Neuromuscular disease registry helps patients access research, clinical trials, new genetic tests, and therapies
With data on more than 4,000 patients, the Canadian Neuromuscular Disease Registry celebrates a decade of facilitating research across Canada, reports the Journal of Neuromuscular Diseases
2021-02-02
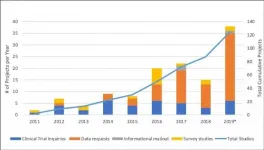
(Press-News.org) Amsterdam, February 2, 2021 - The Canadian Neuromuscular Disease Registry (CNDR) was launched in 2010 to increase efficient patient access to cutting-edge research and clinical trials, to increase understanding of the natural history and epidemiology of neuromuscular disease across Canada, and to facilitate research collaboration. An assessment of CNDR's accomplishments, published in the Journal of Neuromuscular Diseases, found that it has been successful in securing funding and engaging the community over the past 10 years. With more than 4,000 enrolled patients, data from the registry have been used in over 125 research projects as of 2019, including clinical trial and research notifications, patient questionnaires, and data analyses around patient outcomes and care.
"I am very proud of the work that has been done by the registry team and all of our collaborators across Canada," says lead author Lawrence Korngut, MD, MSc, Department of Clinical Neurosciences, and Hotchkiss Brain Institute, University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada. "It takes a great deal of effort to enter high-quality data and it has been very fulfilling to provide use of the data currently more than 150 times in projects for researchers and organizations to benefit the neuromuscular community through positive impact on outcomes and advocacy."
Neuromuscular disease is a broad classification that includes numerous conditions that are individually rare, but collectively common, with a prevalence of 160 patients per 100,000 people. Canada is a very diverse country with a broad geographic spread and two national languages. With limited patient numbers in any individual clinic, the multi-disease methodology employed by the CNDR is an efficient and comprehensive way to facilitate collaboration across the country.
Diagnosis and contact information are collected from patients for all diseases. More detailed information, including a full disease-specific clinical dataset and patient demographics, is collected from individuals with one of five specific diseases: Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS); Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD); Myotonic Dystrophy (DM); Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy (LGMD); and Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA). For these indexed diseases, CNDR estimates that the registry has thus far ascertained variable percentages of the estimated total patient population in Canada, ranging from 9.0% for DM patients to 83.5% of DMD patients.
Among the projects facilitated by CNDR are more than 18 questionnaire studies, including quality of life studies for DMD and SMA patients, access to computer technology for DM patients, and a global study of risk factors for ALS. Organized to encourage companies to choose Canada for clinical trials and help recruit patients for clinical trials, it has also facilitated 37 clinical trial inquiries. Data have also been used to evaluate patients' access to care in different regions of the country and has helped the network of investigators advocate for their patients in access to therapy and care and support services.
As the current therapeutic landscape for neuromuscular disease is evolving, so too are the aims and scope of the CNDR. The registry has collected genetic test results ranging from 16.9% (of registered sporadic ALS patients) to 86.4% (of registered DM patients). Between 8.3% (LGMD) and 28.4% (DMD) of registrants have participated in clinical trials. The registry is now also being used to understand safety and effectiveness of new therapies.
"CNDR has been instrumental in encouraging clinics to assist registered patients in obtaining proper genetic testing," notes Dr. Korngut. "As there has been an increase in the number of disorders with available genetic testing and genetic-based therapies, awareness of and access to formal genetic counseling are essential components of clinician-patient discussions."
Dr. Korngut observes that in this new era of therapeutic discovery for rare neuromuscular diseases, national disease registries and their associated networks of affiliated clinics are essential. "Ultimately, the availability of comprehensive real-world data in Canada has been an asset to all stakeholders in the neuromuscular disease community and will likely become more so."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-02
The mesmerizing flow of a sidewinder moving obliquely across desert sands has captivated biologists for centuries and has been variously studied over the years, but questions remained about how the snakes produce their unique motion. Sidewinders are pit vipers, specifically rattlesnakes, native to the deserts of the southwestern United State and adjacent Mexico.
Scientists had already described the microstructure of the skin on the ventral, or belly, surface of snakes. Many of the snakes studied, including all viper species, had distinctive rearward facing "microspicules" (micron-sized protrusions on scales) that had been interpreted in the context of reducing ...
2021-02-02
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- Studies have shown that nearly half of all medical students in the U.S. report symptoms of burnout, a long-term reaction to stress characterized by emotional exhaustion, cynicism and feelings of decreased personal accomplishment. Beyond the personal toll, the implications for aspiring and practicing physicians can be severe, from reduced quality of care to increased risk of patient safety incidents.
According to a new study published on Tuesday, Feb. 2, in JAMA Network Open, students who identify as lesbian, gay or bisexual ...
2021-02-02
Period poverty, a lack of access to menstrual hygiene products, and other unmet menstrual health needs can have far-reaching consequences for women and girls in the United States and globally.
New research led by George Mason University's College of Health and Human Services found that more than 14% of college women experienced period poverty in the past year, and 10% experienced period poverty every month. Women who experienced period poverty every month (68%) or in the past year (61.2%) were more likely to experience moderate or severe depression than those who did not experience period poverty (43%).
Dr. Jhumka Gupta, an associate professor at George Mason University was senior author of the study published in BMC Women's Health. ...
2021-02-02
MINNEAPOLIS- February 2, 2021 - In Minnesota, there are currently about END ...
2021-02-02
BOSTON - Amyloid-beta and tau are the two key abnormal protein deposits that accumulate in the brain during the development of Alzheimer's disease, and detecting their buildup at an early stage may allow clinicians to intervene before the condition has a chance to take hold. A team led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) has now developed an automated method that can identify and track the development of harmful tau deposits in a patient's brain. The research, which is published in END ...
2021-02-02
Nearly 11 percent of people admitted to an intensive care unit in Sweden between 2010 and 2018 received opioid prescriptions on a regular basis for at least six months and up to two years after discharge. That is according to a study by researchers at Karolinska Institutet published in Critical Care Medicine. The findings suggest some may become chronic opioid users despite a lack of evidence of the drugs' long-term effectiveness and risks linked to increased mortality.
"We know that the sharp rise in opioid prescriptions in the U.S. has contributed to a deadly opioid crisis there," says first author Erik von Oelreich, PhD student in the Department of Physiology and ...
2021-02-02
A decision-support tool that could be accessed via mobile devices may help clinicians in lower-resource settings avoid unnecessary antibiotic prescriptions for children with diarrhoea, a study published today in eLife shows.
The preliminary findings suggest that incorporating real-time environmental, epidemiologic, and clinical data into an easy-to-access, electronic tool could help clinicians appropriately treat children with diarrhoea even when testing is not available. This could help avoid the overuse of antibiotics, which contributes to the emergence of drug-resistant bacteria.
"Diarrhoea is a common condition among children ...
2021-02-02
FRANKFURT. Chronic liver disease and even cirrhosis can go unnoticed for a long time because many patients have no symptoms: the liver suffers silently. When the body is no longer able to compensate for the liver's declining performance, the condition deteriorates dramatically in a very short time: tissue fluid collects in the abdomen (ascites), internal bleeding occurs in the oesophagus and elsewhere, and the brain is at risk of being poisoned by metabolic products. This acute decompensation of liver cirrhosis can develop into acute-on-chronic liver failure with inflammatory reactions throughout the body and failure of several organs.
In the PREDICT study, led ...
2021-02-02
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. - In Lily Tomlin's classic SNL comedy sketch, her telephone operator "Ernestine" famously delivers the punchline, "We don't care. We don't have to. We're the Phone Company." But new research finds that satisfied customers mean increased profits even for public utilities that don't face competition.
Little is known about effect of customer satisfaction at utilities. As a result, utility managers are often unsure how much to invest in customer service - if anything at all. The issue also is of interest to regulators responsible for protecting consumers.
The study, in ...
2021-02-02
CORVALLIS, Ore. - One of birdwatching's most commonly held and colorfully named beliefs, the Patagonia Picnic Table Effect, is more a fun myth than a true phenomenon, Oregon State University research suggests.
Owing its moniker to an Arizona rest area, the Patagonia Picnic Table Effect, often shortened to PPTE, has for decades been cited as a key driver of behavior, and rare-species-finding success, among participants in the multibillion-dollar recreational birding business - an industry that has gotten even stronger during a pandemic that's shut down so many other activities.
But a study led by an OSU College of Science ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Neuromuscular disease registry helps patients access research, clinical trials, new genetic tests, and therapies
With data on more than 4,000 patients, the Canadian Neuromuscular Disease Registry celebrates a decade of facilitating research across Canada, reports the Journal of Neuromuscular Diseases