(Press-News.org) A City of Hope-led research team found that the same gene that increases the risk for Alzheimer's disease, ApoE4, can increase the susceptibility to and severity of COVID-19.
"Our study provides a causal link between the Alzheimer's disease risk factor ApoE4 and COVID-19 and explains why some (e.g., ApoE4 carriers) but not all COVID-19 patients exhibit neurological manifestations" said Yanhong Shi, Ph.D., director of the Division of Stem Cell Biology at City of Hope and co-corresponding author of the new study. "Understanding how risk factors for neurodegenerative diseases impact COVID-19 susceptibility and severity will help us to better cope with COVID-19 and its potential long-term effects in different patient populations."
At the beginning of the study, the team was interested in SARS-CoV-2's effects on the brain. Due to the fact that COVID-19 patients often lose their sense of taste and smell, the team theorized that the virus had an underlying neurological effect.
The team first created brain cells in the lab using pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), which are a kind of stem cell that can become virtually any type of cell. The newly created neurons and astrocytes, a type of helper cell, were then infected with SARS-CoV-2. They found that both cell types were susceptible to infection.
Next, the team used iPSCs to create brain organoids, which are 3D tissue models that mimic certain features of the human brain. They created one organiod model that contained astrocytes and one without them. They infected both brain organoid types with the virus, and discovered that those with astrocytes boosted SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The team went on to further study the effects of ApoE4 on susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2. They did this by generating neurons from iPSCs "reprogrammed" from the cells of an Alzheimer's patient that contained ApoE4. Using gene editing, the team modified some of the iPSCs-created ApoE4 cells so that they contained ApoE3, which is a gene type that is considered neutral. The ApoE3 and ApoE4 iPSCs were then used to generate neurons and astrocytes.
The results were published recently in the journal Cell Stem Cell. The ApoE4 neurons and astrocytes both showed a higher susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection in comparison to the neutral ApoE3 neurons and astrocytes. Moreover, while the virus caused damage to both ApoE3 and ApoE4 neurons, it appeared to have a slightly more severe effect on ApoE4 neurons and a much more severe effect on ApoE4 astrocytes compared to ApoE3 neurons and astrocytes.
In the last part of the study, the researchers tested to see if the antiviral drug remdesivir inhibits virus infection in neurons and astrocytes. They discovered that the drug was able to successfully reduce the viral level in astrocytes and prevent cell death. It was also able to rescue neurons from neurodegeneration.
The team's next step is to continue studying the effects of the virus to better understand the role of ApoE4 in the neurological manifestations of COVID-19. Many people infected with COVID-19 have recovered, but long-term neurological effects such as severe headaches are still seen months after.
"COVID-19 is a complex disease, and we are beginning to understand the risk factors involved in the manifestation of the severe form of the disease" said Vaithilingaraja Arumugaswami, Ph.D., a member of the UCLA Broad Stem Cell Research Center and co-corresponding author. "Our cell-based study provides a possible explanation as to why individuals with Alzheimer's' disease are at increased risk of developing more severe COVID-19 symptoms."
INFORMATION:
The research was supported by the Louise and Herbert Horvitz Charitable Foundation, the Sidell Kagan Foundation, California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (TRAN1-08525, DISC2 12172), the National Institute of Aging of the National Institutes of Health (R01 AG056305, RF1 AG061794, R56 AG061171), and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases of the National Institutes of Health (R21AI129471).
About City of Hope
City of Hope is an independent biomedical research and treatment center for cancer, diabetes and other life-threatening diseases. Founded in 1913, City of Hope is a leader in bone marrow transplantation and immunotherapy such as CAR T cell therapy. City of Hope's translational research and personalized treatment protocols advance care throughout the world. Human synthetic insulin, monoclonal antibodies and numerous breakthrough cancer drugs are based on technology developed at the institution. AccessHopeTM, a wholly owned subsidiary, was launched in 2019 and is dedicated to serving employers and their health care partners by providing access to City of Hope's exceptional cancer expertise. A National Cancer Institute-designated comprehensive cancer center and a founding member of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, City of Hope is ranked among the nation's "Best Hospitals" in cancer by U.S. News & World Report. Its main campus is located near Los Angeles, with additional locations throughout Southern California and in Arizona. For more information about City of Hope, follow us on Facebook, Twitter, YouTube or Instagram.
The distinctive gut microbiome profile of a person with liver cancer linked to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) could be the key to predicting someone's risk of developing the cancer, say researchers from the UNSW Microbiome Research Centre (MRC).
Their new study, published in Nature Communications recently, found the gut microbiome - the kingdom of microorganisms living in our digestive tracts - can modulate the immune response in liver cancer patients with NAFLD, in a way that promotes the cancer's survival.
While the research is still in its early stages, this finding could lead to more effective preventative and therapeutic treatments for people at risk of developing NAFLD-related liver ...
The intestine harbors the largest number of immune cells in our body. Since the intestine is constantly exposed to various antigens like bacteria and food, appropriate induction of gut immune cells plays a pivotal role in gut homeostasis.
A POSTECH research team - led by Professor Seung-Woo Lee, Ph.D. candidate Sookjin Moon and research assistant professor Yunji Park of the Department of Life Sciences - has uncovered for the first the mechanism for regulating the differentiation of T cells (intraepithelial lymphocyte, IEL) via intestinal epithelial cells (IEC). These findings were recently published in the Journal of Experimental Medicine ...
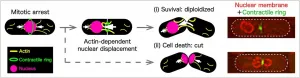
Cells replicate their genetic material and divide into two identical clones, perpetuating life -- until they don't. Some cells pause -- or are intentionally made to pause -- in the process. When the cell resumes division after such a pause, a displaced nucleus -- an essential part of cell survival -- can become caught in the fissure, splitting violently and killing both cells. But that is not always the case; some mutant cells can recover by pushing their nucleus to safety. Researchers from Hiroshima University in Japan are starting to understand how in the first step toward potential cell death rescue applications.
The results were published on Jan. 22 in iScience, a Cell Press journal.
The researchers examined fission yeast, a common model organism ...
This is the finding of an 18-year-study of over 300,000 people with diabetes in England, from scientists from Imperial College London and published in the journal The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.
Thursday Feb 4th is World Cancer Day.
The research, funded by the Wellcome Trust, reveals that between 2001-2018 heart disease and stroke were no longer the leading causes of death among people with diabetes, as they were 18 years ago.
Diabetes affects 4.7 million people in the UK, and is caused by the body being unable to regulate blood sugar levels. Around 90 per cent have type ...
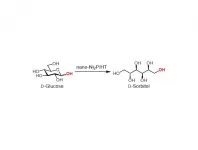
Osaka - Many different catalysts that promote the conversion of glucose to sorbitol have been studied; however, most offer certain properties while requiring compromises on others. Now, researchers from Osaka University have reported a hydrotalcite-supported nickel phosphide nanoparticle catalyst (nano-Ni2P/HT) that ticks all the boxes. Their findings are published in Green Chemistry.
Sorbitol is a versatile molecule that is widely used in the food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals industries. There is therefore a pressing need to produce sorbitol in a sustainable, low-cost, and green manner.
The nickel catalysts that are commonly used in the industrial hydrogenation of glucose to sorbitol are unstable in air and require hash reaction conditions. Rare metal alternatives--despite being ...
Remember the first rule of fight club? That's right: You don't talk about fight club. Luckily, the rules of Hollywood don't apply to science. In new published research, University of Arizona researchers report what they learned when they started their own "fight club" - an exclusive version where only insects qualify as members, with a mission to shed light on the evolution of weapons in the animal kingdom.
In many animal species, fighting is a common occurrence. Individuals may fight over food, shelter or territory, but especially common are fights between males over access to females for mating. Many of the most striking and unusual features of animals are associated with these mating-related fights, including the horns of beetles and the antlers of deer. What is less clear ...
PHILADELPHA--Inflammation in the blood could serve as a new biomarker to help identify patients with advanced pancreatic cancer who won't respond to the immune-stimulating drugs known as CD40 agonists, suggests a new study from researchers in the Abramson Cancer Center of the University of Pennsylvania published in JCI Insight
It is known that pancreatic cancer can cause systemic inflammation, which is readily detectable in the blood. The team found that patients with systemic inflammation had worse overall survival rates than patients without inflammation when treated with both a CD40 agonist and the chemotherapy gemcitabine.
The ...
This study is the first randomised control trial to rigorously test a sequential approach to treating comorbid PTSD and major depressive disorder.
Findings from a trial of 52 patients undergoing three types of treatment regime - using only Cognitive Processing Therapy (CPT), using Behavioural Activation Therapy (BA) with some CPT, or CPT with some BA - found that a combined treatment protocol resulted in meaningful reductions in PTSD and depression severity, with improvements maintained at six-month follow-up investigations.
"We sought to examine whether a protocol that specifically targeted both PTSD and comorbid ...
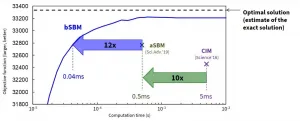
TOKYO --Toshiba Corporation (TOKYO: 6502) and Toshiba Digital Solutions Corporation (collectively Toshiba), industry leaders in solutions for large-scale optimization problems, today announced the Ballistic Simulated Bifurcation Algorithm (bSB) and the Discrete Simulated Bifurcation Algorithm (dSB), new algorithms that far surpass the performance of Toshiba's previous Simulated Bifurcation Algorithm (SB). The new algorithms will be applied to finding solutions to highly complex problems in areas as diverse as portfolio management, drug development and logistics management. ...
Borderline Personality Disorder, or BPD, is the most common personality disorder in Australia, affecting up to 5% of the population at some stage, and Flinders University researchers warn more needs to be done to meet this high consumer needs.
A new study in the Journal of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing (Wiley) describes how people with BPD are becoming more knowledgeable about the disorder and available treatments, but may find it difficult to find evidence-based help for their symptoms.
The South Australian psychiatric researchers warn these services are constrained by stigma ...