(Press-News.org) Classifying a death as suicide may be easiest for medical examiners and coroners in the western United States, which reports the highest suicide rates officially. Suicide by firearm is the leading method there, and usually clear in terms of evidence.
By contrast, suicides by drug overdose, spurred primarily by the opioid epidemic in the remainder of the country, are less obvious to investigators.
But a new West Virginia University-led injury mortality study combines most drug overdose deaths with all suicides into an expanded self-injury category. Exposing a mental health crisis that has unraveled across the United States over the past two decades, study data have direct implications for suicide prevention efforts.
Ian Rockett, professor emeritus of epidemiology in the WVU School of Public Health, spearheaded the research that examined fatal self-injury in the United States from 1999 to 2018. Measuring self-injury mortality (SIM)--suicides plus estimated "non-suicide" drug self-intoxication deaths--circumvents suicide misclassification and more accurately accounts for fatal self-injuries.
"Broadening the definition of SIM to encompass most drug overdose deaths, even if they don't meet the standards used by medical examiners and coroners to classify them as suicides, shows the whole nation is afflicted by a mental health crisis," Rockett said. "On the other hand, if we only represent SIM by registered suicides, this crisis misleadingly appears concentrated in western states."
Rockett, also adjunct professor in the Department of Psychiatry, University of Rochester Medical Center, elaborated on differences in suicide classification between regions.
"Suicides likely have been easiest to detect in the west because the leading method is shooting and it is highly lethal," he said. "The remainder of the country has been more severely affected by the opioid epidemic through the opening decades of the 21st century. Our previous research indicating substantial overlap with a more hidden suicide epidemic, led me to develop SIM in collaboration with a very talented group of multidisciplinary researchers and practitioners about six or seven years ago. That the suicide epidemic was most pronounced in the west and the opioid epidemic elsewhere in the nation -- West Virginia stands out -- motivated us to look at SIM versus suicide rates across the country as a whole and across time."
The findings appear in Lancet's EClinicalMedicine. Other WVU researchers joining Rockett on the study were Brian Hendricks, research assistant professor of epidemiology, and James Berry, chair of the Department of Behavioral Medicine and Psychiatry.
The research team tapped into cause-of-death data for all 50 states and Washington, D.C. from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's Wide-ranging Online Data for Epidemiologic Research.
After broadening the SIM definition, they found the national annual average percentage change in the SIM rate was 4.3% versus 1.8% for the suicide rate. By 2017-2018, all states except Nebraska posted a SIM rate of at least 21 deaths per 100,000 population. All located in the west, only five states had a rate that high in 1999-2000.
"Despite victims sharing many common risk factors, suicide and drug overdose deaths tend to be treated separately in the scientific literature, media, health care system, and by funding agencies and prevention programs," Rockett said. "Among these risk factors are unemployment, family discord, unmanaged and mismanaged physical pain, and various psychiatric disorders that include alcohol and other substance use disorders.
"While most people dying by overdose may not have intended to die, they were engaging in repetitive, intentional, self-injurious behaviors that they understood markedly increased their chances of dying prematurely. Calling these deaths 'accidents' (the forensic classification most often used in the U.S.) or 'unintentional' (the term used by the CDC) mischaracterizes what occurred, even if consistent with the classification criteria used by medical examiners and coroners."
Early data indicate the COVID-19 pandemic is making the national mental health crisis worse.
"Opioid and other drug-overdose deaths continue to rise in spite of medical efforts to make life-saving medications for opioid use disorder available to patients and communities," said co-author Hilary Connery, from McLean Hospital and Harvard Medical School. "Many persons suffering drug use disorders become hopeless--they relapse frequently, continue to experience relationship losses, health consequences, and economic instability, and they frequently suffer other mental disorders, such as depression, post-traumatic stress disorder, and other anxiety disorders. We know that people with addiction have 10 times the rate of suicide compared to those without addiction."
Another of Rockett's co-investigators, Eric Caine, professor of psychiatry at the University of Rochester Medical Center, underscored that this work has major implications for future suicide prevention efforts. It is especially important to deploy programs "upstream" when groups and individuals can be helped with fundamentally distressing problems long before they ever become suicidal, he said. Recognizing a patient's full story - risk factors, long-term health history, socioeconomic experiences - is key to providing lifesaving, comprehensive care.
"Ultimately it is less about 'classifying suicide' and more about understanding that suicide and overdose fatalities reflect common social and psychological risk factors that were present long before death," Caine said.
"There are large groups of persons in our country who have suffered adverse early life experiences, family and social turmoil, economic hardships and life disappoints, as well chronic ailments; many die prematurely. Our goal must be to eliminate or mitigate those circumstances. Separating these groups using misclassified or misleading postmortem labels does little to enhance prevention. We need to focus on the lives of persons in these groups long before they get close to dying if we aspire to overcome these tragic losses of life."
INFORMATION:
Citation: doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100741
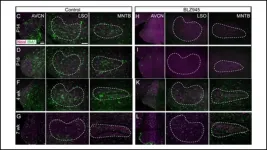
Auditory pathways in the brainstem do not fully mature without microglia clearing away extra cell connections. This crucial function occurs even when pruning by microglia is delayed, according to new research published in eNeuro.
Sensitive hearing requires precise connections between neurons in the auditory brainstem. Early in development, support cells called microglia prune away unnecessary connections and encourage others to expand. Microglia finish their job around two weeks after birth, but the rigidity of this developmental timeframe is unknown.
Milinkeviciute et al. eliminated microglia from the brains of newborn mice using a drug. They stopped the treatment after 10 days, and microglia returned to the brainstem. Initially, the mice with delayed microglia development ...
During every instant of life, over a hundred trillion microbes, collectively known as the microbiome, reside on skin surfaces and course through the human body. In the human gut, vast colonies of bacteria, belonging to around 1000 different species, carry out duties ranging from the digestion of food and the management of body weight to effects on the brain and behavior, many of these still elusive to science.
Recent studies in mice and humans have revealed intriguing links between the composition of gut microbiota and Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), a disease believed to affect ...
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- Passive cooling, like the shade a tree provides, has been around forever.
Recently, researchers have been exploring how to turbo charge a passive cooling technique -- known as radiative or sky cooling -- with sun-blocking, nanomaterials that emit heat away from building rooftops. While progress has been made, this eco-friendly technology isn't commonplace because researchers have struggled to maximize the materials' cooling capabilities.
New research led by University at Buffalo engineers makes significant progress in this area.
A study published Feb. 8 in the journal Cell Reports Physical Science describes a uniquely designed radiative cooling system that:
Lowered the temperature inside ...
Ebola and Marburg are among the most deadly viruses, with mortality rates from these infections ranging from 25% to 90%. While no drugs currently are available on the market to prevent infection from these viruses -- they belong to a category of viruses called filoviruses, which are known to cause hemorrhagic fever -- researchers have identified a few small drug molecules that can block filoviruses from infecting cells by occupying a single site on a glycoprotein in the virus.
Now, researchers at the END ...
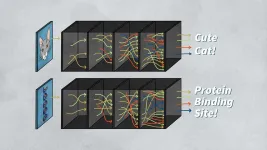
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Assistant Professor Peter Koo and collaborator Matt Ploenzke reported a way to train machines to predict the function of DNA sequences. They used "neural nets", a type of artificial intelligence (AI) typically used to classify images. Teaching the neural net to predict the function of short stretches of DNA allowed it to work up to deciphering larger patterns. The researchers hope to analyze more complex DNA sequences that regulate gene activity critical to development and disease.
Machine-learning researchers can train a brain-like "neural net" computer to recognize objects, ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio - We know that what happens in the mouth doesn't stay in the mouth - but the oral cavity's connection to the rest of the body goes way beyond chewing, swallowing and digestion.
The healthy human oral microbiome consists of not just clean teeth and firm gums, but also energy-efficient bacteria living in an environment rich in blood vessels that enables the organisms' constant communication with immune-system cells and proteins.
A growing body of evidence has shown that this system that seems so separate from the rest of our bodies is actually highly influential on, and influenced by, our overall health, said Purnima Kumar, professor of periodontology at The Ohio State University, speaking at a science conference this week.
For example, type 2 diabetes has long ...
New research finds caffeine consumed during pregnancy can change important brain pathways that could lead to behavioral problems later in life. Researchers in the Del Monte Institute for Neuroscience at the University of Rochester Medical Center (URMC) analyzed thousands of brain scans of nine and ten-year-olds, and revealed changes in the brain structure in children who were exposed to caffeine in utero.
"These are sort of small effects and it's not causing horrendous psychiatric conditions, but it is causing minimal but noticeable behavioral issues that should make us consider long term effects ...
One of humanity's biggest challenges right now is reducing our emissions of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Research groups worldwide are trying to find ways to efficiently separate carbon dioxide (CO2) from the mixture of gases emitted from industrial plants and power stations. Among the many strategies for accomplishing this, membrane separation is an attractive, inexpensive option; it involves using polymer membranes that selectively filter CO2 from a mix of gases.
Recent studies have focused on adding low amounts of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) into polymer matrices to enhance their properties. MOFs are compounds made of a metallic center bonded to organic molecules in a very orderly fashion, producing porous crystals. When added to polymer ...
DURHAM, N.C. -- The world's most technologically advanced robots would lose in a competition with a tiny crustacean.
Just the size of a sunflower seed, the amphipod Dulichiella cf. appendiculata has been found by Duke researchers to snap its giant claw shut 10,000 times faster than the blink of a human eye.
The claw, which only occurs on one side in males, is impressive, reaching 30% of an adult's body mass. Its ultrafast closing makes an audible snap, creating water jets and sometimes producing small bubbles due to rapid changes in water pressure, a phenomenon known ...
Bark beetle outbreaks and wildfire alone are not a death sentence for Colorado's beloved forests--but when combined, their toll may become more permanent, shows new research from the University of Colorado Boulder.
It finds that when wildfire follows a severe spruce beetle outbreak in the Rocky Mountains, Engelmann spruce trees are unable to recover and grow back, while aspen tree roots survive underground. The study, published last month in Ecosphere, is one of the first to document the effects of bark beetle kill on high elevation forests' recovery from wildfire.
"The fact that Aspen is regenerating prolifically after wildfire is not a surprise," said Robert Andrus, who conducted ...