(Press-News.org) The snapping claws of male amphipods--tiny, shrimplike crustaceans--are among the fastest and most energetic of any life on Earth. Researchers reporting in the journal Current Biology on February 8 find that the crustaceans can repeatedly close their claws in less than 0.01% of a second, generating high-energy water jets and audible pops. The snapping claws are so fast, they almost defy the laws of physics.
"What's really amazing about these amphipods is that they're sitting right on the boundary of what we think is possible in terms of how small something can be and how fast it can move without self-destructing," says senior author Sheila Patek, a Professor of Biology at Duke University. "If they accelerated any faster, their bodies would break."
While amphipods are tremendous athletes, they aren't much to look at. They are tiny--only a few millimeters long--and they thrive in cool, scummy water, where they live on a diet of dead algae, seaweed, and other plants and animals.
"They're hard to see, but when you get them under a microscope, it's like the New York City of algae, with all these little creatures interacting and moving in every which way," says Patek. "It's like something out of the movie Microcosm."
Getting acceleration measurements of something so small and so fast is no easy task. The researchers used a highly specialized ultra-high-speed camera and enticed the aggressive crustaceans to snap by dangling single human hairs in front of them.
"It was a huge effort to capture this motion. We couldn't do it in the field because the equipment is so expensive and specialized--basically the Maserati of cameras," says Patek. "Once we could capture it, we saw that they're actually generating a water jet when they snap."
These water jets can occasionally cause cavitation--or the formation of bubbles from rapid changes in water pressure. When cavitation bubbles pop, large amounts of energy are released, enough to degrade the steel used in boat propellers.
"Cavitation is an extremely potent effect. It's one of the most energetic events on planet Earth," says Patek. "It's remarkable that these tiny creatures can cause it."
Although the researchers were able to quantify the mechanics of the amphipod snaps, it remains a mystery exactly why they do it.
"The claws make up a third of a male's body weight," says Patek. "We want to know why they invest so much into this action, whether it plays into male-female interaction or territorial disputes. That's something we're excited to pursue."
The researchers also hope that exploring creatures such as amphipods that push physics to the limit might provide inspiration to engineers and designers.
"There's a two-way street between engineering and biology. Sometimes we discover something in nature that engineering can't do, and sometimes engineers help us figure out how something works in nature," says Patek. "It's important to think about design from an evolutionary perspective because life has had millions of years to get it right."
INFORMATION:
This work was supported by the Army Research Office, an element of the U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command's Army Research Laboratory.
Current Biology, Longo et al.: "Snaps of a tiny amphipod push the boundary of ultrafast, repeatable movement" https://www.cell.com/current-biology/fulltext/S0960-9822(20)31877-7
Current Biology (@CurrentBiology), published by Cell Press, is a bimonthly journal that features papers across all areas of biology. Current Biology strives to foster communication across fields of biology, both by publishing important findings of general interest and through highly accessible front matter for non-specialists. Visit: http://www.cell.com/current-biology. To receive Cell Press media alerts, contact press@cell.com.
What The Study Did: The National Health Service in Italy provides universal coverage to citizens but because no approved drug was available for COVID-19, patients received potentially effective drugs, participated in clinical trials, accessed compassionate drug use programs or self-medicated. This study evaluated changes in drug demand during the early phase of the COVID-19 outbreak in Italy compared with the period before the outbreak.
Authors: Adriana Ammassari, M.D., of the Italian Medicines Agency in Rome, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37060)
Editor's ...
Philadelphia, February 8, 2021--Adding to a growing body of research affirming the benefits of fetal surgery for spina bifida, new findings show prenatal repair of the spinal column confers physical gains that extend into childhood. The researchers found that children who had undergone fetal surgery for myelomeningocele, the most severe form of spina bifida, were more likely than those who received postnatal repair to walk independently, go up and down stairs, and perform self-care tasks like using a fork, washing hands and brushing teeth. They also had stronger leg muscles and walked faster than children who had their spina bifida surgery ...
What The Study Did: This observational study compared different measures of prediabetes and the risk of progression to diabetes among adults age 71 to 90.
Authors: Mary R. Rooney, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.8774)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and ...
What The Study Did: Researchers assessed what percentage of the Virginia population had been exposed to SARS-CoV-2 after the first wave of COVID-19 infections in the U.S.
Authors: Eric R. Houpt, M.D., of the University of Virginia in Charlottesville, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.35234)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for ...
If temperature varies strongly from day to day, the economy grows less. Through these seemingly small variations climate change may have strong effects on economic growth. This shows data analyzed by researchers from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK), Columbia University and the Mercator Research Institute on Global Commons and Climate Change (MCC). In a new study in Nature Climate Change, they juxtapose observed daily temperature changes with economic data from more than 1,500 regions worldwide over 40 years - with startling results.
"We ...
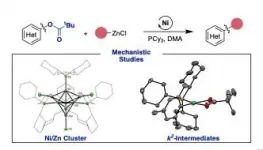
Negishi cross-coupling reactions have been widely used to form C-C bonds since the 1970s and are often perceived as the result of two metals (i.e zinc and palladium/nickel) working in synergy. But like all relationships, there is more under the surface than what we first expected. PhD student Craig Day and Dr. Rosie Somerville from the Martin group at ICIQ have delved into the Negishi cross-coupling of aryl esters using nickel catalysis to understand how this reaction works at the molecular level and how to improve it. The results have been published in Nature Catalysis.
Compared to palladium, nickel has the advantage of being readily available transition metal, ...
It's clear that rising greenhouse gas emissions are the main driver of global warming. But on a regional level, several other factors are at play. That's especially true in the Arctic - a massive oceanic region around the North Pole which is warming two to three times faster than the rest of the planet. One consequence of the melting of the Arctic ice cap is a reduction in albedo, which is the capacity of surfaces to reflect a certain amount of solar radiation. Earth's bright surfaces like glaciers, snow and clouds have a high reflectivity. As snow and ice decrease, albedo decreases and more radiation is absorbed by the Earth, leading to a rise in ...
What The Study Did: Researchers investigated the association between the use of proton pump inhibitors among children and adolescents in Sweden and the risk of asthma.
Authors: Yun-Han Wang, M.Sc., B.Pharm., of the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.5710)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict ...
What The Article Says: In this essay, the authors describe a 97-year-old patient who learned to titrate condensed chicken soup like a medicine during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Authors: Yuenting Diana Kwong, M.D., M.A.S., University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.8897)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, ...
What The Study Did: Salary information from faculty at U.S. medical schools was used to examine the association between the percentage of female clinicians in a medical specialty and the average and median salaries for that specialty.
Authors: Terrill Bravender, M.D., M.P.H., of the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.5683)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author ...