(Press-News.org) In Rome lies the Santi Apostoli church, cared for by Franciscan brothers for more than 500 years. For more than 1500 years, this site has held the believed remains of two of the earliest Christians and Jesu apostles: St. Philip and St. James the Younger - relics of the Holy Catholic Church.
In the first few centuries of Christianity, life was difficult for the Christian minority, but gradually towards sixth century Christianity became the dominant religion and after Emperor Constantine on his deathbed declared Christianity the state religion, churches were erected all over the Roman Empire.
Shortly after the churches were erected, remains of worshipped Christian martyrs were moved from their graves to designated worship churches in the towns. This also applied for the remains of the two apostles, St. Philip and St. James. Such movements of remains were called translations.
A foot, a femur and a tibia
It is unknown who translated the believed remains of St. Philip and St. James and where from, but it is a fact, that they came to glorify the current church of Santi Apostoli in Rome, constructed in their honor. It is also a fact that the remains have been kept in the church since the sixth century.
So, are the relics really the remains of St. James and St. Philip? And what else can we learn from the bones?
The skeletons are today far from complete. Only fragments of a tibia, a femur and a mummified foot remain. The tibia and foot are attributed to St. Philip, the femur to St. James. It appears likely that this has been the case since the sixth century.
Radiocarbon dating
Professor of chemistry and archaeometry, Kaare Lund Rasmussen from University of Southern Denmark has led the scientific investigations of these remains supported by a team consisting of colleagues from University of Groningen in Holland, University of Pisa in Italy, Cranfield Forensic Institute in England, Pontifical Institute of Christian Archaeology in Italy and the National Museum of Denmark.
The results are published in the scientific journal Heritage Science.
The researchers considered the remains of St. Philip too difficult to de-contaminate and radiocarbon date, and their age thus remains unknown so far. But the femur, believed to belong to St. James, underwent several analyses. Most importantly, it was radiocarbon dated to AD 214-340.
Thus, the preserved relic, the femur, is not that of St. James. It originates from an individual some 160-240 years younger than St. James, explains Professor Kaare Lund Rasmussen, University of Southern Denmark, adding:
- Though the relic is not that of St James, it casts a rare flicker of light on a very early and largely unaccounted for time in the history of early Christianity.
Who that person was, is of course impossible to say.
Searching for martyr corpses
- We consider it very likely, that whoever moved this femur to the Santi Apostoli church, believed it belonged to St. James. They must have taken it from a Christian grave, so it belonged to one of the early Christians, apostle or not, comments Professor Kaare Lund Rasmussen.
The same goes for the believed remains of St. Philip, he adds.
- One can imagine that when the early church authorities were searching for the corpse of the apostle, who had lived hundreds of years earlier, they would look in ancient Christian burial grounds where bodies of holy men might have been put to rest at some earlier time, the researchers write in Heritage Science.
Moving bones - a popular tradition:
The first known movement of a martyr's remains to a church is that of St Babylas in AD 354. His remains were transferred from a cemetery in Antioch to Daphne and placed in a church especially built for the purpose by Governor Caesar Gallus
Immediately after this, translations got popular: the translations of St Timotheus, St Andrew, and St Lukas to Constantinople followed in a year's time
At the same time, sources reflect an increasing popularity and circulation of relics from the second part of the 4th century onwards
Despite the criticism of bishop Athanasius of Alexandria († 373) and Shenoute († 465) at the end of the same century and in the following, relics of martyrs and saints began to be moved into the churches
Throughout the Roman empire, bodies or body parts were exhumated, transferred, and reburied in the apse in close vicinity of the altar of many important churches.
INFORMATION:
Read the research paper 'Investigations of the relics and altar materials relating to the apostles St James and St Philip at the Basilica dei Santi XII Apostoli in Rome'
The application Radar COVID detects twice as many close contacts of people infected with the virus SARS-Cov2 as the manual tracing system. This is the conclusion of the first scientific study that was carried out to assess the application in a trial carried out last summer on the island of La Gomera in the Canary Islands. The following researchers were involved in the project; Àlex Arenas, professor from the Department of Computer Engineering and Mathematics; Lucas Lacasa, from the Queen Mary University, London; and Pablo Rodríguez, from the Association of Computing Machinery, United States. The results have been published in the scientific journal Nature Communications.
The aim of the study was to check the technical and ...
An atlas of harmful algal blooms across the Red Sea reveals their link with industrial aquaculture and how these blooms have changed in recent decades.
Warming oceans and anthropogenic pollution have led to more frequent and extensive harmful algal blooms (HABs) worldwide. These rapid surges in productivity occur when algae suddenly experience advantageous conditions, usually an influx of nutrients, and take over their environment, suffocating other marine life and spreading toxins through the food chain. These blooms harm wild and farmed fish and reduce marine biodiversity.
"HABs are a global problem," says ...
Per capita income, population volume and density, the structure of cities, transport infrastructure or whether districts have their own schools are all factors that can affect the spread of COVID-19. This has been confirmed by a study carried out in 73 districts in Barcelona by researchers from the departments of Geography and Economics of the Universitat Rovira i Virgili, the results of which have been published in the Journal of Public Health. The research reveals that the analysis of the characteristics of every district can facilitate decisions on the specific measures to be applied to individual districts ...
Flinders University researchers have discovered a new anti-inflammatory role for well-known blood clot protein fibrinogen, which could support targeted new treatments for kidney, heart and other common diseases.
The study in Redox Biology describes how fibrinogen can be protective against hypochlorite - a chemical generated by the body during inflammation - and so act as a kind of antioxidant in blood plasma.
"Our team found that fibrinogen, which forms extraordinarily large assemblies when it reacts with hypochlorite, doesn't harm cells in the same way as hypochlorite-modified albumin which exacerbates kidney and heart disease, ...
Researchers at the Garvan Institute of Medical Research have discovered that three patients with a severe genetic immunodeficiency spontaneously repaired the harmful variants in their DNA and restored normal immune function over time.
As cells grow and divide to produce new cells, DNA is copied from the parent cell to provide instructions for the new daughter cells. Random changes that occur as the DNA is copied are usually harmless but in some cases are associated with the development of diseases like cancer.
However, the Garvan-led Clinical Immunogenomics Research Consortium Australasia (CIRCA) found three patients with DOCK8 deficiency had repaired the faulty genes through a ...
New research from the Prevention Research Center of the Pacific Institute for Research and Evaluation examines whether recreational marijuana legalization in Oregon and marijuana and alcohol retail outlet density levels are associated with co-use and beliefs supportive of use of each among teens.
Using data from 11th graders who participated in the Student Wellness Survey from 2010-2018, researchers assessed past-30-day co-use changes in counties with low, medium, and high densities of licensed marijuana and alcohol outlets.
Findings include:
A significant post-legalization increase ...
Australians love their beaches, and now a new study also confirms the broad appeal of other coastal assets such as tidal wetlands, nature trails and protected areas including bird and dolphin sanctuaries.
In one of the first studies of its kind in Australia, ahead of World Wetlands Day (2 February), Flinders University environment and marine ecology experts have conducted an Adelaide-based survey of how residents connect with and rate the attributes of Adelaide's northern metropolitan coastal wetlands.
The findings, just published in the journal Environmental Science and Policy, report strong appreciation of the natural features of these coastal places, with study participants ...
Soil temperature has a significant impact on land-atmosphere interaction within the Earth system, affecting surrounding ecology, agriculture, and much more. This influence is a primary component of what is called a "thermal regime" of land, or a regular pattern of temperature change within the soil. Climatologists are intrigued by fluctuating soil temperatures, especially during the first decade of the 21st century where global surface warming has slowed down. The thermal regime, according to scientists, is greatly influential on climate, particularly seasonal climate prediction. Now, ...
Humoral and cellular adaptive immunity are two immune mechanisms that act against pathogens. Humoral immunity is mediated by antibodies, while cellular immunity does not involve antibodies and is, instead, facilitated by T cells. Studying how these immune mechanisms mediate SARS-CoV-2 infections could be beneficial in controlling the progression of the disease. However, their roles in viral control or disease pathogenesis is not fully understood and only a few studies have thoroughly monitored COVID-19 patients longitudinally, especially during the acute phase of infection.
To fill this knowledge gap, the team of ...
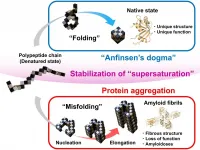
Correct, or native, protein folding is essential for correct protein function. Protein misfolding can lead to the formation of amyloid fibrils, and amyloidosis, which is implicated in various human neurodegenerative diseases, including Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, and Huntington's diseases. In this study Yuji Goto and colleagues describe, for the first time, a dynamic link between protein folding and misfolding, and the threshold that must be overcome for the formation of amyloid fibrils.
Technological advances are at the forefront of many scientific discoveries. The atomic structures of some amyloid fibrils were recently revealed as a result of advances in solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance and cryogenic electron microscopy. While an important step forward for the ...