INFORMATION:
Iodine oxoacids drive rapid aerosol formation in pristine atmospheric areas
2021-02-04
(Press-News.org) Iodine plays a bigger role than thought in rapid new particle formation (NPF) in relatively pristine regions of the atmosphere, such as along marine coasts, in the Arctic boundary layer or in the upper free troposphere, according to a new study. The authors say their measurements indicate that iodine oxoacid particle formation can compete with sulfuric acid - another vapor that can form new particles under atmospheric conditions - in pristine atmospheric regions. Tiny particles suspended high in the atmosphere - aerosols - play an essential role in Earth's climate system. Clouds require airborne particles, or cloud condensation nuclei (CCN), to form, and aerosols serve as the seeds from which they grow. Atmospheric aerosols can have many terrestrial sources, like windblown dust, for example. However, under the right conditions, gas molecules can condense, cluster and grow large enough to form new aerosol particles. While NPF is estimated to account for more than half of all CCN, much about aerosol-cloud interaction remains a mystery and represents a major source of uncertainty in current climate models. So far, only a few vapors that can form new particles under atmospheric conditions have been identified. Along with sulfuric acid and a few others, iodic acid (HIO3) is one of the few vapors known to form new particles under atmospheric conditions, especially in coastal and marine regions, although the rates at which it's formed are poorly understood and presently considered to have limited global significance. Here, Xucheng He and colleagues present experimental evidence that suggests iodine plays a critical role in NPF, particularly in relatively pristine regions of the atmosphere. Using the CERN CLOUD (Cosmics Leaving Outdoor Droplets) chamber, He et al. found that the nucleation rates of HIO3 particles are rapid and even exceed that of anthropogenic sulfuric acid-ammonia under similar conditions. What's more, the authors discovered that different iodic oxoacids play an important role in facilitating this rapid formation.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fecal microbiota transplants help patients with advanced melanoma respond to immunotherapy
2021-02-04
For patients with cancers that do not respond to immunotherapy drugs, adjusting the composition of microorganisms in the intestines--known as the gut microbiome--through the use of stool, or fecal, transplants may help some of these individuals respond to the immunotherapy drugs, a new study suggests. Researchers at the National Cancer Institute (NCI) Center for Cancer Research, part of the National Institutes of Health, conducted the study in collaboration with investigators from UPMC Hillman Cancer Center at the University of Pittsburgh.
In the study, some patients with advanced melanoma who initially did not respond to treatment with an immune checkpoint inhibitor, a type of immunotherapy, did respond to the drug after receiving a transplant ...
Some sperms poison their competitors
2021-02-04
Competition among sperm cells is fierce - they all want to reach the egg cell first to fertilize it. A research team from Berlin now shows in mice that the ability of sperm to move progressively depends on the protein RAC1. Optimal amounts of active protein improve the competitiveness of individual sperm, whereas aberrant activity can cause male infertility.
It is literally a race for life when millions of sperm swim towards the egg cells to fertilize them. But does pure luck decide which sperm succeeds? As it turns out, there are differences in competitiveness between individual sperm. ...
In a desert seared by climate change, burrowers fare better than birds
2021-02-04
Berkeley -- In the arid Mojave Desert, small burrowing mammals like the cactus mouse, the kangaroo rat and the white-tailed antelope squirrel are weathering the hotter, drier conditions triggered by climate change much better than their winged counterparts, finds a new study published today in Science.
Over the past century, climate change has continuously nudged the Mojave's searing summer temperatures ever higher, and the blazing heat has taken its toll on the desert's birds. Researchers have documented a collapse in the region's bird populations, likely resulting ...
Human immune cells have natural alarm system against HIV
2021-02-04
Treatment for HIV has improved tremendously over the past 30 years; once a death sentence, the disease is now a manageable lifelong condition in many parts of the world. Life expectancy is about the same as that of individuals without HIV, though patients must adhere to a strict regimen of daily antiretroviral therapy, or the virus will come out of hiding and reactivate. Antiretroviral therapy prevents existing virus from replicating, but it can't eliminate the infection. Many ongoing clinical trials are investigating possible ways to clear HIV infection.
In a study published Feb. 4 in the journal Science, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have identified a potential way to eradicate ...
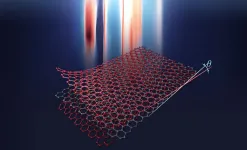
Harvard scientists use trilayer graphene to observe more robust superconductivity
2021-02-04
In 2018, the physics world was set ablaze with the discovery that when an ultrathin layer of carbon, called graphene, is stacked and twisted to a "magic angle," that new double layered structure converts into a superconductor, allowing electricity to flow without resistance or energy waste. Now, in a literal twist, Harvard scientists have expanded on that superconducting system by adding a third layer and rotating it, opening the door for continued advancements in graphene-based superconductivity.
The work is described in a new paper in Science and can one day help lead toward superconductors that operate at higher or even close to room temperature. These superconductors are considered the holy grail of condensed matter physics ...
Food allergies are more common among Black children
2021-02-04
Black children have significantly higher rates of shellfish and fish allergies than White children, in addition to having higher odds of wheat allergy, suggesting that race may play an important role in how children are affected by food allergies, researchers at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago, Rush University Medical Center and two other hospitals have found.
Results of the study were published in the February issue of the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice.
"Food allergy is a common condition in the U.S., and we know from our previous research that there are important differences between Black and White children with food allergy, but there is so much we need to know to be able to help our patients ...
Pharmacologist offers plan to solve disparities in designing medicine
2021-02-04
In a new perspective piece published in the Feb. 5 issue of Science, pharmacologist Namandje Bumpus, Ph.D. -- who recently became the first African American woman to head a Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine department, and is the only African American woman leading a pharmacology department in the country -- outlines the molecular origins for differences in how well certain drugs work among distinct populations. She also lays out a four-part plan to improve the equity of drug development.
"Human beings are more similar than we are different," says Bumpus. "Yet, the slightest variations in our genetic material ...
Studies use mathematics to analyze the semantics of dream reports during the pandemic
2021-02-04
The COVID-19 pandemic has affected people's behavior everywhere. Fear, apprehensiveness, sadness, anxiety, and other troublesome feelings have become part of the daily lives of many families since the first cases of the disease were officially recorded early last year.
These turbulent feelings are often expressed in dreams reflecting a heavier burden of mental suffering, fear of contamination, stress caused by social distancing, and lack of physical contact with others. In addition, dream narratives in the period include a larger proportion of terms relating to cleanliness and contamination, as well as anger and sadness.
All this is reported in a study published in PLOS ONE. The principal investigator was Natália ...
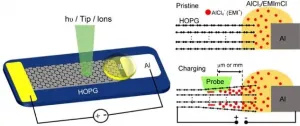
Surface effect of electrodes revealed by operando surface science methodology
2021-02-04
Surface and interface play critical roles in energy storage devices, thus calling for in-situ/operando methods to probe the electrified surface/interface. However, the commonly used in-situ/operando characterization techniques such as X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray spectroscopy and topography, and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) are based on the structural, electronic and chemical information in bulk region of the electrodes or electrolytes.
Surface science methodology including electron spectroscopy and scanning probe microscopy can provide rich information about how reactions ...
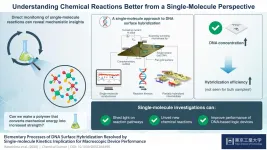
A single-molecule guide to understanding chemical reactions better
2021-02-04
Scientists globally aim to control chemical reactions--an ambitious goal that requires identifying the steps taken by initial reactants to arrive at the final products as the reaction takes place. While this dream remains to be realized, techniques for probing chemical reactions have become sufficiently advanced to render it possible. In fact, chemical reactions can now be monitored based on the change of electronic properties of a single molecule! Thanks to the scanning tunneling microscope (STM), this is also simple to accomplish. Why not then utilize ...