(Press-News.org) Laparoscopic surgery, a less invasive alternative to conventional open surgery, involves inserting thin tubes with a tiny camera and surgical instruments into the abdomen. To visualize specific surgical targets, ultrasound imaging is used in conjunction with the surgery. However, ultrasound images are viewed on a separate screen, requiring the surgeon to mentally combine the camera and ultrasound data.
Modern augmented reality (AR)-based methods have overcome this issue by embedding ultrasound images into the video taken by the laparoscopic camera. These AR methods precisely map the ultrasound data coordinates to the coordinates of the images seen through the camera. Although the process is mathematically straightforward, it can only be done if the pose (position and orientation) of the ultrasound probe (transducer) is known by the camera coordinate system. This has proven to be challenging, despite many strategies for tracking the laparoscopic transducer. Hardware-based tracking by attaching electromagnetic (EM) sensors to the probe is a feasible approach, but it is prone to errors due to calibration and hardware limitations. Camera vision (CV) systems can also be used to process the images acquired by the camera and determine the probe's pose. However, because they rely entirely on camera data, such methods fail if the probe is defocused or if the camera's view is occluded. Thus, such CV systems are not yet ready for clinical settings.
To this end, in a END
Best of both worlds: A hybrid method for tracking laparoscopic ultrasound transducers
Combined hardware- and computer vision-based strategy will help improve laparoscopic ultrasound imaging
2021-02-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ultimately, beneficial fungi could be more effective than pesticides against nematodes
2021-02-04
Over the past 30 years, the use of soil fumigants and nematicides used to protect cole crops, such as broccoli and Brussel sprouts, against cyst nematode pathogens in coastal California fields has decreased dramatically. A survey of field samples in 2016 indicated the nematode population has also decreased, suggesting the existence of a natural cyst nematode controlling process in these fields.
Thanks to California's pesticide-use reporting program, nematologists have been able to follow the amounts of fumigants and nematicides used to control cyst nematodes over the past three decades.
"Application of these pesticides steadily declined until they were completely eliminated in ...
COVID-19 health threat increases psychological distress among Black Americans
2021-02-04
As the coronavirus pandemic continues to devastate communities worldwide, Black Americans who face racial discrimination in hospitals and doctor's offices weather additional stresses that can exacerbate threats from COVID-19. A new University of Georgia study examines the interplay between the perceptions of coronavirus threat and psychological distress among Black Americans.
The additional stresses arise from the prevalent belief among Black Americans worried that they might not recover from how hospitals treat them if they become infected with the coronavirus.
"While the notion has been floated among commentators, this is the first study that uses nationally representative data to assess whether this threat, or feeling, ...
Study reveals how air pollution may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease
2021-02-04
BOSTON - Tiny particles of air pollution -- called fine particulate matter -- can have a range of effects on health, and exposure to high levels is a known risk factor for cardiovascular disease. New research led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) reveals that fine particulate matter has a detrimental impact on cardiovascular health by activating the production of inflammatory cells in the bone marrow, ultimately leading to inflammation of the arteries. The findings are published in the END ...
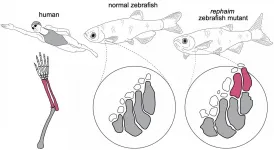
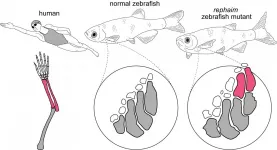
Researchers replicate a potential step of the fin-to-limb transition in zebrafish
2021-02-04
By tweaking a single gene, Harvard scientists engineered zebrafish that show the beginning formation of limb-like appendages. The researchers stumbled upon this mutation, which may shed light on the sea-to-land transition of vertebrates, while screening for various gene mutants and their impact on fish development. Their discovery, outlined February 4th in the journal Cell, marks a fundamental step in our understanding of fin-to-limb evolution and how surprisingly simple genetic changes can create great leaps in the development of complex structures.
"It was a little bit unbelievable that just one mutation was able to create completely new bones and joints," says M. Brent Hawkins (@Homeobox), first author of ...
Can a fin become a limb?
2021-02-04
Fin-to-limb transition is an icon of key evolutionary transformations. Many studies focus on understanding the evolution of the simple fin into a complicated limb skeleton by examining the fossil record. In a paper published February 4 in Cell, researchers at Harvard and Boston Children's Hospital examined what's occurring at the genetic level to drive different patterns in the fin skeleton versus the limb skeleton.
Researchers, led by M. Brent Hawkins, a recent doctoral recipient in the Department of Organismic and Evolutionary Biology, performed forward genetic screens in zebrafish looking for mutations that affect the fin skeleton. Unlike tetrapod limbs, which have complex skeletons with many bones that articulate ...
Fast-flying bats rely on late-night updrafts to reach great heights
2021-02-04
Although scientists knew that some bats could reach heights of over 1,600 meters (or approximately one mile) above the ground during flight, they didn't understand how they managed to do it without the benefit of thermals that aren't typically available to them during their nighttime forays. Now, researchers reporting in the journal Current Biology on February 4th have uncovered the bats' secret to high-flying.
It turns out that the European free-tailed bats they studied--powerful fliers that the researchers documented sometimes reaching speeds of up to 135 kilometers (84 miles) per hour in self-powered flight--do depend on orographic uplift that ...
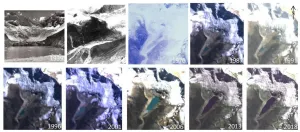
Global warming found to be culprit for flood risk in Peruvian Andes, other glacial lakes
2021-02-04
As the planet warms, glaciers are retreating and causing changes in the world's mountain water systems. For the first time, scientists at the University of Oxford and the University of Washington have directly linked human-induced climate change to the risk of flooding from a glacial lake known as one of the world's greatest flood risks.
The study examined the case of Lake Palcacocha in the Peruvian Andes, which could cause flooding with devastating consequences for 120,000 residents in the city of Huaraz. The paper, published Feb. 4 in Nature Geoscience, provides new evidence for an ongoing legal case that hinges on the link between greenhouse gas emissions and particular climate change impacts.
"The scientific challenge was to provide the clearest and cleanest assessment ...
Adolescent involvement with firearms linked to gun violence in adulthood
2021-02-04
CHICAGO - A new study by Northwestern University researchers finds involvement with firearms by high-risk youth is associated with firearm violence during adulthood.
"Association of Firearm Access, Use, and Victimization During Adolescence with Firearm Perpetration During Adulthood in a 16-year Longitudinal Study of Youth Involved in the Juvenile Justice System" will publish in JAMA Network Open at 10 a.m. CST, Thursday, Feb. 4. Access the full study online.
The longitudinal study of juvenile justice youth is the first to analyze firearm victimization and access during adolescence and its association with firearm violence in adulthood.
The study is based ...
Clinical trial: Using MRI for prostate cancer diagnosis equals or beats current standard
2021-02-04
Toronto - (February 4, 2021) The results of a Phase III randomized clinical trial have shown that when it comes to detecting clinically significant prostate cancer, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) with targeted biopsies (MRI-TBx) matches the current standard and brings a multitude of advantages. The PRostate Evaluation for Clinically Important Disease: MRI vs Standard Evaluation Procedures (PRECISE) study will help to make prostate cancer diagnosis more accurate and less invasive.
PRECISE included 453 participants at Canadian academic cancer centres who were either assigned to receive MRI ...
Factors, rate of nurse burnout in US
2021-02-04
What The Study Did: Researchers estimated the rate of nurse burnout in the United States and the factors associated with leaving or considering leaving their jobs due to burnout.
Authors: Megha K. Shah, M.D., M.Sc., of the Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.36469)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Of crocodiles, counting and conferences
AERA announces 2026 award winners in education research
Saving two lives with one fruit drop
Photonic chips advance real-time learning in spiking neural systems
Share of migratory wild animal species with declining populations despite UN treaty protections worsens from 44% to 49% in two years; 24% face extinction, up 2%
One in 20 babies experiences physical abuse, global review finds
Tundra tongue: The science behind a very cold mistake
Targeting a dangerous gut infection
Scientists successfully harvest chickpeas from “moon dirt”
Teen aggression a warning sign for faster aging later in life
Study confirms food fortification is highly cost-effective in fighting hidden hunger across 63 countries
Special issue elevates disease ecology in marine management
A kaleidoscope of cosmic collisions: the new catalogue of gravitational signals from LIGO, Virgo and KAGRA
New catalog more than doubles the number of gravitational-wave detections made by LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA observatories
Antifibrotic drug shows promise for premature ovarian insufficiency
Altered copper metabolism is a crucial factor in inflammatory bone diseases
Real-time imaging of microplastics in the body improves understanding of health risks
Reconstructing the world’s ant diversity in 3D
UMD entomologist helps bring the world’s ant diversity to life in 3D imagery
ESA’s Mars orbiters watch solar superstorm hit the Red Planet
The secret lives of catalysts: How microscopic networks power reactions
Molecular ‘catapult’ fires electrons at the limits of physics
Researcher finds evidence supporting sucrose can help manage painful procedures in infants
New study identifies key factors supporting indigenous well-being
Bureaucracy Index 2026: Business sector hit hardest
ECMWF’s portable global forecasting model OpenIFS now available for all
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
[Press-News.org] Best of both worlds: A hybrid method for tracking laparoscopic ultrasound transducersCombined hardware- and computer vision-based strategy will help improve laparoscopic ultrasound imaging