New research sheds light on vision loss in Batten disease
2021-02-05
(Press-News.org) Progressive vision loss, and eventually blindness, are the hallmarks of juvenile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (JNCL) or CLN3-Batten disease. New research shows how the mutation associated with the disease could potentially lead to degeneration of light sensing photoreceptor cells in the retina, and subsequent vision loss.
"The prominence and early onset of retinal degeneration in JNCL makes it likely that cellular processes that are compromised in JNCL are critical for health and function of the retina," said Ruchira Signh, Ph.D., an associate professor in the Department of Ophthalmology and Center for Visual Science and lead author of the study which appears in the journal Communications Biology. "It is important to understand how vision loss is triggered in this disease, what is primary and what is secondary, and this will allow us to develop new therapeutic strategies."
Batten disease is caused by a mutation in the CLN3 gene, which is found on chromosome 16. Most children suffering from JNCL have a missing part in the gene which inhibits the production of certain proteins. Rapidly progressive vision loss can start in children as young as 4 and eventually develop learning and behavior problems, slow cognitive decline, seizures, and loss of motor control. Most patients with the disease die between the ages of 15 and 30.
It has been well established that vision loss in JNCL is due to degeneration of the light-sensing tissue in the retina. The vision loss associated with JNCL can precede other neurological symptoms by many years in some instances, which often leads to patients being misdiagnosed with other more common retinal degenerations. However, one of the barriers to studying vision loss in Batten disease is that mouse models of CLN3 gene mutation do not produce the retinal degeneration or vision loss found in humans. Additionally, examination of eye tissue after death reveals extensive degeneration of retinal cells which does not allow researchers to understand the precise mechanisms that lead to vision loss.
URMC is a hub for Batten disease research. The Medical Center is home to the University of Rochester Batten Center (URBC), one of the nation's premier centers dedicated to the study and treatment of this condition. The URBC is led by pediatric neurologist Jonathon Mink, M.D., Ph.D., who is a co-author of the study. Batten disease is also one of the key research projects that will be undertaken by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development-supported University of Rochester Intellectual and Development Diseases Research Center.
To study Batten disease in patient's own cells, the research team reengineered skin cells from patients and unaffected family members to create human-induced pluripotent stem cells. These cells, in turn, were used to create retinal cells which possessed the CLN3 mutation. Using this new human cell model of the disease, the new study shows for the first time that proper function of CLN3 is necessary for retinal pigment epithelium cell structure, the cell layer in the retina that nourishes light sensing photoreceptor cells in the retina and is critical for their survival and function and thereby vision.
Singh points out that understanding how RPE cell dysfunction contributes to photoreceptor cell loss in Batten disease is important first step, and it will enable researchers to target specific cell type in the eye using potential future gene therapies, cell transplantation, and drug-based interventions.
INFORMATION:
Additional co-authors of the study include Cynthia Tang, Jimin Han, Sonal Dalvi, Kannan Marian, Lauren Winschel, Celia Soto, Chad Galloway, Whitney Spencer, Michael Roll, Lisa Latchney, Erika Augustine, Vamsi Gullapalli, and Mina Chung with URMC, David Williams and Stephanie Volland with the University of California, Los Angeles, Vera Boniha with the Cleveland Clinic, and Tyler Johnson with Sanford Research. The research was supported with funding from the National Eye Institute BrightFocus Foundation, the David Bryant Trust, the Foundation of Fighting Blindness, the Knights Templar Eye Foundation, the Retina Research Foundation, and Research to Prevent Blindness.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-05
Washington, D.C.. -- The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic caused a sharp decline in living standards and rising food insecurity in developing countries across the globe, according to a new study by an international team of economists.
The study, published Feb. 5 in the journal Science Advances, provides an in-depth view of the health crisis's initial socioeconomic effects in low- and middle-income countries, using detailed micro data collected from tens of thousands of households across nine countries. The phone surveys were conducted from April through July 2020 of nationally and sub-nationally representative samples in Bangladesh, Burkina Faso, Colombia, Ghana, Kenya, Nepal, Philippines, Rwanda, and Sierra Leone. Across the board, study ...
2021-02-05
The largest single cell study to date of the childhood cancer, neuroblastoma, has answered important questions about the genesis of the disease. The researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH) and the Princess Máxima Center for Pediatric Oncology, discovered that all neuroblastomas arise from a single type of embryonic cell called sympathoblasts.
The study, published today (5 February 2021) in Science Advances, sought to understand why neuroblastomas range in severity, with some easy to treat and others having relatively low five-year survival rates. The fact that all neuroblastomas arise from sympathoblasts makes them an attractive ...
2021-02-05
Berkeley -- The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic last year led to a devastating loss of jobs and income across the global south, threatening hundreds of millions of people with hunger and lost savings and raising an array of risks for children, according to new research co-authored at the University of California, Berkeley.
The research, to be published Friday Feb. 5, 2021, in the journal Science Advances, found "staggering" income losses after the pandemic emerged last year, with a median 70% of households across nine countries in Africa, Asia and Latin America reporting financial losses. By April last year, roughly 50% ...
2021-02-05
Scientists led by Eliza Harris and Michael Bahn from the Institute of Ecology at the University of Innsbruck have succeeded in studying emissions of the greenhouse gas N2O under the influence of environmental impacts in an unprecedented level of detail. The study, which has now been published in Science Advances, is thus also a starting point for the creation of models that could predict future trends in the greenhouse gas emission dynamics of ecosystems under global climate change.
Nitrous oxide (N2O) is a potent greenhouse gas whose atmospheric growth rate has accelerated over the past decade. The largest share of anthropogenic N2O emissions results from the fertilization of soils with nitrogen, which is converted into N2O via various abiotic ...
2021-02-05
Genes that determine the shape of a person's facial profile have been discovered by a UCL-led research team.
The researchers identified 32 gene regions that influenced facial features such as nose, lip, jaw, and brow shape, nine of which were entirely new discoveries while the others validated genes with prior limited evidence.
The analysis of data from more than 6,000 volunteers across Latin America was published today in Science Advances.
The international research team, led from UCL, Aix-Marseille University and The Open University, found that one of the genes appears ...
2021-02-05
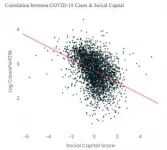
US counties with more social capital have fewer COVID-19 infections and deaths - perhaps because these communities have greater concern for the health of others.
INFORMATION:
Article Title: "How social capital helps communities weather the COVID-19 pandemic"
Funding: This research was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research [CIHR, FRN-170368; PI: Cary Wu].
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0245135
...
2021-02-05
New research from Simon Fraser University shows that women's voices continue to be underrepresented in the media, despite having prominent female leaders across Canada and internationally. Researchers in SFU's Discourse Processing Lab found that men outnumber women quoted in Canadian news media about three to one. The findings from the team's Gender Gap Tracker study were published this week in the journal PLOS ONE.
The research team collected data from seven major Canadian media outlets from October 2018 to September 2020. Over the two-year period, 29 per cent of people ...
2021-02-05
The development of scanning probe microscopes in the early 1980s brought a breakthrough in imaging, throwing open a window into the world at the nanoscale. The key idea is to scan an extremely sharp tip over a substrate and to record at each location the strength of the interaction between tip and surface. In scanning force microscopy, this interaction is -- as the name implies -- the force between tip and structures on the surface. This force is typically determined by measuring how the dynamics of a vibrating tip changes as it scans over objects deposited on a substrate. A common analogy is tapping a finger across a table and sensing objects placed ...
2021-02-05
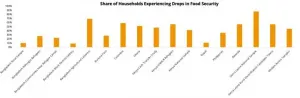
A new study by Indiana University found women, younger individuals, those with lower levels of formal education, and people of color are being hit hardest by the COVID-19 pandemic.
The study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences journal, found that Black adults were three times as likely as whites to report food insecurity, being laid off, or being unemployed during the pandemic. Additionally, residents without a college degree were twice as likely to report food insecurity (compared to those with some college) while those not completing high school are four times as likely to report it, compared ...
2021-02-05
Cases of symptomatic COVID-19 were extremely low among children and staff at a network of YMCA summer camps held last year in North Carolina that took precautions like masking and physical distancing, with close to zero transmissions occurring at the camps, according to researchers at Duke Health, Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian.
In the camps' 2020 sessions, there were 19 cases of COVID-19 among 5,344 staff and 1,486 youth, only two of which were linked to possible on-site transmission at a group of YMCA of the Triangle camps, at a time ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New research sheds light on vision loss in Batten disease