(Press-News.org) A novel artificial intelligence (AI) approach based on wireless signals could help to reveal our inner emotions, according to new research from Queen Mary University of London.
The study, published in the journal PLOS ONE, demonstrates the use of radio waves to measure heartrate and breathing signals and predict how someone is feeling even in the absence of any other visual cues, such as facial expressions.
Participants were initially asked to watch a video selected by researchers for its ability to evoke one of four basic emotion types; anger, sadness, joy and pleasure. Whilst the individual was watching the video the researchers then emitted harmless radio signals, like those transmitted from any wireless system including radar or WiFi, towards the individual and measured the signals that bounced back off them. By analysing changes to these signals caused by slight body movements, the researchers were able to reveal 'hidden' information about an individual's heart and breathing rates.
Previous research has used similar non-invasive or wireless methods of emotion detection, however in these studies data analysis has depended on the use of classical machine learning approaches, whereby an algorithm is used to identify and classify emotional states within the data. For this study the scientists instead employed deep learning techniques, where an artificial neural network learns its own features from time-dependent raw data, and showed that this approach could detect emotions more accurately than traditional machine learning methods.
Achintha Avin Ihalage, a PhD student at Queen Mary, said: "Deep learning allows us to assess data in a similar way to how a human brain would work looking at different layers of information and making connections between them. Most of the published literature that uses machine learning measures emotions in a subject-dependent way, recording a signal from a specific individual and using this to predict their emotion at a later stage.
"With deep learning we've shown we can accurately measure emotions in a subject-independent way, where we can look at a whole collection of signals from different individuals and learn from this data and use it to predict the emotion of people outside of our training database."
Traditionally, emotion detection has relied on the assessment of visible signals such as facial expressions, speech, body gestures or eye movements. However, these methods can be unreliable as they do not effectively capture an individual's internal emotions and researchers are increasingly looking towards 'invisible' signals, such as ECG to understand emotions.
ECG signals detect electrical activity in the heart, providing a link between the nervous system and heart rhythm. To date the measurement of these signals has largely been performed using sensors that are placed on the body, but recently researchers have been looking towards non-invasive approaches that use radio waves, to detect these signals.
Methods to detect human emotions are often used by researchers involved in psychological or neuroscientific studies but it is thought that these approaches could also have wider implications for the management of health and wellbeing.
In the future, the research team plan to work with healthcare professionals and social scientists on public acceptance and ethical concerns around the use of this technology.
Ahsan Noor Khan, a PhD student at Queen Mary and first author of the study, said: "Being able to detect emotions using wireless systems is a topic of increasing interest for researchers as it offers an alternative to bulky sensors and could be directly applicable in future 'smart' home and building environments. In this study, we've built on existing work using radio waves to detect emotions and show that the use of deep learning techniques can improve the accuracy of our results."
"We're now looking to investigate how we could use low-cost existing systems, such as WiFi routers, to detect emotions of a large number of people gathered, for instance in an office or work environment. This type of approach would enable us to classify emotions of people on individual basis while performing routine activities. Moreover, we aim to improve the accuracy of emotion detection in a work environment using advanced deep learning techniques."
Professor Yang Hao, the project lead added: "This research opens up many opportunities for practical applications, especially in areas such as human/robot interaction and healthcare and emotional wellbeing, which has become increasingly important during the current Covid-19 pandemic."
INFORMATION:
Notes to editors
* Research publication: 'Deep learning framework for subject-independent emotion detection using wireless signals' Ahsan Noor Khan, Achintha Avin Ihalage, Yihan Ma, Baiyang Liu, Yujie Liu, Yang Hao, PLOS ONE.
* Once the embargo lifts the paper will be available at:
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0242946.
* For more information or a copy of the paper please contact:
Sophie McLachlan
Faculty Communications Manager (Science & Engineering)
Queen Mary University of London
sophie.mclachlan@qmul.ac.uk
Tel: 020 7882 3787
About Queen Mary
Queen Mary University of London is a research-intensive university that connects minds worldwide. A member of the prestigious Russell Group, we work across the humanities and social sciences, medicine and dentistry, and science and engineering, with inspirational teaching directly informed by our world-leading research. In the most recent Research Excellence Framework we were ranked 5th in the country for the proportion of research outputs that were world-leading or internationally excellent. We have over 25,000 students and offer more than 240 degree programmes. Our reputation for excellent teaching was rewarded with silver in the most recent Teaching Excellence Framework. Queen Mary has a proud and distinctive history built on four historic institutions stretching back to 1785 and beyond. Common to each of these institutions - the London Hospital Medical College, St Bartholomew's Medical College, Westfield College and Queen Mary College - was the vision to provide hope and opportunity for the less privileged or otherwise under-represented. Today, Queen Mary University of London remains true to that belief in opening the doors of opportunity for anyone with the potential to succeed and helping to build a future we can all be proud of.
(Boston)-- While a number of topical products designed to reduce the occurrence of sexually transmitted infections have been tested with largely disappointing results, researchers at Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM), Alpert Medical School of Brown University and Mapp Biopharmaceutical have now found that MB66, a vaginal film product containing monoclonal antibodies against human immunodeficiency virus-type 1 (HIV-1) and herpes simplex viruses types 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and 2), is safe and effective.
HIV-1 and HSV-1 and 2 are relatively common sexually transmitted infections associated with significant illness and sometimes even death. Though antiviral drugs can suppress viral concentrations and dramatically slow ...
Humans continuously observe and evaluate interactions between third parties to decide with whom to interact in the future. But it is difficult to measure what information animals gain when they eavesdrop on vocal interactions between conspecifics: If they do understand such conversations, they do not necessarily exhibit behavioral expressions that can be easily observed. To overcome this hurdle, anthropologists from the University of Zurich created a study combining call simulations, thermography methods and behavioral preference measures.
Using thermal imaging, the researchers were able to non-invasively measure temperature changes in the faces of marmoset monkeys to quantify ...
Narrowing of the trachea or the main bronchi due to injury or illness can end very badly. If patients get too little air,oxygen, they risk suffocating and often need medical help as quickly as possible.
Surgeons insert stents made of medically usable silicone or metal as a way of treating these patients. Although they quickly bring relief, the implants also have disadvantages: Metal stents have to be removed surgically with some effort, which is a burden for the patients, while silicone stents often migrate away from the insertion site. The reason for this is that the implants are not adapted to a patient's anatomy.
An ETH Zurich research team, composed of members of the Complex Materials and Drug Formulation and Delivery groups, has now developed an ...
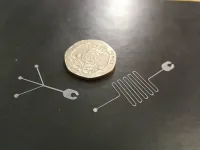
New technology developed by the University of Bristol has the potential to accelerate uptake and development of on-chip diagnostic techniques in parts of the world where rapid diagnoses are desperately needed to improve public health, mortality and morbidity.
Microfluidic devices underpin lab-on-a-chip (LOC) technologies which are developed to provide the rapid diagnoses at that are needed at point of care (POC) for the swift and effective treatment of many diseases.
Researchers at Bristol have developed a fast, reliable and cost-effective alternative for producing the soft-lithographic moulds used for fabricating microfluidic devices, published in the journal ...
PITTSBURGH, Feb. 3, 2020 - In a recurring pattern of evolution, SARS-CoV-2 evades immune responses by selectively deleting small bits of its genetic sequence, according to new research from the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine.
Since these deletions happen in a part of the sequence that encodes for the shape of the spike protein, the formerly neutralizing antibody can't grab hold of the virus, the researchers report today in Science. And because the molecular "proofreader" that usually catches errors during SARS-CoV-2 replication is "blind" to fixing deletions, they become cemented into the variant's genetic material.
"You can't ...
Researchers have identified a pattern of deletions in the spike (S) glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 that can prevent antibody binding. Virus lineages featuring this mechanism are currently being transmitted between individuals globally, they say. Their results - reported after analyzing nearly 150,000 S gene sequences collected from many parts of the world - exhibit a form of virus "escape" that resulted from a common, strong selective pressure; for example, the authors identified at least nine instances where deletion variants arose in patients whose COVID-19 infections were persistent. So far, the strongest indicator of protection against SARS-CoV-2 appears to be humoral immunity, such as by antibodies, ...
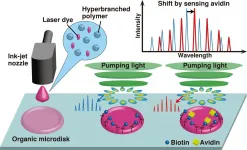
WASHINGTON -- Researchers have developed a unique inkjet printing method for fabricating tiny biocompatible polymer microdisk lasers for biosensing applications. The approach enables production of both the laser and sensor in a room temperature, open-air environment, potentially enabling new uses of biosensing technologies for health monitoring and disease diagnostics.
"The ability to use an inexpensive and portable commercial inkjet printer to fabricate a sensor in an ambient environment could make it possible to produce biosensors on-site as needed," said research team leader Hiroaki Yoshioka from Kyushu University in Japan. "This could help make biosensing widespread even in economically disadvantaged ...
Coffee rust is a parasitic fungus and a big problem for coffee growers around the world. A study in the birthplace of coffee - Ethiopia - shows that another fungus seems to have the capacity to supress the rust outbreaks in this landscape.
"Coffee leaf rust is a fungal disease that is a problem for coffee growers around the world, especially on Arabica coffee, which accounts for three quarters of global coffee production and has the finest cup quality. There is a need to learn more about natural solutions instead of just applying pesticides," says Kristoffer Hylander, professor at the Department of Ecology, Environment and Plant Sciences (DEEP) at Stockholm ...
Many nations place drugs into various schedules or categories according to their risk of being abused and their medical value. At times, drugs are rescheduled to a more restrictive category to reduce misuse by constricting supply. A new study examined lessons from past efforts worldwide to schedule and reschedule drugs to identify general patterns and found that rescheduling drugs can lower use as well as the dangers associated with the drug. The findings have implications for policy.
The study, by researchers at Carnegie Mellon University (CMU), is published in the International Journal of Drug Policy.
"Our review suggests that rescheduling drugs can often disrupt trends in prescribing, use, or harms," says Jonathan Caulkins, professor of operations research and public policy at CMU's ...
In the first longitudinal study to follow Georgia pre-K students through middle school, Stacey Neuharth-Pritchett, associate dean for academic programs and professor in UGA's Mary Frances Early College of Education, found that participating in pre-K programs positively predicted mathematical achievement in students through seventh grade.
"Students who participated in the study were twice as likely to meet the state standards in their mathematics achievement," said Neuharth-Pritchett. "School becomes more challenging as one progresses through the grades, and so if ...