Examining association between percentage of women in medical specialties, salaries
2021-02-08
(Press-News.org) What The Study Did: Salary information from faculty at U.S. medical schools was used to examine the association between the percentage of female clinicians in a medical specialty and the average and median salaries for that specialty.
Authors: Terrill Bravender, M.D., M.P.H., of the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.5683)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this news release.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapediatrics/fullarticle/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.5683?guestAccessKey=645a451e-d00c-43df-93d1-9550576e89df&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=020821
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-08
Coral reefs are beautiful and diverse ecosystems that power the economies of many coastal communities. They're also facing threats that are driving their decline, including the planet's warming waters.
This threat hit extreme levels in 2015, when high temperatures were turning corals white around the globe. Kaneohe Bay in Hawaii was hit hard; nearly half of its corals bleached.
Hidden in the aftermath of this extreme event, however, were biochemical clues as to why some corals bleached while others were resistant, information that could help reefs better weather warming waters in the future. These clues have now been uncovered by researchers at Michigan State University and the University of Hawaii at Manoa.
"It was kind of horrifying," said coral biologist Crawford Drury, who witnessed ...
2021-02-08
Researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst have gained new insight into the biological processes of a chytrid fungus responsible for a deadly skin infection devastating frog populations worldwide.
Led by cell biologist Lillian Fritz-Laylin, the team describes in a paper published Feb. 8 in Current Biology how the actin networks of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis (Bd) also serve as an "evolutionary Rosetta Stone," revealing the loss of cytoskeletal complexity in the fungal kingdom.
"Fungi and animals seem so different, but they are actually pretty closely related," says Fritz-Laylin, whose lab studies how cells move, which is a central ...
2021-02-08
The findings are published in the prestigious journal, Nature Climate Change, and calls on businesses, the financial services industry and regulators to work more closely with climate scientists.
Regulators and governments - both domestic and international - are increasingly requiring that businesses assess and disclose their vulnerability to the physical effects of climate change, for example, increased drought, bushfires and sea level rise.
"People are making strategically material decisions on a daily basis, and raising debt or capital to finance these, but the decisions may not have properly considered climate risk," said lead author Dr Tanya Fiedler from the University of Sydney Business School. ...
2021-02-08
Under increasing global warming, tropical fish are escaping warmer seas by extending their habitat ranges towards more temperate waters.
But a new study from the University of Adelaide, published in Nature Climate Change, shows that the ocean acidification predicted under continuing high CO2 emissions may make cooler, temperate waters less welcoming.
"Every summer hundreds of tropical fish species extend their range to cooler and temperate regions as the waters of their natural habitat become a little too warm for comfort," says lead author Ericka Coni, PhD student in the University's School of Biological Sciences. "For at least two decades, Australian temperate reefs have been receiving new guests ...
2021-02-08
Recycling cans and bottles is a good practice. It helps keep the planet clean.
The same is true for recycling within cells in the body. Each cell has a way of cleaning out waste in order to regenerate newer, healthier cells. This "cell recycling" is called autophagy.
Targeting and changing this process has been linked to helping control or diminish certain cancers. Now, University of Cincinnati researchers have shown that completely halting this process in a very aggressive form of breast cancer may improve outcomes for patients one day.
These results are published in the Feb. 8 print edition of the journal Developmental Cell.
"Autophagy is sort of like cell cannibalism," ...
2021-02-08
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- In cells, numerous important biochemical functions take place within spherical chambers made from proteins and RNA.
These compartments are akin to specialized rooms inside a house, but their architecture is radically different: They don't have walls. Instead, they take the form of liquid droplets that don't have a membrane, forming spontaneously, similar to oil droplets in water. Sometimes, the droplets are found alone. Other times, one droplet can be found nested inside of another. And these varying assemblies can regulate the functions the droplets perform.
A study published on Feb. 8 in Nature Communications explores how these ...
2021-02-08
Some coronaviruses can add to their genetic pool some genes belonging to the host they infected. In this way, they can blend in and be less detectable to the immune system. This discovery was published in the journal Viruses by an Italian research team from the IIS (Italian Healthcare Institute), ISPRA (Institute for Environmental Protection and Research), IZSLER (Italian health authority and research organization for animal health and food safety of Lombardy and Emilia-Romagna) and the University of Bologna.
The outcome of this study demonstrates that coronaviruses encompass a sophisticated evolutionary mechanism ...
2021-02-08
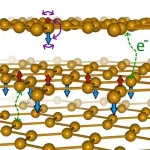
Electrons in materials have a property known as 'spin', which is responsible for a variety of properties, the most well-known of which is magnetism. Permanent magnets, like the ones used for refrigerator doors, have all the spins in their electrons aligned in the same direction. Scientists refer to this behaviour as ferromagnetism, and the research field of trying to manipulate spin as spintronics.
Down in the quantum world, spins can arrange in more exotic ways, giving rise to frustrated states and entangled magnets. Interestingly, a property similar to spin, known as "the valley," appears in graphene materials. This unique feature has given rise to the field of valleytronics, which aims to exploit the ...
2021-02-08
The lung is a complex organ whose main function is to exchange gases. It is the largest organ in the human body and plays a key role in the oxygenation of all the organs. Due to its structure, cellular composition and dynamic microenvironment, is difficult to mimic in vitro.
A specialized laboratory of the ARTORG Center for Biomedical Engineering Research, University of Bern, headed by Olivier Guenat has developed a new generation of in-vitro models called organs-on-chip for over 10 years, focusing on modeling the lung and its diseases. After a first successful lung-on-chip system exhibiting essential features of the lung, the Organs-on-Chip (OOC) Technologies laboratory has now developed a purely ...
2021-02-08
Researchers have identified a new form of magnetism in so-called magnetic graphene, which could point the way toward understanding superconductivity in this unusual type of material.
The researchers, led by the University of Cambridge, were able to control the conductivity and magnetism of iron thiophosphate (FePS3), a two-dimensional material which undergoes a transition from an insulator to a metal when compressed. This class of magnetic materials offers new routes to understanding the physics of new magnetic states and superconductivity.
Using new high-pressure techniques, the researchers have shown what happens to magnetic graphene during the transition from insulator to conductor and into ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Examining association between percentage of women in medical specialties, salaries