Some types of coronavirus steal the hosts' genes to elude their immune system
2021-02-08
(Press-News.org) Some coronaviruses can add to their genetic pool some genes belonging to the host they infected. In this way, they can blend in and be less detectable to the immune system. This discovery was published in the journal Viruses by an Italian research team from the IIS (Italian Healthcare Institute), ISPRA (Institute for Environmental Protection and Research), IZSLER (Italian health authority and research organization for animal health and food safety of Lombardy and Emilia-Romagna) and the University of Bologna.
The outcome of this study demonstrates that coronaviruses encompass a sophisticated evolutionary mechanism and therefore puts increasing emphasis on the importance of studying wildlife diseases. Research in this field is fundamental to understand the functioning of illnesses that can spread from animals to humans so that we can efficiently manage ecosystems and provide a balance between the species inhabiting them", says Mauro Delogu, a researcher at the University of Bologna and one of the authors of this study.
Researchers discovered this while analysing coronaviruses found in specimens of European hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus). They classified this strain as EriCoV. These viruses belong to the same strain of Beta-CoV responsible for COVID-19 as well as MERS. However, there is no evidence that they can spread to humans.
These hedgehog coronaviruses are able to steal a gene (CD200) that belongs to the host. When combine with its receptor, this gene allows to prevent an excessive inflammatory response. By incorporating this gene, the virus can hinder the immune defence of the host.
Events like this have never been observed before in coronaviruses. With this evolutionary strategy, coronaviruses can influence the duration of the infection and therefore prolong the time necessary to eliminate the virus, eventually leading to chronic infections. These process goes to the advantage of the virus, as it multiplies its ability to propagate and spread thanks to a specific evolutionary strategy.
"These results pave the way for further investigations into the ability of coronaviruses of interfering with the inhibitory signals of immune cells", continues Delogu. "In this way, coronaviruses can disguise themselves so that it is harder for the immune system of the host to detect, recognize and destroy them".
INFORMATION:
Viruses Journal published this study titled "Can Coronaviruses Steal Genes from the Host as Evidenced in Western European Hedgehogs by EriCoV Genetic Characterization?". Claudia Cotti and Mauro Delogu from the Service for Wildlife at Department of Veterinary Medical Sciences of University of Bologna are co-authors of the study.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-08
Electrons in materials have a property known as 'spin', which is responsible for a variety of properties, the most well-known of which is magnetism. Permanent magnets, like the ones used for refrigerator doors, have all the spins in their electrons aligned in the same direction. Scientists refer to this behaviour as ferromagnetism, and the research field of trying to manipulate spin as spintronics.
Down in the quantum world, spins can arrange in more exotic ways, giving rise to frustrated states and entangled magnets. Interestingly, a property similar to spin, known as "the valley," appears in graphene materials. This unique feature has given rise to the field of valleytronics, which aims to exploit the ...
2021-02-08
The lung is a complex organ whose main function is to exchange gases. It is the largest organ in the human body and plays a key role in the oxygenation of all the organs. Due to its structure, cellular composition and dynamic microenvironment, is difficult to mimic in vitro.
A specialized laboratory of the ARTORG Center for Biomedical Engineering Research, University of Bern, headed by Olivier Guenat has developed a new generation of in-vitro models called organs-on-chip for over 10 years, focusing on modeling the lung and its diseases. After a first successful lung-on-chip system exhibiting essential features of the lung, the Organs-on-Chip (OOC) Technologies laboratory has now developed a purely ...
2021-02-08
Researchers have identified a new form of magnetism in so-called magnetic graphene, which could point the way toward understanding superconductivity in this unusual type of material.
The researchers, led by the University of Cambridge, were able to control the conductivity and magnetism of iron thiophosphate (FePS3), a two-dimensional material which undergoes a transition from an insulator to a metal when compressed. This class of magnetic materials offers new routes to understanding the physics of new magnetic states and superconductivity.
Using new high-pressure techniques, the researchers have shown what happens to magnetic graphene during the transition from insulator to conductor and into ...
2021-02-08
A Rochester Institute of Technology researcher has validated a tool measuring adherence to a popular child feeding approach used by pediatricians, nutritionists, social workers and child psychologists to assess parents' feeding practices and prevent feeding problems.
The best-practice approach, known as the Satter Division of Responsibility in Feeding, has now been rigorously tested and peer reviewed, resulting in the quantifiable tool sDOR.2-6y. The questionnaire will become a standard parent survey for professionals and researchers working in the early childhood development field, predicts lead researcher ...
2021-02-08
Astronomers may have found our galaxy's first example of an unusual kind of stellar explosion. This discovery, made with NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory, adds to the understanding of how some stars shatter and seed the universe with elements critical for life on Earth.
This intriguing object, located near the center of the Milky Way, is a supernova remnant called Sagittarius A East, or Sgr A East for short. Based on Chandra data, astronomers previously classified the object as the remains of a massive star that exploded as a supernova, one of many kinds of exploded stars that scientists have catalogued.
Using longer Chandra observations, a team of astronomers has now instead concluded that the object is left over from a different type of ...
2021-02-08
Findings from a new study on Alzheimer's disease (AD), led by researchers at the University of Saskatchewan (USask), could eventually help clinicians identify people at highest risk for developing the irreversible, progressive brain disorder and pave the way for treatments that slow or prevent its onset.
The research, published in the journal Scientific Reports in early January, has demonstrated that a shorter form of the protein peptide believed responsible for causing AD (beta-amyloid 42, or Aβ42) halts the damage-causing mechanism of ...
2021-02-08
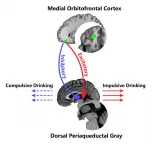
A pathway in the brain where alcohol addiction first develops has been identified by a team of British and Chinese researchers in a new study
Could lead to more effective interventions when tackling compulsive and impulsive drinking
More than 3 million deaths every year are related to alcohol use globally, according to the World Health Organisation
The physical origin of alcohol addiction has been located in a network of the human brain that regulates our response to danger, according to a team of British and Chinese researchers, co-led by the University of Warwick, the University ...
2021-02-08
On a brisk November morning in 2018, a fire sparked in a remote stretch of canyon in Butte County, California, a region nestled against the western slopes of the Sierra Nevada mountains. Fueled by a sea of tinder created by drought, and propelled by powerful gusts, the flames grew and traveled rapidly. In less than 24 hours, the fire had swept through the town of Paradise and other communities, leaving a charred ruin in its wake.
The Camp Fire was the costliest disaster worldwide in 2018 and, having caused 85 deaths and destroyed more than 18,000 buildings, it became both the deadliest and most destructive wildfire ...
2021-02-08
An unusual biologically active porphyrin compound was isolated from seabed dweller Ophiura sarsii. The substance might be used as an affordable light-sensitive drug for innovative photodynamic therapy and for targeted treatment of triple-negative breast cancer and some other cancers. Researchers from the School of Biomedicine of Far Eastern Federal University (FEFU) and the University of Geneva reported the findings in Marine Drugs.
The seabed dweller Ophiura sarsii, the source of the new compound, was isolated at a depth of 15-18 meters in Bogdanovich Bay, Russky Island (Vladivostok, Russia). Ophiuras may resemble ...
2021-02-08
DALLAS - Feb. 8, 2021 - Pregnant women, who are at increased risk of preterm birth or pregnancy loss if they develop a severe case of COVID-19, need the best possible guidance on whether they should receive a COVID-19 vaccine, according to an article by two UT Southwestern obstetricians published today in JAMA. That guidance can take lessons from what is already known about other vaccines given during pregnancy.
In the Viewpoint article, Emily H. Adhikari, M.D., and Catherine Y. Spong, M.D., describe how the available safety and effectiveness data, basic science of mRNA vaccines, and long history ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Some types of coronavirus steal the hosts' genes to elude their immune system