Yale researchers develop injection to treat skin cancer
2021-02-02
(Press-News.org) Yale researchers are developing a skin cancer treatment that involves injecting nanoparticles into the tumor, killing cancer cells with a two-pronged approach, as a potential alternative to surgery.
The results are published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
"For a lot of patients, treating skin cancer is much more involved than it would be if there was a way to effectively treat them with a simple procedure like an injection," said Dr. Michael Girardi, professor and vice chair of dermatology at Yale School of Medicine and senior author of the study. "That's always been a holy grail in dermatology -- to find a simpler way to treat skin cancers such as basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma."
For the treatment, tumors are injected with polymer-based nanoparticles carrying a chemotherapy agent. Key to the treatment's success is that the nanoparticles are bioadhesive -- that is, they bind to the tumors and remain attached long enough to kill a significant number of the cancer cells.
"When you inject our nanoparticles into a tumor, it turns out that they're retained within that tumor very well," said co-author Mark Saltzman, the Goizueta Foundation Professor of Biomedical Engineering, Chemical and Environmental Engineering, and professor of physiology. "They accumulate and bind to the tumor matrix, so one single injection lasts for a very long time -- the particles stay there and slowly release the compounds. You need that to get rid of the lesion."
For comparison, the same drug was injected freely into tumors of control models without the nanoparticles. They found that the tumors were significantly more diminished when the drugs were delivered by nanoparticles.
Also critical to the therapy is that the treatment can be combined with an agent that stimulates the body's immune system.
"I call the phenomenon 'kill and thrill,'" Girardi said. "You don't want to just kill the cells and leave them there, you want to stimulate the immune system to clean up the mess and also react against cells that might not have been killed directly. So it's a two-pronged attack on the cancer."
In many cases, ridding tumors with an injection could eliminate the need for surgery, the researchers said. It may also then avoid potential wound infections and other complications. Additionally, some patients with other medical conditions are poor candidates for surgery.
An injection-based therapy would also mean that patients could have multiple tumors treated in a single visit.
"In these studies, we did just a single injection, and that's how we'd like it to work clinically," Saltzman said. "You go to a dermatologist, they see a lesion and inject into it, and it's gone and you don't have to come back."
Saltzman's lab, which specializes in nanoparticles, worked to optimize the particles' drug-carrying ability to deliver as much of the chemotherapy agent in a single dose as possible. Because the contents of the nanoparticle remain at the site of the tumor, the delivery system allows for the use of particularly powerful drugs. Conventional chemotherapy affects the entire body and can have severe side effects, so the toxicity of drugs is more limited.
Both Yale Cancer Center members, Girardi and Saltzman are working with the start-up company Stradefy Biosciences Inc., which plans to advance the technology's preclinical development and then conduct clinical trials.
"Mike and Mark have been doing outstanding science together for a number of years," said Brian R. Dixon, president and CEO of Stradefy. "It's really hard to beat that kind of team. We believe that their groundbreaking work is going to lead to truly helpful therapies for patients."
INFORMATION:
Other Yale investigators involved in the project included Jamie K. Hu, Hee-Won Suh, Munibah Qureshi, Julia Lewis, Sharon Yaqoob, Zoe Moscato, Sofia Griff, Alison Lee, and Em
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-02
A new study from scientists of the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Biology in Plön, Germany, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Beijing shows that the potential genetic burden of mutations arising from retrogenes is significantly greater than originally thought.
Genetic information is stored in DNA and transcribed as mRNA. The mRNA is usually translated into proteins. However, it has long been known that mRNA can also be reverse transcribed to DNA and integrated back into the genome. Such cases are referred to as retrogenes. In an article, a team from the Max Planck Institute for ...
2021-02-02
When different groups of people come into contact, what's the key to motivating advantaged racial groups to join historically disadvantaged racial minority groups to strive for racial equality and social justice? It's a complex conundrum studied for years by social scientists like Linda Tropp, professor of social psychology at the University of Massachusetts Amherst.
Her latest research, published in the International Journal of Intercultural Relations, tested and supported Tropp and colleagues' proposition that having open communication about group differences is a crucial pathway.
While greater contact between racial groups is typically associated with less ...
2021-02-02
New drivers between the ages of 15 and 25 account for nearly half of the more than one million road deaths that occur worldwide each year, according to the World Health Organization. Educational programs often use fear-based messaging and films of crash scenes to reduce risky driving behavior among young people. But does this "scary" approach work?
A new study published in the journal Risk Analysis suggests that fear-based messaging fails to reduce risky driving behavior, while fear-based Virtual Reality (VR) films depicting a violent collision may actually lead young drivers to take more chances behind the wheel.
A team of psychologists led by University of Antwerp researcher Clara Alida Cutello, PhD, conducted a study of 146 students ...
2021-02-02
Are Gut Microbes the Key to Unlocking Anxiety
A mouse study suggests the genetic contribution to anxiety is partially mediated by the gut microbiome
By Greta Lorge
The prevalence of anxiety disorders, already the most common mental illness in many countries, including the U.S., has surged during the novel coronavirus pandemic. A study led by researchers in Berkeley Lab's Biosciences Area provides evidence that taking care of our gut microbiome may help mitigate some of that anxiety.
The team used a genetically heterogeneous lineage of mice known as the Collaborative Cross (CC) to probe connections among genes, gut microbiome ...
2021-02-02
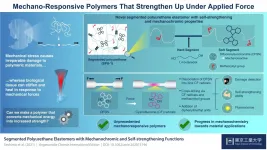
A fascinating and crucial ability of biological tissue, such as muscle, is self-healing and self-strengthening in response to damage caused by external forces. Most human-made polymers, on the other hand, break irreversibly under enough mechanical stress, which makes them less useful for certain critical applications like manufacturing artificial organs. But what if we could design polymers that reacted chemically to mechanical stimuli and used this energy to enhance their properties?
This goal, which has proven to be a big challenge, is under the spotlight in the field of mechanochemistry. In a recent study published in Angewandte Chemie ...
2021-02-02
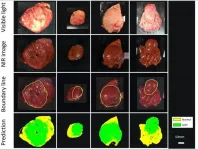
Tumors can be damaging to surrounding blood vessels and tissues even if they're benign. If they're malignant, they're aggressive and sneaky, and often irrevocably damaging. In the latter case, early detection is key to treatment and recovery. But such detection can sometimes require advanced imaging technology, beyond what is available commercially today.
For instance, some tumors occur deep inside organs and tissues, covered by a mucosal layer, which makes it difficult for scientists to directly observe them with standard methods like endoscopy (which inserts a small camera into a patient's body via a thin ...
2021-02-02
Telehealth use has surged during the pandemic at clinics that serve lower-income Americans, which allowed the clinics to maintain access to care at a time when many other health care organizations saw significant declines in utilization, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
However, most of the telehealth appointments have been audio-only visits, which may pose challenges in the future if payers consider dropping reimbursement for such services.
Studying more than 500 clinic locations across California, researchers found that while overall visit volume remained stable during the pandemic, about half of primary care medical visits from March to August 2020 ...
2021-02-02
Nanoscience - Blowing the whistle on COVID-19
Collaborators at Oak Ridge National Laboratory and the University of Tennessee Health Science Center are developing a breath-sampling whistle that could make COVID-19 screening easy to do at home.
The technology incorporates a unique hydrogel material to capture aerosols from exhaled breath and preserve the samples, which could either be sent to a lab for analysis or, for a fully at-home approach, transferred to an accompanying test kit that could detect the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19.
"Our motivation ...
2021-02-02
Topological insulators are one of the most puzzling quantum materials - a class of materials whose electrons cooperate in surprising ways to produce unexpected properties. The edges of a TI are electron superhighways where electrons flow with no loss, ignoring any impurities or other obstacles in their path, while the bulk of the material blocks electron flow.
Scientists have studied these puzzling materials since their discovery just over a decade ago with an eye to harnessing them for things like quantum computing and information processing.
Now researchers at the Department ...
2021-02-02
Ten months into COVID-19 living, people are adapting to speaking from behind, and understanding others who are wearing, a cloth face mask, University of California, Davis, researchers suggest in a new study.
Researchers in the Department of Linguistics at UC Davis and University of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, investigated how well speech is understood from those speaking while wearing a cloth mask. Due to social distancing measures, speakers for the study consisted of individuals from the same household, who recorded sentences while face-masked and non-face-masked. The researchers tested how well a separate group ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Yale researchers develop injection to treat skin cancer