Severe undercounting of COVID-19 cases in U.S., other countries estimated via model
2021-02-08
(Press-News.org) A new machine-learning framework uses reported test results and death rates to calculate estimates of the actual number of current COVID-19 infections within all 50 U.S. states and 50 countries. Jungsik Noh and Gaudenz Danuser of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on February 8, 2021.
During the ongoing pandemic, U.S. states and many countries have reported daily counts of COVID-19 infections and deaths confirmed by testing. However, many infections have gone undetected, resulting in under-counting of the total number of people currently infected at any given point in time--an important metric to guide public health efforts.
Now, Noh and Danuser have developed a computational model that uses machine-learning strategies to estimate the actual daily number of current infections for all 50 U.S. states and the 50 most-infected countries. To make the calculations, the model draws on previously published pandemic parameters and publicly available daily data on confirmed cases and deaths. Visualizations of these daily estimates are freely available online.
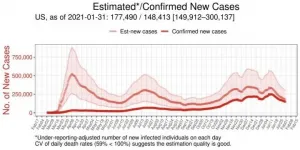
The model's estimates indicate severe undercounting of cases across the U.S. and worldwide. The cumulative number of actual cases in 9 out of 50 countries is estimated to be at least five times higher than confirmed cases. Within the U.S., estimates of the cumulative number of actual cases within states were in line with the results of an antibody testing study conducted in 46 states.
For some countries, such as the U.S., Belgium, and the U.K., estimates indicate that more than 20 percent of the total population has experienced infection. As of January 31, 2021, some U.S. states--including Pennsylvania, Arizona, and Florida--have currently active cases totaling more than 5 percent of the state's entire population. In Washington, the active cases were estimated to be one percent of the population that day.
Looking ahead, the model has been estimating current COVID-19 case counts within communities, which could help inform contact-tracing and other public health efforts.
The authors add: "Given that the confirmed cases only capture the tip of the iceberg in the middle of the pandemic, the estimated sizes of current infections in this study provide crucial information to determine the regional severity of COVID-19 that can be misguided by the confirmed cases."
INFORMATION:
Citation: Noh J, Danuser G (2021) Estimation of the fraction of COVID-19 infected people in U.S. states and countries worldwide. PLoS ONE 16(2): e0246772.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0246772
Funding: This work was supported by Lyda Hill Philanthropies. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE:
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0246772
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-08
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) -- Researchers in the labs of Christopher Bates, an assistant professor of materials at UC Santa Barbara, and Michael Chabinyc, a professor of materials and chair of the department, have teamed to develop the first 3D-printable "bottlebrush" elastomer. The new material results in printed objects that have unusual softness and elasticity -- mechanical properties that closely resemble those of human tissue.
Conventional elastomers, i.e. rubbers, are stiffer than many biological tissues. That's due to the size and shape of their constituent polymers, which are long, linear molecules that easily entangle like cooked spaghetti. In contrast, bottlebrush polymers ...
2021-02-08
Classifying a death as suicide may be easiest for medical examiners and coroners in the western United States, which reports the highest suicide rates officially. Suicide by firearm is the leading method there, and usually clear in terms of evidence.
By contrast, suicides by drug overdose, spurred primarily by the opioid epidemic in the remainder of the country, are less obvious to investigators.
But a new West Virginia University-led injury mortality study combines most drug overdose deaths with all suicides into an expanded self-injury category. Exposing a mental health crisis that has unraveled across the United States over the past two decades, study data have direct implications for suicide prevention efforts.
Ian Rockett, professor ...
2021-02-08
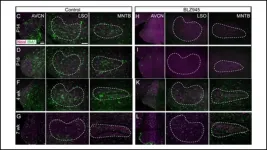
Auditory pathways in the brainstem do not fully mature without microglia clearing away extra cell connections. This crucial function occurs even when pruning by microglia is delayed, according to new research published in eNeuro.
Sensitive hearing requires precise connections between neurons in the auditory brainstem. Early in development, support cells called microglia prune away unnecessary connections and encourage others to expand. Microglia finish their job around two weeks after birth, but the rigidity of this developmental timeframe is unknown.
Milinkeviciute et al. eliminated microglia from the brains of newborn mice using a drug. They stopped the treatment after 10 days, and microglia returned to the brainstem. Initially, the mice with delayed microglia development ...
2021-02-08
During every instant of life, over a hundred trillion microbes, collectively known as the microbiome, reside on skin surfaces and course through the human body. In the human gut, vast colonies of bacteria, belonging to around 1000 different species, carry out duties ranging from the digestion of food and the management of body weight to effects on the brain and behavior, many of these still elusive to science.
Recent studies in mice and humans have revealed intriguing links between the composition of gut microbiota and Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), a disease believed to affect ...
2021-02-08
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- Passive cooling, like the shade a tree provides, has been around forever.
Recently, researchers have been exploring how to turbo charge a passive cooling technique -- known as radiative or sky cooling -- with sun-blocking, nanomaterials that emit heat away from building rooftops. While progress has been made, this eco-friendly technology isn't commonplace because researchers have struggled to maximize the materials' cooling capabilities.
New research led by University at Buffalo engineers makes significant progress in this area.
A study published Feb. 8 in the journal Cell Reports Physical Science describes a uniquely designed radiative cooling system that:
Lowered the temperature inside ...
2021-02-08
Ebola and Marburg are among the most deadly viruses, with mortality rates from these infections ranging from 25% to 90%. While no drugs currently are available on the market to prevent infection from these viruses -- they belong to a category of viruses called filoviruses, which are known to cause hemorrhagic fever -- researchers have identified a few small drug molecules that can block filoviruses from infecting cells by occupying a single site on a glycoprotein in the virus.
Now, researchers at the END ...
2021-02-08
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Assistant Professor Peter Koo and collaborator Matt Ploenzke reported a way to train machines to predict the function of DNA sequences. They used "neural nets", a type of artificial intelligence (AI) typically used to classify images. Teaching the neural net to predict the function of short stretches of DNA allowed it to work up to deciphering larger patterns. The researchers hope to analyze more complex DNA sequences that regulate gene activity critical to development and disease.
Machine-learning researchers can train a brain-like "neural net" computer to recognize objects, ...
2021-02-08
COLUMBUS, Ohio - We know that what happens in the mouth doesn't stay in the mouth - but the oral cavity's connection to the rest of the body goes way beyond chewing, swallowing and digestion.
The healthy human oral microbiome consists of not just clean teeth and firm gums, but also energy-efficient bacteria living in an environment rich in blood vessels that enables the organisms' constant communication with immune-system cells and proteins.
A growing body of evidence has shown that this system that seems so separate from the rest of our bodies is actually highly influential on, and influenced by, our overall health, said Purnima Kumar, professor of periodontology at The Ohio State University, speaking at a science conference this week.
For example, type 2 diabetes has long ...
2021-02-08
New research finds caffeine consumed during pregnancy can change important brain pathways that could lead to behavioral problems later in life. Researchers in the Del Monte Institute for Neuroscience at the University of Rochester Medical Center (URMC) analyzed thousands of brain scans of nine and ten-year-olds, and revealed changes in the brain structure in children who were exposed to caffeine in utero.
"These are sort of small effects and it's not causing horrendous psychiatric conditions, but it is causing minimal but noticeable behavioral issues that should make us consider long term effects ...
2021-02-08
One of humanity's biggest challenges right now is reducing our emissions of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Research groups worldwide are trying to find ways to efficiently separate carbon dioxide (CO2) from the mixture of gases emitted from industrial plants and power stations. Among the many strategies for accomplishing this, membrane separation is an attractive, inexpensive option; it involves using polymer membranes that selectively filter CO2 from a mix of gases.
Recent studies have focused on adding low amounts of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) into polymer matrices to enhance their properties. MOFs are compounds made of a metallic center bonded to organic molecules in a very orderly fashion, producing porous crystals. When added to polymer ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Severe undercounting of COVID-19 cases in U.S., other countries estimated via model