Role of aspirating system type in SARS-CoV-2 seropositivity among dental staff
2021-02-08
(Press-News.org) Alexandria, Va., USA -- High-volume aspirators are recommended in dental clinics during the COVID-19 pandemic, but the study "SARS-CoV-2 Seropositivity Among Dental Staff and the Role of Aspirating Systems" published in the JDR Clinical & Translational Research (JDR CTR), shows that the type of aspirating system significantly affects the incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection among dental specialists.
In this retrospective cohort study of 157 healthcare workers in Ekaterinburg, Russia, data on the seroprevalence of COVID-19 from dental clinics using three different types of aspirating systems were compared. Clinic A and B used a V6000 aspirating system with a vacuum controller and high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters, but the aspirating system in clinic A functioned in dry mode and the system in clinic B function in semi-dry mode. Clinic C used the VS900 system which discharges air into the dental operatory, closely resembling natural dispersion, and no HEPA filter.
The estimated prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection was 11.5% (19 HCWs) across all clinics over the 5-month period (May to August 2020). The results show that the prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection was significantly higher in clinic C, which did not utilize HEPA filters, and was significantly lower in clinic A, which did utilize HEPA filters and operated in dry mode. In dry suction systems, the separation of aspirated fluids from the air occurs at every treatment unit, whereas in semi-dry suction systems the separation occurs via a central separation unit connected to multiple treatment units.
"No comparative studies have investigated the effects of the type of aspirating system on the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection among dentists and dental assistants," said JDR CTR Editor-in-Chief Jocelyne S. Feine, McGill University, Montréal, Quebec, Canada. "Based on the results of this pilot study, we recommend the use of aspirating systems installed with HEPA filters that evacuate and dissipate aerosols into specialized areas. Studies that provide a deeper understanding of this topic are warranted."
INFORMATION:
About the JDR Clinical and Translational Research
The JDR Clinical & Translational Research is a quarterly publication. This peer-reviewed journal is dedicated to publishing original dental, oral and craniofacial research at the interface between discovery science and clinical application with the translation of research into healthcare delivery systems at the individual patient, clinical practice and community levels. The JDR CTR has been accepted for inclusion in MEDLINE.
International Association for Dental Research
The International Association for Dental Research (IADR) is a nonprofit organization with over 10,000 individual members worldwide, with a Mission to drive dental, oral and craniofacial research to advance health and well-being worldwide. To learn more, visit http://www.iadr.org. The American Association for Dental Research (AADR) is the largest Division of IADR with 3,100 members in the United States. To learn more, visit http://www.iadr.org/aadr.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-08
Systems designed to detect deepfakes --videos that manipulate real-life footage via artificial intelligence--can be deceived, computer scientists showed for the first time at the WACV 2021 conference which took place online Jan. 5 to 9, 2021.
Researchers showed detectors can be defeated by inserting inputs called adversarial examples into every video frame. The adversarial examples are slightly manipulated inputs which cause artificial intelligence systems such as machine learning models to make a mistake. In addition, the team showed that the attack still works after videos are ...
2021-02-08
The Atala butterfly (Eumaeus atala) and its five closest relatives in the genus Eumaeus like to display their toxicity. This sextet's toxicity comes from what they eat as caterpillars: plants called cycads that have been around since before dinosaurs roamed the Earth and contain a potent liver toxin called cycasin.
Because they are filled with poison, Eumaeus are big, gaudily iridescent and flap about like they have no place to go. Even their caterpillars are conspicuous, congregating in groups to munch cycad plants all while sporting flashy red and gold ...
2021-02-08
CLEVELAND - A Cleveland Clinic-led team of researchers has developed a personalized genomic medicine platform that will help advance accelerate genomic medicine research and genome-informed drug discovery, according to new study results published recently in END ...
2021-02-08
CHICAGO --- Northwestern University professor and researcher Linda Teplin will discuss the psychosocial outcomes of incarcerated youth at the virtual 2021 American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) annual meeting.
Teplin will moderate the scientific session "Consequences of Incarceration on Health Inequity and Racial Injustice" at 2 p.m. EST, Monday, Feb. 8. During the session, she will also present "Consequences of Incarceration in Detained Youth: A 15-Year Longitudinal Study."
Nearly 2.2 million Americans are incarcerated annually, ...
2021-02-08
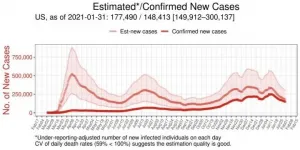
A new machine-learning framework uses reported test results and death rates to calculate estimates of the actual number of current COVID-19 infections within all 50 U.S. states and 50 countries. Jungsik Noh and Gaudenz Danuser of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on February 8, 2021.
During the ongoing pandemic, U.S. states and many countries have reported daily counts of COVID-19 infections and deaths confirmed by testing. However, many infections have gone undetected, resulting in under-counting of the total number of people currently infected at any ...
2021-02-08
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) -- Researchers in the labs of Christopher Bates, an assistant professor of materials at UC Santa Barbara, and Michael Chabinyc, a professor of materials and chair of the department, have teamed to develop the first 3D-printable "bottlebrush" elastomer. The new material results in printed objects that have unusual softness and elasticity -- mechanical properties that closely resemble those of human tissue.
Conventional elastomers, i.e. rubbers, are stiffer than many biological tissues. That's due to the size and shape of their constituent polymers, which are long, linear molecules that easily entangle like cooked spaghetti. In contrast, bottlebrush polymers ...
2021-02-08
Classifying a death as suicide may be easiest for medical examiners and coroners in the western United States, which reports the highest suicide rates officially. Suicide by firearm is the leading method there, and usually clear in terms of evidence.
By contrast, suicides by drug overdose, spurred primarily by the opioid epidemic in the remainder of the country, are less obvious to investigators.
But a new West Virginia University-led injury mortality study combines most drug overdose deaths with all suicides into an expanded self-injury category. Exposing a mental health crisis that has unraveled across the United States over the past two decades, study data have direct implications for suicide prevention efforts.
Ian Rockett, professor ...
2021-02-08
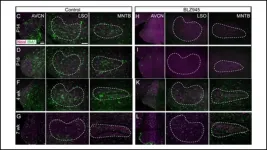
Auditory pathways in the brainstem do not fully mature without microglia clearing away extra cell connections. This crucial function occurs even when pruning by microglia is delayed, according to new research published in eNeuro.
Sensitive hearing requires precise connections between neurons in the auditory brainstem. Early in development, support cells called microglia prune away unnecessary connections and encourage others to expand. Microglia finish their job around two weeks after birth, but the rigidity of this developmental timeframe is unknown.
Milinkeviciute et al. eliminated microglia from the brains of newborn mice using a drug. They stopped the treatment after 10 days, and microglia returned to the brainstem. Initially, the mice with delayed microglia development ...
2021-02-08
During every instant of life, over a hundred trillion microbes, collectively known as the microbiome, reside on skin surfaces and course through the human body. In the human gut, vast colonies of bacteria, belonging to around 1000 different species, carry out duties ranging from the digestion of food and the management of body weight to effects on the brain and behavior, many of these still elusive to science.
Recent studies in mice and humans have revealed intriguing links between the composition of gut microbiota and Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), a disease believed to affect ...
2021-02-08
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- Passive cooling, like the shade a tree provides, has been around forever.
Recently, researchers have been exploring how to turbo charge a passive cooling technique -- known as radiative or sky cooling -- with sun-blocking, nanomaterials that emit heat away from building rooftops. While progress has been made, this eco-friendly technology isn't commonplace because researchers have struggled to maximize the materials' cooling capabilities.
New research led by University at Buffalo engineers makes significant progress in this area.
A study published Feb. 8 in the journal Cell Reports Physical Science describes a uniquely designed radiative cooling system that:
Lowered the temperature inside ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Role of aspirating system type in SARS-CoV-2 seropositivity among dental staff