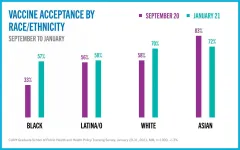(Press-News.org) Under the Biden Administration, New Yorkers' acceptance of the Covid-19 vaccine has increased significantly. In September, 55% of residents reported they would take the vaccine when it became available and this January, 64% reported they would take it.
Differences in vaccine acceptance persist across racial and ethnic groups. Among Whites and Asians acceptance is 70-72%; among Blacks and Latina/os it is 57-58%. On a positive note, the largest increase in rate of acceptance was seen among Black respondents, up from 33% in September to 57% in January.
These are key findings from the most recent tracking survey of public perceptions and experiences in New York City during the Covid-19 pandemic, conducted January 29-31 by the City University of New York Graduate School of Public Health and Health Policy (CUNY SPH).
"Obtaining a steady supply of Covid-19 vaccines and distributing them equitably and efficiently, as well as reaching and convincing New Yorkers to take the vaccine are the pivotal challenges that lie ahead of us," said Dr. Ayman El-Mohandes, Dean of CUNY SPH. "The current strategy does not meet the needs of those with the greatest vulnerability."
Of concern, more than half (54%) of New York City respondents believe the state is not doing a good job of managing the vaccine rollout. Highest levels of disapproval were reported by Staten Island (59%) the Bronx (50%) and Manhattan (50%).
Almost half of New York City residents think that recovery will not happen until most New Yorkers are vaccinated. In contrast, only 53% of residents in the Bronx are willing to take the vaccine. This finding is of great concern, since the Bronx continues to bear the highest burden of infection and mortality associated with the pandemic.
Employment and Covid-19 Vaccine Acceptance
Respondents who are currently employed were more willing to accept Covid-19 vaccines (68%) as well as more likely to actually have been vaccinated. Among respondents who lost their job during the pandemic and remain unemployed, only 56% said they were willing to accept the vaccine.
These data suggest that a concerted effort will be needed to reach, inform, and motivate unemployed New York City residents to participate in the vaccination rollout.
The complete survey results and related commentary can be found at https://sph.cuny.edu/research/covid-19-tracking-survey/january-vaccines/ and JHC Impact, an initiative of the Journal of Health Communication: International Perspectives.
Methodology
The CUNY Graduate School of Public Health and Health Policy (CUNY SPH) survey was the third study of a repeated cross sectional sample using n=1,000 New York City residents from January 29-31, 2021, the previous two surveys were conducted at the end of September and November 2020.
The representative area-based probability sample for New York City was n=1,000, with a margin of error (MOE) of +/- 3 percentage points. The data set was weighted by gender, age, ethnicity, education, and borough based on the 2019 1-year American Community Survey model. Additional considerations beyond the ACS model influenced weights for race/ethnicity as the Census Bureau collects two sets of race/ethnicity data by grouping Hispanics and races together (e.g., Hispanic Whites) as well as separating non-Hispanic and Hispanic groups. To create one data set that more appropriately represents the racial diversity in the city, we grouped Hispanic and Latina/os respondents together. It is important to remember that subsets based on gender, age, ethnicity, and region carry with them higher margins of error, as the sample size is reduced.
Sampling parameters were set based borough-level population data:
Queens: 27% of total (n=271)
Manhattan: 19% of total (n=194)
The Bronx: 17% of total (n=171)
Staten Island: 5% of total (n=57)
Brooklyn: 31% of total (n=308)
The data was collected by Consensus Strategies using an Interactive Voice Response (IVR) system of landlines (n=511), SMS-to-online (n=490).
Demographics:
1,001 Residents NYC
Age
18-19 23%
30-44 28%
45-59 24%
60+ 26%
Gender
Male 46%
Female 50%
Prefer not to say 2%
Other 1%
Race and ethnicity
Latina/o/Hispanic 29%
Black/African American 22%
Asian 14%
Caucasian/White 32%
Multiple/other 3%
Education Level
High school 42%
Some college 20%
Bachelor's 22%
Post-grad 16%
Household Income
$100,000 13%
INFORMATION:
The colors in a flower patch appear completely different to a bear, a honeybee, a butterfly and humans. The ability to see these colors is generated by specific properties of opsins - light-sensitive proteins in the retina of our eyes. The number of opsins expressed and the molecular structure of the receptor proteins determines the colors we see.
In a paper published February 9 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences a team of researchers led by Harvard University develop a novel method to express long wavelength invertebrate opsin proteins in vitro and detail the molecular structure of redshift (long-wavelength) ...
In 2018, a faulty electric transmission line ignited the Camp Fire in Northern California, ultimately consuming 239 square miles and several communities, including the town of Paradise, which was 95 percent destroyed. At least 85 people died.
Structures have been rebuilt, but some things are worse. In a paper published February 2, 2021 in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, scientists at University of California San Diego, with colleagues elsewhere, describe chronic mental health problems among some residents who experienced the Camp Fire in varying degrees.
Direct exposure to large-scale fires significantly ...
Photoionization of water involves the migration and solvation of electrons, with many transient and highly active intermediates. The process results in a large blue shift in the absorption spectrum, from the THz or gigahertz region to the visible range. While the behavior of low-density quasifree electrons excited by small pump power density has been investigated extensively, we still know little about the transient evolution of photoexcited plasma in liquid water. Valuable insights were recently provided by an international research team in a study published in Advanced Photonics.
According to Liangliang Zhang, physics professor at Capital Normal University in Beijing and one of the senior authors on the study, the physical mechanism of plasma evolution on the ...
The structure of organic substances tetrahydroisoquinolines (THIQ) includes a benzene ring fused with a nitrogen-containing cycle. These compounds are in high demand in the pharmaceutical industry. They are used in the synthesis of myorelaxants, antidepressants, and drugs against hypertension, cough, and insomnia. Although different variations of THIQ structures can be found in natural sources (for example, as parts of phytotoxins), modern-day pharmaceutical manufacturers are also interested in their rare types, such as spirocyclic THIQs. In their molecules, two adjacent cycles share one common atom, thus creating an unusual and very stable 3D structure. This feature ...
The development of the so-called small molecules is a promising field of the pharmaceutical industry. Small molecules are organic compounds with a small molecular mass. They are often based on heterocycles--carbon rings that also include atoms of nitrogen and other elements. The synthesis of small molecules is much cheaper than the development of drugs based on antibodies or other biological molecules; however, their properties are still understudied. Even the slightest modifications can change the characteristics of a small molecule and open a whole new range of its practical applications. Therefore, many research teams working in the field of chemical pharmacology improve synthesis methods to create libraries of ...
The COVID-19 pandemic that shuttered cities around the world did not just affect the way we work, study and socialize. It also affected our mobility. With millions of workers no longer commuting, vehicle traffic across Canada has plummeted. This has had a significant impact on the quality of air in major Canadian cities, according to a new study by Concordia researchers.
A paper published in the journal Science of the Total Environment looked at downtown air quality monitoring station data from Vancouver, Edmonton, Saskatoon, Winnipeg, Toronto, Montreal, Halifax ...
To achieve target delivery of drugs to cells and organs, scientists have to be able to transport the molecules of pharmaceutical substances to targets using a controllable carrier. The role of such a carrier can be played by special particles, such as lipid droplets or magnetic nanoparticles. Among the latter, the most popular are the ones based on iron oxides. Their sizes range from 1 to 100 nm, which is dozens of times smaller than animal cells, and they can be moved within a body using an external magnetic field.
However, in practice, it is quite difficult to control nanoparticles with magnets, as the magnetic field quickly becomes weaker when the distance from the magnet increases. This problem ...
WASHINGTON, February 9, 2021 -- As COVID-19 spreads via respiratory droplets, researchers have become increasingly interested in the drying of droplets on impermeable and porous surfaces. Surfaces that accelerate evaporation can decelerate the spread of the COVID-19 virus.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from IIT Bombay show a droplet remains liquid for a much shorter time on a porous surface, making it less favorable to survival of the virus.
The researchers found the coronavirus can survive for four days on glass, seven days on plastic, and seven days on stainless steel. But on paper and cloth, the virus survived for only three hours and two days, respectively.
"Based on our study, we recommend that furniture in hospitals and offices, ...
What The Study Did: Researchers examined how common SARS- CoV-2 infection was among migrant workers in Singapore.
Authors: Vernon J. Lee, M.B.B.S., Ph.D., of the Ministry of Health in Singapore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2020.24071)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full article is linked to this news release.
Embed ...
WASHINGTON, February 9, 2021 -- The detailed physical processes and pathways involved in the transmission of COVID-19 are still not well understood. Researchers decided to use advanced computational fluid dynamics tools on supercomputers to deepen understanding of transmission and provide a quantitative assessment of how different environmental factors influence transmission pathways and airborne infection risk.
A restaurant outbreak in China was widely reported as strong evidence of airflow-induced transmission of COVID-19. But it lacked a detailed investigation about exactly how transmission occurred.
Why did some people get infected while others within the same area did not? ...