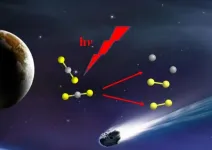
Dalian coherent light source reveals the origin of interstellar medium S2 fragments
2021-01-28
Studying the creation and evolution of sulfur-containing compounds in outer space is essential for understanding interstellar chemistry. CS2 is believed to be the most important molecule in comet nuclei, interstellar dust, or ice cores. CS and S2 are the photodissociation fragments of CS2.
Forty years ago, the emission spectra of only CS and S2 species, and not those of CS2 species, were observed from several comets by the International Ultraviolet Explorer satellite. The photodissociation mechanism of CS2 molecules remains unclear, and S2 fragments have not been experimentally observed before.
Recently, a team led by Prof. YUAN Kaijun from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), in cooperation with Prof. WANG Xing'an's group ...
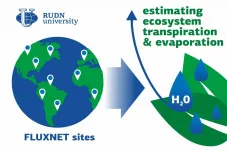
Ecologists conducted a novel study on vegetation transpiration from a global network of 251 sites
2021-01-28
An ecologist from RUDN University together with colleagues from 14 countries compared three methods for estimating ecosystem transpiration in a study. In the first ever research with such a comprehensive data-set, the team used land-atmosphere water vapor flux data of collected at 251 locations all over the planet, from Australia to Greenland. The outcome of the research help to understand the role of plants in the global water and carbon cycles in the current predicament of global warming. The results of the study were published in the December 2020 issue of the journal Global ...
Three mental health conditions contribute to violent offenses, WCU study finds
2021-01-28
Western Carolina University researchers find a disproportionate number of inmates with violent offenses suffer from post-traumatic stress disorder, panic disorder and alcohol use disorder, and published their findings in the Journal of Criminal Psychology.
Alexa Barrett, clinical psychology master's student at WCU, and Al Kopak, associate professor of criminology and criminal justice at WCU, discovered the combination of PTSD, PD and AUD significantly increased the likelihood of violent offenses while conducting research at three county detention centers in North Carolina.
Supported by a Summer Research Assistantship provided by the Graduate School, the purpose of this study was to detail ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
[Press-News.org] New catalyst moves seawater desalination, hydrogen production closer to commercializationFast, one-step assembly at room temperature yields high efficiency at low cost