Helping consumers save more by bursting their bubble of financial responsibility
News from the Journal of Marketing
2021-02-04
(Press-News.org) Researchers from University of Notre Dame, York University (Canada), and University of New England (Australia) published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that identifies a novel reason why people under-save and demonstrates a simple, short, and inexpensive intervention that increases intentions to save and actual savings.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Popping the Positive Illusion of Financial Responsibility Can Increase Personal Savings: Applications in Emerging and Western Markets" and is authored by Emily Garbinsky, Nicole Mead, and Daniel Gregg.
People around the world are not saving enough money. Since increasing personal savings is critical for individual and societal welfare, many researchers have tried to identify reasons why people under-save. Most of these reasons, however, do not lend themselves to behavioral interventions.
Garbinsky explains that "We show that one reason people under-save is because they hold the positive illusion of being financially responsible. In other words, most people hold positively distorted beliefs about how well they save and manage their money because this allows them to feel good about themselves. In our study, we show that most people view themselves as more financially responsible than their average peer, which is statistically impossible."
Building on this finding, the research demonstrates that offsetting this positive illusion of financial responsibility motivates people to restore this diminished self-view. In other words, when people perceive that their past financial behaviors have fallen short of their desired standard (in this case, to be a financially responsible person), they enact behaviors to close the gap (in this case, by allocating more money to their savings).
"As part of the study," Gregg says, "we created what we call the 'superfluous-spender intervention' that influenced people to believe they were not saving as well as they believed. Across a series of six experiments, we show that people receiving the superfluous-spender intervention increased both intentions to save and actual savings relative to those who do not receive the intervention. Our theoretical reasoning is that the intervention increases saving by inducing one's desire to restore diminished perceptions of financial responsibility."
The study also sheds light on two managerially relevant factors about when and for whom the intervention is most likely to be effective. More specifically, the intervention is only expected to increase savings if people can draw perceptions about their own level of financial responsibility. Because past research has shown that people reach conclusions about themselves only when past behavior was freely chosen, the intervention is only effective when past financial behaviors are highlighted that were under one's control and therefore attributable to the self. Also, the intervention is most effective among people who are motivated to perceive themselves as financially responsible.
In closing, although it may be tempting to think that the savings silver bullet is to make consumers feel better about themselves in the financial domain, the empirical data from this research suggest otherwise. "We illuminate that the illusion of financial responsibility is a novel antecedent to saving and that financial stakeholders can combat this self-enhancing bias to encourage consumers to commit to saving more," says Mead.
INFORMATION:
Full article and author contact information available at: https://doi.org/10.1177/0022242920979647
About the Journal of Marketing
The Journal of Marketing develops and disseminates knowledge about real-world marketing questions useful to scholars, educators, managers, policy makers, consumers, and other societal stakeholders around the world. Published by the American Marketing Association since its founding in 1936, JM has played a significant role in shaping the content and boundaries of the marketing discipline. Christine Moorman (T. Austin Finch, Sr. Professor of Business Administration at the Fuqua School of Business, Duke University) serves as the current Editor in Chief.
https://www.ama.org/jm
About the American Marketing Association (AMA)
As the largest chapter-based marketing association in the world, the AMA is trusted by marketing and sales professionals to help them discover what is coming next in the industry. The AMA has a community of local chapters in more than 70 cities and 350 college campuses throughout North America. The AMA is home to award-winning content, PCM® professional certification, premiere academic journals, and industry-leading training events and conferences.
https://www.ama.org
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-04
WASHINGTON--The start of California's annual rainy season has been pushed back from November to December, prolonging the state's increasingly destructive wildfire season by nearly a month, according to new research. The study cannot confirm the shift is connected to climate change, but the results are consistent with climate models that predict drier autumns for California in a warming climate, according to the authors.
Wildfires can occur at any time in California, but fires typically burn from May through October, when the state is in its dry season. The start of the rainy season, historically in November, ends wildfire season as plants become too moist to burn.
California's rainy season has been starting progressively later in recent decades and climate ...
2021-02-04
Researchers from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore), Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) and Khoo Teck Puat Hospital (KTPH) have developed a new way to create "food inks" from fresh and frozen vegetables, that preserves their nutrition and flavour better than existing methods.
Food inks are usually made from pureed foods in liquid or semi-solid form, then 3D-printed by extrusion from a nozzle, and assembled layer by layer.
Pureed foods are usually served to patients suffering from swallowing difficulties known as dysphagia. To present the ...
2021-02-04
Politicians around the world must be held to account for mishandling the covid-19 pandemic, argues a senior editor at The BMJ today.
Executive editor, Dr Kamran Abbasi, argues that at the very least, covid-19 might be classified as 'social murder' that requires redress.
Today 'social murder' may describe a lack of political attention to the conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work and age that exacerbate the pandemic.
When politicians and experts say that they are willing to allow tens of thousands of premature deaths, for the sake of population immunity or in the hope of propping up the economy, is that not premeditated ...
2021-02-03
Piezoelectric materials hold great promise as sensors and as energy harvesters but are normally much less effective at high temperatures, limiting their use in environments such as engines or space exploration. However, a new piezoelectric device developed by a team of researchers from Penn State and QorTek remains highly effective at elevated temperatures.
Clive Randall, director of Penn State's Materials Research Institute (MRI), developed the material and device in partnership with researchers from QorTek, a State College, Pennsylvania-based company specializing in smart material devices and high-density power electronics.
"NASA's need ...
2021-02-03
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Muscle wasting, or the loss of muscle tissue, is a common problem for people with cancer, but the precise mechanisms have long eluded doctors and scientists. Now, a new study led by Penn State researchers gives new clues to how muscle wasting happens on a cellular level.
Using a mouse model of ovarian cancer, the researchers found that cancer progression led to fewer skeletal muscle ribosomes -- particles in the cell that make proteins. Because muscle mass is mainly determined by protein synthesis, having less ribosomes likely explains why muscles waste away in cancer.
Gustavo Nader, associate professor of kinesiology and physiology at Penn State, said the findings suggest a mechanism for muscle wasting that could be relevant ...
2021-02-03
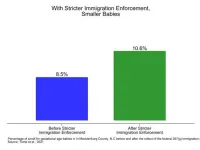
DURHAM, N.C. -- Harsher immigration law enforcement by U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement leads to decreased use of prenatal care for immigrant mothers and declines in birth weight, according to new Duke University research.
In the study, published in PLOS ONE, researchers examine the effects of the federal 287(g) immigration program after it was introduced in North Carolina in 2006. Under 287(g) programs, which are still in effect, local law officers are deputized to act as Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) agents, with authority to question individuals about immigration status, detain them, and if necessary, begin deportation proceedings.
According to the study findings, the 2006 policy change reduced birth weight ...
2021-02-03
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. - Hypoxia -- where a tissue is deprived of an adequate supply of oxygen -- is a feature inside solid cancer tumors that renders them highly invasive and resistant to treatment. Study of how cells adapt to this critical stressor, by altering their metabolism to survive in a low-oxygen environment, is important to better understand tumor growth and spread.
Researchers led by Rajeev Samant, Ph.D., professor of pathology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, now report that chronic hypoxia, surprisingly, upregulates RNA polymerase I activity and alters the methylation patterns on ribosomal RNAs. These altered epigenetic marks on the ribosomal RNAs appear to create a pool of specialized ribosomes that can differentially ...
2021-02-03
As a native animal, kangaroos aren't typically considered a threat to Australian vegetation.
While seen as a pest on farmland - for example, when competing with livestock for resources - they usually aren't widely seen as a pest in conservation areas.
But a new collaborative study led by UNSW Sydney found that conservation reserves are showing signs of kangaroo overgrazing - that is, intensive grazing that negatively impacts the health and biodiversity of the land.
Surprisingly, the kangaroos' grazing impacts appeared to be more damaging to the land than rabbits, an introduced species.
"The kangaroos had severe impacts on soils and vegetation that were symptomatic of overgrazing," says Professor Michael Letnic, senior author of the paper and ...
2021-02-03
Mathematicians from RUDN University suggested and tested a new method to assess the productivity of fifth-generation (5G) base stations. The new technology would help get rid of mobile access stations and even out traffic fluctuations. The results of the study were published in the IEEE Conference Publication.
Stations of the new 5G New Radio (NR) communication standard developed by the 3GPP consortium are expected to shortly be installed in large quantities all over the world. First of all, the stations will be deployed in places with high traffic ...
2021-02-03
ITHACA, N.Y. -Wind energy scientists at Cornell University have released a new global wind atlas - a digital compendium filled with documented extreme wind speeds for all parts of the world - to help engineers select the turbines in any given region and accelerate the development of sustainable energy.
This wind atlas is the first publicly available, uniform and geospatially explicit (datasets tied to locations) description of extreme wind speeds, according to the research, "A Global Assessment of Extreme Wind Speeds For Wind Energy Applications," published in Nature Energy.
"Cost-efficient expansion of the wind-energy industry is enabled by access ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Helping consumers save more by bursting their bubble of financial responsibility
News from the Journal of Marketing