(Press-News.org) The ability to manipulate near-infrared (NIR) radiation has the potential to enable a plethora of technologies not only for the biomedical sector (where the semitransparency of human tissue is a clear advantage) but also for security (e.g. biometrics) and ICT (information and communication technology), with the most obvious application being to (nearly or in)visible light communications (VLCs) and related ramifications, including the imminent Internet of Things (IoT) revolution. Compared with inorganic semiconductors, organic NIR sources offer cheap fabrication over large areas, mechanical flexibility, conformability, and, potentially, bio-compatibility. However, the emission efficiency of organic emitters in the NIR is hindered by the detrimental effects of certain types of aggregation/packing of the emitters in the solid state and by the generally observed increase of non-radiative rates upon reduction of the energy gap (EG), i.e. the so-called "energy-gap law" (EG-law) for radiationless transitions. Hybrid organic/inorganic innovative materials such as perovskite methylammonium lead halide and quantum dots may offer a high external quantum efficiency (EQE) alternative, but their heavy-metal content will prevent their use in most applications, especially biocompatible or wearable ones. Toxicity issues can also affect phosphorescent materials incorporating toxic heavy elements.
In a new paper published in Light: Science & Applications, an international team of scientists, led by Professor Franco Cacialli at University College London and Professor Harry Anderson at the University of Oxford report novel non-toxic and heavy-metal-free organic NIR emitters and OLEDs characterised by emission peaking at ~ 850 nm and a maximum 3.8% external quantum efficiency (EQE).
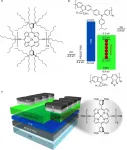
The authors use optical spectroscopy to elucidate how it is possible to leverage the increasing spatial extent of excited states with oligomer length to favourably manipulate the competition between radiative and nonradiative processes (quantified by the radiative and nonradiative rates, kr and knr respectively), while simultaneously suppressing aggregation. Surprisingly, instead of a decreasing photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) with oligomer length (and thus with reducing gap), a steady increase and eventual saturation of the PLQY is observed at around the hexamer (l-P6(THS)). While surprising, this behaviour can be understood by considering that in these systems conjugated triple-bond-based bridges between the porphyrins allow effective intra-molecular electronic coupling among the macrocycles, and so enable the radiative (singlet) excited state (exciton) to delocalize over increasing portions of the molecule. This forces an increasing mismatch of the spatial extent of the radiative (singlet) and of the non-radiative (triplet) excitons, in view of the intrinsically localized nature of the triplets. Such a mismatch is expected to suppress intersystem crossing (ISC) between singlets and triplets and therefore the non-radiative rate (knr). In addition, exciton delocalization is also expected to favour decoupling from vibrational ladders (and thus circumvent the EG-law). Remarkably, the growth of the nonradiative rate as a function of the decrease of the energy gap (forced by the increased oligomer length) is characterized in these systems by a logarithmic rate an order of magnitude smaller than in previous studies. Second, bulky trihexylsilyl side chains are attached to the porphyrins to prevent aggregation quenching, through steric hindrance, which limits π-π interactions (see chemical structure in Figure 1).
The basic photophysics and material design breakthrough has been confirmed by incorporating an F8BT:l-P6(THS) blend in OLEDs, with which an average EQE of 1.1% and a maximum EQE of 3.8% at a peak wavelength of 850 nm were demonstrated (Figure 2). A novel quantitative model was also developed to analyse the results, which implies the importance of triplets to singlets conversion processes (e.g. reverse inter-system crossing, and/or thermally activated delayed fluorescence) to account for the EQE values beyond the apparent limit imposed by spin-statistics.
The EQEs presented in the paper are, to the best of the authors knowledge, the highest reported so far in this spectral range from a "heavy-metal-free" fluorescent emitter.
The authors summarise the significance of their work by saying:
"Not only do our results demonstrate milder increases of knr with (reducing) EG than in the literature, but, most importantly, they also provide a general strategy for designing high-luminance NIR emitters."
"In the short term, they may enable further development of OLEDs in this challenging spectral range for a wide range of potential applications spanning from the life-sciences (biochemical wearable sensors, in vivo sub-surface bio-imaging, to name just two), security (e.g. biometrics), horticulture, and (in)visible light communications (iVLC), a serious contestant to alleviate the bandwidth demands of the imminent Internet-of-thing (IoT) revolution."
"More importantly, and in perspective, these findings are significant to a range of disciplines."
INFORMATION:
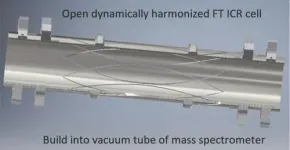
Mass spectrometers are widely used to analyze highly complex chemical and biological mixtures. Skoltech scientists have developed a new version of a mass spectrometer that uses rotation frequencies of ionized molecules in strong magnetic fields to measure masses with higher accuracy (FT ICR). The team has designed an ion trap that ensures the utmost resolving power in ultra-strong magnetic fields. The research was published in the journal Analytical Chemistry.
The ion trap is shaped like a cylinder made up of electrodes, with electric and magnetic fields generated inside. The exact masses of the test sample's ions can be determined from their rotation frequencies. The electrodes must create a harmonized field of a particular shape ...
Skoltech researchers and their colleagues from Russia and Germany have designed an on-chip printed 'electronic nose' that serves as a proof of concept for low-cost and sensitive devices to be used in portable electronics and healthcare. The paper was published in the journal ACS Applied Materials Interfaces.
The rapidly growing fields of the Internet of Things (IoT) and advanced medical diagnostics require small, cost-effective, low-powered yet reasonably sensitive, and selective gas-analytical systems like so-called 'electronic noses.' These ...
A genetic engineering method makes it possible to observe how woody cell walls are built in plants. The new research in wood formation, conducted by the University of Copenhagen and others, opens up the possibility of developing sturdier construction materials and perhaps more climate efficient trees.
The ability of certain tree species to grow taller than 100 meters is due to complex biological engineering. Besides needing the right amounts of water and light to do so, this incredible ability is also a result of cell walls built sturdily enough to keep a tree both upright and able to withstand the tremendous pressure created as water is sucked up from its roots and into its leaves.
This ability is made possible by what are known as the secondary cell ...
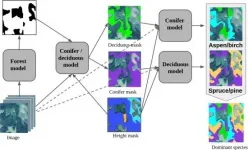
Skoltech scientists have developed an algorithm that can identify various tree species in satellite images. Their research was published in the IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing.
Identifying tree species is essential for efficient forest management and monitoring. Satellite imagery is an easier and cheaper way to deal with this task than other approaches that require ground observations of vast and remote areas.
Researchers from the Skoltech Center for Computational and Data-Intensive Science and Engineering (CDISE) and Skoltech Space Center used a neural network to automate dominant tree species' identification in high and medium resolution images. A hierarchical classification model and additional data, such as vegetation height, helped ...
People with combined vision and hearing loss are nearly four times more likely to experience depression and more than three times more likely to suffer chronic anxiety, according to a new study published in the journal Frontiers in Psychology and led by Anglia Ruskin University (ARU).
Researchers analysed a health survey of 23,089 adults in Spain and found that while people suffering either vision or hearing loss both were more likely to report depression as those that were not, that risk increased to 3.85 times higher when respondents reported problems with both senses combined.
The study also found people with combined vision and hearing loss were 3.38 times more likely than the general population to report chronic anxiety.
It is understood to be the first study looking at ...
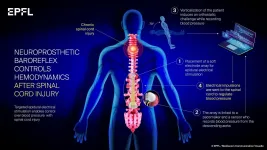
An international team of scientists headed by Grégoire Courtine at EPFL and CHUV and Aaron Phillips at the University of Calgary has developed a treatment that can dramatically improve the lives of patients with a spinal cord injury.
VIDEO: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UGXnuHgDWFU
"A serious and underrecognized result of these injuries is unstable blood pressure, which can have devastating consequences that reduce quality of life and are life threatening. Unfortunately, there are no effective therapies for unstable blood pressure after spinal cord injury". said Dr. Aaron Phillips, co-lead author of the study (see affiliations below). ...
Thursday, 28 January 2021: A study has found that adolescents who frequently use cannabis may experience a decline in Intelligence Quotient (IQ) over time. The findings of the research provide further insight into the harmful neurological and cognitive effects of frequent cannabis use on young people.
The paper, led by researchers at RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences, is published in Psychological Medicine.
The results revealed that there were declines of approximately 2 IQ points over time in those who use cannabis frequently compared to those who didn't use cannabis. Further analysis suggested that this decline in IQ points was primarily related to reduction in verbal IQ.
The research involved systematic review and statistical analysis on seven longitudinal studies ...
New insight into how human brains detect and perceive different types of touch, such as fluttery vibrations and steady pressures, has been revealed by UCL scientists with the help of the ancient Chinese cooking ingredient, Szechuan pepper.
Humans have many different types of receptor cells in the skin that allow us to perceive different types of touch. For more than a century, scientists have puzzled over whether touch signals from each type of receptor are processed independently by the brain, or whether these different signals interact before reaching conscious perception.
For the study, published in Proceedings of the Royal Society B, UCL researchers took a novel approach to this question by stimulating one type of touch receptor chemically, and another type mechanically. ...
Investors' moods are affected by gloomy weather. New research from Copenhagen Business School recommends entrepreneurs looking for finance should be aware of the weather forecast at the time they want to launch their crowdfunding campaigns.
The researchers wanted to explore whether weather-induced moods can explain crowdfunders' contributions and focused on the role of investors' moods and emotions including day-to-day decisions on the crowdfunding platform Companisto.
"Financial investment plays a vital role in the success of an entrepreneurial venture ...
Molecules consisting of many atoms are complex structures. The outer electrons are distributed among the different orbitals, and their shape and occupation determine the chemical behaviour and reactivity of the molecule. The configuration of these orbitals can be analysed experimentally. Synchrotron sources such as BESSY II provide a method for this purpose: Resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS). However, to obtain information about the orbitals from experimental data, quantum chemical simulations are necessary. Typical computing times for larger molecules take weeks, even on high-performance computers.
Speeding up the evaluation
"Up to now, these calculations have mostly been carried out subsequent to the measurements", explains theoretical chemist Dr. Vinicius Vaz da Cruz, ...