INFORMATION:
Study coauthors are Mark J. Lieser, MD, FACS, and John Chipko, MD, of Research Medical Center, Kansas City, Mo.; Tabatha Cooper, MS, of the Data Analytics Research and Reporting, Clinical Operations Group, HCA Healthcare, Nashville; Dorraine D. Watts, PhD, RN, Nina Y. Wilson, MSN, RN, Ransom J. Wyse, MPH, and Jeneva M. Garland, PharmD, RPh, of the Center for Trauma and Acute Care Surgery Research, Clinical Operations Group, HCA Healthcare; Matthew M. Carrick, MD, FACS, of Medical Center Plano in Plano, Texas; and Gina M. Berg, PhD, of Wesley Medical Center, Wichita, Kan.
"FACS" designates that a surgeon is a Fellow of the American College of Surgeons.
Dr. Fakhry has no conflicts of interest related to this research and study coauthors have no relevant relationships to disclose.
Citation: Critical Role of Trauma and Emergency Surgery Physicians in Patient Satisfaction: An Analysis of HCAHPS Data from 186,779 Patients and 168 Hospitals in a National Healthcare System. Journal of the American College of Surgeons. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2020.12.017.
About the American College of Surgeons
The American College of Surgeons is a scientific and educational organization of surgeons that was founded in 1913 to raise the standards of surgical practice and improve the quality of care for all surgical patients. The College is dedicated to the ethical and competent practice of surgery. Its achievements have significantly influenced the course of scientific surgery in America and have established it as an important advocate for all surgical patients. The College has more than 82,000 members and is the largest organization of surgeons in the world. For more information, visit http://www.facs.org.
Trauma surgeons and emergency surgeons positively impact patient satisfaction
Journal of the American College of Surgeons study of 186,779 discharged patients from national CMS survey data set confirms important role of physician communication in overall patient satisfaction
2021-01-29
(Press-News.org) CHICAGO (January 29, 2021): Trauma patients and patients who need emergency surgery have little to no opportunity to get acquainted with the surgeon and team that will perform their operation. However, a large study has found that effective and meaningful physician communication is a more important contributor to the overall satisfaction of trauma patients and those having emergency surgery than it is for patients admitted to the hospital for medical reasons or for elective procedures.
The study was selected for the 2020 Southern Surgical Association Program and published as an "article in press" on the website of the Journal of the American College of Surgeons in advance of print.
The researchers found an unexpectedly significant effect of physician communication among patients admitted through a hospital's trauma bay or emergency department. They analyzed patient survey data to determine how several factors, including interactions with nurses and doctors, contributed to satisfaction ratings in five different patient categories: trauma, direct-admit (elective) surgery, emergency department (ED)-admitted (emergency) surgery, ED-admitted medical, and direct-admit medical.
"Nurses uniformly come out as the most highly ranked, and that's because they provide wonderful bedside care and have so much contact with the patients," said lead study author Samir M. Fakhry, MD, FACS, vice president of the Center for Trauma and Acute Care Surgery Research for HCA Healthcare, a publicly traded company based in Nashville, Tenn., that operates 187 hospitals and other health care facilities. "But in the case of the trauma patients, and to a lesser degree the emergency surgical patients, physician communication ranked as the number two factor," he said.
Among elective surgery and medical admission patients, physician communication didn't register even as a third or fourth factor. "There's something about the way the trauma surgeons are delivering their care that is an important driver of the satisfaction scoring that is provided by our patients," Dr. Fakhry said.
The authors noted that no previous large study has investigated overall satisfaction among trauma and emergency surgery patients. Study investigators analyzed Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems (HCAHPS) survey data of 186,779 non-maternity patients discharged from 168 HCA Healthcare hospitals in 2018 and 2019. HCAHPS is a post-discharge survey that asks patients about their hospital experience. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services uses HCAHPS data to generate hospital ratings reported on its Hospital Compare website. The survey captures patient impressions of a number of factors about the hospital experience, including communication with doctors and nurses.
The researchers found that physician communication had a greater impact on overall satisfaction after accounting for nursing factors among trauma and emergency surgery patients, representing a 12 percent boost in the former and an 8.6 percent boost in the latter. In categories in which physician communication received low ratings, it was unlikely that high scores in other factors could compensate to bring the overall satisfaction score above the 50th percentile.
"The things trauma surgeons and the people around them are doing seem to be very important to their patients," Dr. Fakhry said. "For many people in hospital leadership, the trauma service is an important mission of the hospital, but they wouldn't expect the trauma service to contribute very much to a positive patient experience because we're dealing with injured people. However, this study shows trauma care has a significant impact on hospital ratings."
The authors noted that future research should explore what specific aspects of the physician's behavior in trauma, emergency surgery, and ED admissions contribute to patient satisfaction.
"We like to say in the world of trauma that the 't' in trauma is for team, so it would be important to stress that the team approach we employ in trauma may be an important part of the findings of the study," Dr. Fakhry said. "That's something we're going to explore in future studies to try to determine what it is, specifically, that trauma surgeons are doing, how they relate to the nurses, and if the interaction between the doctor and the nurse are all something we can turn into an even more positive experience for the patient."
In an invited commentary, Thomas J. Esposito, MD, MPH, FACS, a professor at the University of Illinois College of Medicine, Peoria, noted the study focuses attention on the importance of communication, but also expressed reservations about the "reliability and veracity" of surveys, citing the inaccuracy of pre-election opinion polls in the last two presidential election cycles. "I would encourage these investigators to expand their research and further dive into the data as well as the survey process," Dr. Esposito wrote.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
BioNTech-Pfizer mRNA vaccine largely effective against UK variant, Sera from 40 patients show
2021-01-29
In a study evaluating the BioNTech-Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine's ability to neutralize the B.1.1.7 ("UK") viral variant, researchers found no loss of immune protection compared to that against the original Wuhan reference strain. Their analysis was based on blood samples from 40 people who had received the BioNTech-Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine during clinical trials. The authors conclude their results show it is "unlikely that the UK variant virus will escape ... protection" as mediated by this vaccine. In September 2020, the SARS-CoV-2 lineage B.1.1.7 was discovered in the United Kingdom. It subsequently increased in prevalence, showed enhanced transmissibility, and spread to other continents. ...
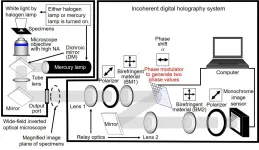
High-speed holographic fluorescence microscopy system with submicron resolution
2021-01-29
[Abstract]
The National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT), Tohoku University, Toin University of Yokohama, and Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) have succeeded in developing a scanless high-speed holographic fluorescence microscopy system with submicron resolution for a 3D space. The system is based on digital holography. The developed microscopy system has an algorithm to acquire 3D information of fluorescent objects toward scanless 3D measurement in less than 1 millisecond. Scanless 3D sensing with submicron resolution and color-multiplexed holographic fluorescence imaging have been demonstrated using the algorithm. The microscopy system will be further developed to achieve holographic 3D motion-picture sensing of specimens ...
Biobased anti-thrombosis agent
2021-01-29
Thrombosis, the clogging of blood vessels, is a major cause of heart attacks and embolism. Scientists have now engineered the first inhibitors of thrombin, a protease promoting thrombosis, that is three-fold efficient. In a study published in the journal Angewandte Chemie, the authors demonstrate that attacking three sites of the thrombin molecule is more efficient than attacking only two sites, which is the mode of action of many natural agents.
Soon after an injury, thrombin appears at the site of the wound, promoting platelet coagulation and fibrin development to clog the wound and grow new tissue. Unfortunately, inside blood ...
How lipids distribute proteins within cells
2021-01-29
An international team of scientists, coordinated by the Seville Institute of Biomedicine (IBiS) and the University of Seville has solved one of the hitherto unresolved enigmas of basic biology: how exactly do lipids distribute proteins within a cell? To do this, they used a new, completely innovative microscopy technology, which they applied to "mutant" cells they designed in their laboratory.
This discovery represents a major advance in understanding how proteins are distributed in cells to perform their vital functions, and could open the door to understanding the causes of diseases associated with failures in protein distribution at the ...
Yangtze River observational system to improve East Asian rainy season forecasting
2021-01-29
Researchers have completed the first ever multi-level hydrological tracking of the Yangtze River from the ground, air and space in order to investigate the properties of cloud formation during the mei-yu--an intense rainy season that forms part of East Asia's summer monsoon. The effort should permit greater understanding of the mei-yu precipitation process and thus enable much more accurate forecasts of this key meteorological phenomenon in the region.
The mei-yu, also known as the "Plum Rain", is a period of severe, concentrated rainfall that lasts for up to two months during the late ...
Schoolchildren are learning about health through football (soccer)
2021-01-29
Knowledge about health is a cornerstone in a child's development of physical and psychosocial health.
Since 2016, around 25,000 pupils in years 4-6 in 86 of Denmark's municipalities have taken part in the project "11 for Health in Denmark", an 11-week exercise and health education programme offered to all schools in a collaboration between the University of Southern Denmark and the Danish Football Association.
More than 3,000 of these pupils completed questionnaires before and after the programme aimed at determining their knowledge about health and understanding their experience of the 11-week programme.
An increase of 10 percentage ...
Local emissions amplify regional haze and particle growth
2021-01-29
New particle formation (NPF) is a major source of aerosol particles in the global atmosphere. In polluted megacities, such as Beijing, the role of new particle formation events and their contribution to haze formation through subsequent growth is still unclear.
To improve the understanding of the sources, meteorological conditions, and chemistry behind air pollution, the research teams led by Prof. Yele Sun with the Institute of Atmospheric Physics at the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Prof. Markku Kulmala with the University of Helsinki performed simultaneous measurements ...
Production of 'post-lithium-ion batteries' requires new skills
2021-01-29
Research on manufacturing battery cells is gaining momentum - and there is a strong need, considering the future demand for energy storage: For the year 2030, global production of rechargeable batteries will double from today's 750 gigawatt hours (GWh) per year to 1,500 GWh. A recently published review article in the magazine "Nature Energy" on cell production of various battery types suggests that the currently established lithium-ion batteries (LIB) dominate the market of rechargeable high-energy batteries in the coming years. Alternative battery technologies, ...
Past river activity in northern Africa reveals multiple Sahara greenings
2021-01-29
Large parts of today's Sahara Desert were green thousands of years ago. Prehistoric engravings of giraffes and crocodiles testify to this, as does a stone-age cave painting in the desert that even shows swimming humans. However, these illustrations only provide a rough picture of the living conditions. Recently, more detailed insights have been gained from sediment cores extracted from the Mediterranean Sea off the coast of Libya. An international research team examined these cores and discovered that the layers of the seafloor tell the story of major environmental changes in North Africa over ...
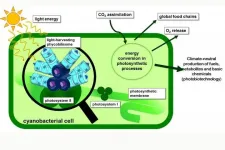
A small protein in bacteria overlooked up to now
2021-01-29
The biological process of photosynthesis is found at the beginning of nearly all food chains. It produces oxygen to breathe and provides the energetic foundation for using biotechnological processes to synthesize biofuels and chemical feedstock. Therefore, researchers are particularly interested in rapidly growing cyanobacteria. These organisms use light as an energy source and can carry out photosynthesis, similar to plants. However, the required photosynthetic protein complexes bind many nutrients. Vanessa Krauspe and Prof. Dr. Wolfgang Hess from the working group for Genetics & Experimental Bioinformatics of the Faculty of Biology of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
[Press-News.org] Trauma surgeons and emergency surgeons positively impact patient satisfactionJournal of the American College of Surgeons study of 186,779 discharged patients from national CMS survey data set confirms important role of physician communication in overall patient satisfaction