(Press-News.org) Washington, D.C.. -- The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic caused a sharp decline in living standards and rising food insecurity in developing countries across the globe, according to a new study by an international team of economists.
The study, published Feb. 5 in the journal Science Advances, provides an in-depth view of the health crisis's initial socioeconomic effects in low- and middle-income countries, using detailed micro data collected from tens of thousands of households across nine countries. The phone surveys were conducted from April through July 2020 of nationally and sub-nationally representative samples in Bangladesh, Burkina Faso, Colombia, Ghana, Kenya, Nepal, Philippines, Rwanda, and Sierra Leone. Across the board, study participants reported drops in employment, income, and access to markets and services, translating into high levels of food insecurity. Many households reported being unable to meet basic nutritional needs.
"COVID-19 and its economic shock present a stark threat to residents of low- and middle-income countries -- where most of the world's population resides -- which lack the social safety nets that exist in rich countries," said economist Susan Athey, of Stanford University's Graduate School of Business. "The evidence we've collected show dire economic consequences, including rising food insecurity and falling income, which, if left unchecked, could thrust millions of vulnerable households into poverty."
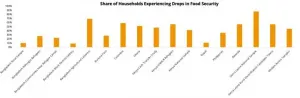
Across the 16 surveys, the percentage of respondents reporting losses in income ranged from 8% in Kenya to 86% in Colombia. The median, or midpoint of the range, was a staggering 70%. The percentage reporting loss of employment ranged from 6% in Sierra Leone to 51% in Colombia with a median of 29%.
"Painting a comprehensive picture of the economic impact of this global crisis requires the collection of harmonized data from all over the world," said Edward Miguel, the Oxfam Professor of Environmental and Resource Economics at the University of California, Berkeley, Director of the Center for Effective Global Action, and a co-author of the study. "Our work is an exciting example of fruitful collaboration among research teams from UC Berkeley, Northwestern, Innovations for Poverty Action, The Busara Center for Behavioral Economics in Kenya, Yale, and many others working in multiple countries simultaneously to improve our understanding of how COVID-19 has affected the living standards of people in low- and middle-income countries on three continents."
Significant percentages of respondents across the surveys reported being forced to miss meals or reduce portion sizes, including 48% of rural Kenyan households, 69% of landless, agricultural households in Bangladesh, and 87% of rural households in Sierra Leone -- the highest level of food insecurity. Poorer households generally reported higher rates of food insecurity, though rates were substantial even among the better off. The steep rise in food insecurity reported among children was particularly alarming given the potentially large negative long-run effects of under-nutrition on outcomes later in life, according to the study.
Survey results from Bangladesh and Nepal suggest that levels of food insecurity were far higher during the pandemic than during the same season in previous years.
In most countries, a large share of respondents reported reduced access to markets, consistent with lockdowns and other restrictions on mobility implemented between March and June 2020 to contain the spread of the virus. The amount of social support available to respondents from governments or non-governmental organizations varied widely across the surveys, but the high rates of food insecurity reported suggest that support was insufficient even when present, the researchers state.
The study shows that in addition to increasing food insecurity, the pandemic and accompanying containment measures have undermined several other aspects of household wellbeing. Schools in all sample countries were closed during most or all of the survey period. Respondents also reported reduced access to health services, including prenatal care and vaccinations. Combined, these factors could be particularly damaging to children in the long run, the researchers note.
"The pandemic's economic shock in these countries, where so many people depend on casual labor to feed their families, causes deprivations and adverse consequences in the long term, including excess mortality," said study co-author Ashish Shenoy, of the University of California, Davis. "Our findings underscore the importance of gathering survey data to understand the effects of the crisis and inform effective policy responses. We demonstrate the efficacy of large-scale phone surveys to provide this crucial data."
Current circumstances may call for social protection programs that prioritize addressing immediate poverty and under-nutrition before tackling deeper underlying causes, the researchers state. They suggest policymakers consider identifying poor households using mobile phones and satellite data and then provide them mobile cash transfers. The researchers also recommend providing support for basic utilities, such as water and electricity, through subsidies and by removing penalties for unpaid bills. They note a fundamental link between containing COVID-19 and providing economic relief as households facing acute shortages may be less willing than others to follow social distancing rules so that they can find opportunities to meet basic needs.
INFORMATION:
Researchers on the study represent the following institutions: University of California, Berkeley and the Center for Effective Global Action; The World Bank; Innovations for Poverty Action; University of California, Davis; Northwestern University, Global Poverty Lab and the Kellogg School of Management; Yale University and Y-RISE; University of Basel, Switzerland; Princeton University; Busara Center for Behavioral Economics, Nairobi, Kenya; Stanford University; WZB Berlin Social Science Center; Columbia University; London School of Economics and Political Science, International Growth Centre; Vyxer Remit Kenya, Busia, Kenya; American University; University of Goettingen, Germany; Harvard University; and Wageningen University, Netherlands.
The largest single cell study to date of the childhood cancer, neuroblastoma, has answered important questions about the genesis of the disease. The researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH) and the Princess Máxima Center for Pediatric Oncology, discovered that all neuroblastomas arise from a single type of embryonic cell called sympathoblasts.
The study, published today (5 February 2021) in Science Advances, sought to understand why neuroblastomas range in severity, with some easy to treat and others having relatively low five-year survival rates. The fact that all neuroblastomas arise from sympathoblasts makes them an attractive ...
Berkeley -- The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic last year led to a devastating loss of jobs and income across the global south, threatening hundreds of millions of people with hunger and lost savings and raising an array of risks for children, according to new research co-authored at the University of California, Berkeley.
The research, to be published Friday Feb. 5, 2021, in the journal Science Advances, found "staggering" income losses after the pandemic emerged last year, with a median 70% of households across nine countries in Africa, Asia and Latin America reporting financial losses. By April last year, roughly 50% ...
Scientists led by Eliza Harris and Michael Bahn from the Institute of Ecology at the University of Innsbruck have succeeded in studying emissions of the greenhouse gas N2O under the influence of environmental impacts in an unprecedented level of detail. The study, which has now been published in Science Advances, is thus also a starting point for the creation of models that could predict future trends in the greenhouse gas emission dynamics of ecosystems under global climate change.
Nitrous oxide (N2O) is a potent greenhouse gas whose atmospheric growth rate has accelerated over the past decade. The largest share of anthropogenic N2O emissions results from the fertilization of soils with nitrogen, which is converted into N2O via various abiotic ...
Genes that determine the shape of a person's facial profile have been discovered by a UCL-led research team.
The researchers identified 32 gene regions that influenced facial features such as nose, lip, jaw, and brow shape, nine of which were entirely new discoveries while the others validated genes with prior limited evidence.
The analysis of data from more than 6,000 volunteers across Latin America was published today in Science Advances.
The international research team, led from UCL, Aix-Marseille University and The Open University, found that one of the genes appears ...
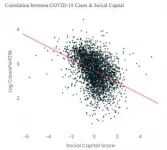
US counties with more social capital have fewer COVID-19 infections and deaths - perhaps because these communities have greater concern for the health of others.
INFORMATION:
Article Title: "How social capital helps communities weather the COVID-19 pandemic"
Funding: This research was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research [CIHR, FRN-170368; PI: Cary Wu].
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0245135
...
New research from Simon Fraser University shows that women's voices continue to be underrepresented in the media, despite having prominent female leaders across Canada and internationally. Researchers in SFU's Discourse Processing Lab found that men outnumber women quoted in Canadian news media about three to one. The findings from the team's Gender Gap Tracker study were published this week in the journal PLOS ONE.
The research team collected data from seven major Canadian media outlets from October 2018 to September 2020. Over the two-year period, 29 per cent of people ...
The development of scanning probe microscopes in the early 1980s brought a breakthrough in imaging, throwing open a window into the world at the nanoscale. The key idea is to scan an extremely sharp tip over a substrate and to record at each location the strength of the interaction between tip and surface. In scanning force microscopy, this interaction is -- as the name implies -- the force between tip and structures on the surface. This force is typically determined by measuring how the dynamics of a vibrating tip changes as it scans over objects deposited on a substrate. A common analogy is tapping a finger across a table and sensing objects placed ...
A new study by Indiana University found women, younger individuals, those with lower levels of formal education, and people of color are being hit hardest by the COVID-19 pandemic.
The study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences journal, found that Black adults were three times as likely as whites to report food insecurity, being laid off, or being unemployed during the pandemic. Additionally, residents without a college degree were twice as likely to report food insecurity (compared to those with some college) while those not completing high school are four times as likely to report it, compared ...
Cases of symptomatic COVID-19 were extremely low among children and staff at a network of YMCA summer camps held last year in North Carolina that took precautions like masking and physical distancing, with close to zero transmissions occurring at the camps, according to researchers at Duke Health, Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian.
In the camps' 2020 sessions, there were 19 cases of COVID-19 among 5,344 staff and 1,486 youth, only two of which were linked to possible on-site transmission at a group of YMCA of the Triangle camps, at a time ...
The modern world is powered by electrical circuitry on a "chip"--the semiconductor chip underpinning computers, cell phones, the internet, and other applications. In the year 2025, humans are expected to be creating 175 zettabytes (175trillion gigabytes) of new data. How can we ensure the security of sensitive data at such a high volume? And how can we address grand-challenge-like problems, from privacy and security to climate change, leveraging this data, especially given the limited capability of current computers?
A promising alternative is emerging quantum communication and computation technologies. For this to happen, however, it will require the widespread ...