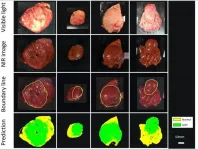
(Press-News.org) Tumors can be damaging to surrounding blood vessels and tissues even if they're benign. If they're malignant, they're aggressive and sneaky, and often irrevocably damaging. In the latter case, early detection is key to treatment and recovery. But such detection can sometimes require advanced imaging technology, beyond what is available commercially today.
For instance, some tumors occur deep inside organs and tissues, covered by a mucosal layer, which makes it difficult for scientists to directly observe them with standard methods like endoscopy (which inserts a small camera into a patient's body via a thin tube) or reach them during biopsies. In particular, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs)--typically found in the stomach and the small intestines--require demanding techniques that are very time-consuming and prolong the diagnosis. Now, to improve GIST diagnosis, Drs. Daiki Sato, Hiroaki Ikematsu, and Takeshi Kuwata from the National Cancer Center Hospital East in Japan, Dr. Hideo Yokota from the RIKEN Center for Advanced Photonics, Japan, and Drs. Toshihiro Takamatsu and Kohei Soga from Tokyo University of Science, Japan, led by Dr. Hiroshi Takemura, have developed a technology that uses near-infrared hyperspectral imaging (NIR-HSI) along with machine learning. Their findings are published in END
Deep Vision: Near-infrared imaging and machine learning can identify hidden tumors
Near-infrared hyperspectral imaging combined with machine learning can visualize tumors in deep tissue and covered by a mucosal layer, scientists show
2021-02-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Nearly all telehealth appointments at clinics for lower-income Americans were audio-only
2021-02-02
Telehealth use has surged during the pandemic at clinics that serve lower-income Americans, which allowed the clinics to maintain access to care at a time when many other health care organizations saw significant declines in utilization, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
However, most of the telehealth appointments have been audio-only visits, which may pose challenges in the future if payers consider dropping reimbursement for such services.
Studying more than 500 clinic locations across California, researchers found that while overall visit volume remained stable during the pandemic, about half of primary care medical visits from March to August 2020 ...
Story tips: COVID breath-sampling, welding advances and powered by water
2021-02-02
Nanoscience - Blowing the whistle on COVID-19
Collaborators at Oak Ridge National Laboratory and the University of Tennessee Health Science Center are developing a breath-sampling whistle that could make COVID-19 screening easy to do at home.
The technology incorporates a unique hydrogel material to capture aerosols from exhaled breath and preserve the samples, which could either be sent to a lab for analysis or, for a fully at-home approach, transferred to an accompanying test kit that could detect the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19.
"Our motivation ...
A new hands-off probe uses light to explore electron behavior in a topological insulator
2021-02-02
Topological insulators are one of the most puzzling quantum materials - a class of materials whose electrons cooperate in surprising ways to produce unexpected properties. The edges of a TI are electron superhighways where electrons flow with no loss, ignoring any impurities or other obstacles in their path, while the bulk of the material blocks electron flow.
Scientists have studied these puzzling materials since their discovery just over a decade ago with an eye to harnessing them for things like quantum computing and information processing.
Now researchers at the Department ...
Speaking and listening seem more difficult in a masked world, but people are adapting
2021-02-02
Ten months into COVID-19 living, people are adapting to speaking from behind, and understanding others who are wearing, a cloth face mask, University of California, Davis, researchers suggest in a new study.
Researchers in the Department of Linguistics at UC Davis and University of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, investigated how well speech is understood from those speaking while wearing a cloth mask. Due to social distancing measures, speakers for the study consisted of individuals from the same household, who recorded sentences while face-masked and non-face-masked. The researchers tested how well a separate group ...
Lack of ICU beds tied to thousands of excess COVID-19 deaths, Yale study finds
2021-02-02
New Haven, Conn. --A new study by Yale researchers found a significant association between the availability of hospital resources -- particularly ICU beds -- and patient mortality during the early weeks of the COVID-19 pandemic.
This was especially true at hospitals in the northeastern U.S. which were hardest hit by the first surge of patient cases, according to the study published in the Journal of Hospital Medicine.
"There is a general narrative among people in healthcare that the more resources there are, the better we can take care of patients," said lead author Dr. Alexander Janke, a Yale Emergency Scholar in the fourth year of a five-year combined residency and health services research fellowship. "This study begs ...
An origami-inspired medical patch for sealing internal injuries
2021-02-02
Many surgeries today are performed via minimally invasive procedures, in which a small incision is made and miniature cameras and surgical tools are threaded through the body to remove tumors and repair damaged tissues and organs. The process results in less pain and shorter recovery times compared to open surgery.
While many procedures can be performed in this way, surgeons can face challenges at an important step in the process: the sealing of internal wounds and tears.
Taking inspiration from origami, MIT engineers have now designed a medical patch that can be folded around minimally invasive surgical tools and delivered through airways, intestines, and other narrow spaces, to patch up internal injuries. ...
The Lancet: Study reports preliminary efficacy and safety results from interim analysis of Russian COVID-19 phase 3 vaccine trial
2021-02-02
Interim analysis from phase 3 trial of nearly 20,000 participants suggests efficacy of two-dose regimen of the adenovirus-based vaccine is 91.6% against symptomatic COVID-19 - trial reports 16 COVID-19 cases in the vaccine group (0.1% [16/14,964) and 62 cases (1.3% [62/4,902]) in the placebo group.
No serious adverse events were deemed to be associated with vaccination, and most reported adverse events were mild, including flu-like symptoms, pain at injection site and weakness or low energy.
Sub-analysis of 2,000 adults older than 60 years suggests the vaccine is similarly effective and well tolerated in this group.
Trial is ongoing ...
Toward safer steroids: Scientists devise method for improving safety of drug used to treat COVID-19, autoimmune disorders and more
2021-02-02
JUPITER, FL - A collaboration led by Scripps Research has developed a way to separate the beneficial anti-inflammatory properties of a group of steroids called glucocorticoids from some of their unwanted side-effects, through an optimization process they named "ligand class analysis."
Their process enabled them to engineer two new, drug-like compounds that show steroidal anti-inflammatory action and other specific traits. One boosts muscle and energy supply, while the other reduces risk of muscle-wasting and bone loss typical of such drugs.
Their report, titled, "Chemical systems biology ...
Moffitt researchers identify why CAR T therapy may fail in some lymphoma patients
2021-02-02
TAMPA, Fla. -- Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy, or CAR T, has been a breakthrough in the treatment of blood cancers such as acute lymphoblastic leukemia and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Clinical studies have shown overall response rates of more than 80% with an ongoing response of nearly 40% more than two years after therapy. However, the cellular immunotherapy doesn't work for every patient. Moffitt Cancer Center, one of the leading centers for cellular immunotherapy, is researching why some patients have a better CAR T response than others and what can be done to improve the treatment's effectiveness. In a new study ...
Modeling the brain during pain processing
2021-02-02
The many different sensations our bodies experience are accompanied by deeply complex exchanges of information within the brain, and the feeling of pain is no exception. So far, research has shown how pain intensity can be directly related to specific patterns of oscillation in brain activity, which are altered by the activation and deactivation of the 'interneurons' connecting different regions of the brain. However, it remains unclear how the process is affected by 'inhibitory' interneurons, which prevent chemical messages from passing between these regions. Through new research published in EPJ ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Stem cells from human baby teeth show promise for treating cerebral palsy
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
UF research finds a gentler way to treat aggressive gum disease
[Press-News.org] Deep Vision: Near-infrared imaging and machine learning can identify hidden tumorsNear-infrared hyperspectral imaging combined with machine learning can visualize tumors in deep tissue and covered by a mucosal layer, scientists show