Endovascular aneurysm repair linked to higher readmission rates
Chances of readmission were 1.5 times higher with less-invasive technique
2021-02-10
(Press-News.org) Ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms (rAAA) are responsible for nearly 2% of all deaths in U.S. men over the age of 65. Endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) has emerged as a newer and less invasive alternative to open repair for rAAA, and current guidelines recommend EVAR as a first-line option for treatment of rAAA when certain criteria are met. But researchers from the University of Missouri School of Medicine have discovered that while EVAR is more commonly utilized for rAA, shortens hospital stay and has a lower initial mortality rate, the odds of hospital readmission after EVAR are 1.5 times higher compared to traditional open repair.
"A high rate of readmissions in vascular surgery patients is associated with increased patient morbidity and mortality, along with increased costs to both hospitals and patients," said Todd Vogel, MD, associate professor of vascular and endovascular surgery. "Understanding contributing factors leading to hospital readmission after emergency rAAA procedures may lead to improved patient outcomes and decreased costs."
Vogel's team analyzed 3,629 emergency or urgent open rAAA and 5,037 EVAR procedures over three years. They found EVAR had a significantly lower hospital mortality rate (21.4% for EVAR vs. 33.5% for open) and a 3.5-day shorter length of stay. However, EVAR patients had a significantly higher readmission rate within 30 days (EVAR 18.9% vs 14.3% for open). Infection complications were the most common reason for readmission for both types of procedures, but Vogel identified additional risk factors specific to EVAR.
"After adjusting for comorbidities and procedure type, we found additional EVAR-specific risk factors for readmission included prior EVAR repair, longer length of initial hospital stay and presence of chronic kidney disease or coronary artery disease," Vogel said. "Further investigation into reasons why a less invasive procedure has a higher readmission rate are needed"
In addition, Vogel said understanding post-discharge infection complications will also be important to help lower readmission and subsequent health care utilization after rAAA.
INFORMATION:
Other MU School of Medicine study authors include Drew Braet, MD, resident; John Taaffee, medical student; Priyanka Singh, PhD, data scientist; Jonathan Bath, MD, assistant professor of surgery; and Robin Kruse, PhD, research professor emerita.
The study, "Readmission and Utilization After Repair of Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms in the United States," was recently published by the journal Vascular and Endovascular Surgery. The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-10
Researchers at the RIKEN Center for Biosystems Dynamics Research in Japan have discovered a recipe for continuous cyclical regeneration of cultured hair follicles from hair follicle stem cells.
Scientists have been making waves in recent years by developing ways to grow a variety of useful items in laboratories, from meat and diamonds to retinas and other organoids. At the RIKEN Center for Biosystems Dynamics Research in Japan, a team led by Takashi Tsuji has been working on ways to regenerate lost hair from stem cells. In an important step, a new study identifies a population of hair follicle stem cells in the skin and a recipe for normal cyclical regeneration in the lab.
The researchers took fur and whisker cells ...
2021-02-10
Experts from the Natural History Museum, The Francis Crick Institute and the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History Jena have joined together to untangle the different meanings of ancestry in the evolution of our species Homo sapiens.
Most of us are fascinated by our ancestry, and by extension the ancestry of the human species. We regularly see headlines like 'New human ancestor discovered' or 'New fossil changes everything we thought about our ancestry', and yet the meanings of words like ancestor and ancestry are rarely discussed in detail. In the new paper, published in Nature, experts review our current understanding of how modern human ancestry around the globe can be traced into the distant ...
2021-02-10
MINNEAPOLIS/ST.PAUL (02/10/2021) -- University of Minnesota Medical School researchers studied SARS-CoV-2 infections at individual cellular levels and made four major discoveries about the virus, including one that validates the effectiveness of remdesivir - an FDA-approved antiviral drug - as a form of treatment for severe COVID-19 disease.
"Since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, the way that each individual responds differently to the infection has been closely studied. In our new study, we examined variations in the way individual cells reacted differently to the coronavirus and responded to antiviral treatment," said Ryan Langlois, PhD, senior author of the study, associate professor in the Department ...
2021-02-10
PHILADELPHIA -- Past exposure to seasonal coronaviruses (CoVs), which cause the common cold, does not result in the production of antibodies that protect against the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, according to a study led by Scott Hensley, PhD, an associate professor of Microbiology at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.
Prior studies have suggested that recent exposure to seasonal CoVs protects against SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. However, research from Hensley's team, published in Cell, suggests that if there is such protection, it does not come from antibodies.
"We found that many people possessed antibodies that could bind to SARS-CoV-2 before the pandemic, but these antibodies could not prevent infections," Hensley said. ...
2021-02-10
Researchers from the University of Basel have developed a virtual reality app for smartphones to reduce fear of heights. Now, they have conducted a clinical trial to study its efficacy. Trial participants who spent a total of four hours training with the app at home showed an improvement in their ability to handle real height situations.
Fear of heights is a widespread phenomenon. Approximately 5% of the general population experiences a debilitating level of discomfort in height situations. However, the people affected rarely take advantage of the available treatment options, such as exposure therapy, which involves putting the person in the anxiety-causing situation under the guidance of a professional. On the one hand, people ...
2021-02-10
Rituximab, an anti-cancer drug targeting the membrane protein CD20, was the first approved therapeutic antibody against B tumor cells. Immunologists at the University of Freiburg have now solved a mystery about how it works. A team headed by Professor Dr. Michael Reth used cell cultures, healthy cells, and cells from cancer patients to investigate how CD20 organizes the nanostructures on the B cell membrane. If the protein is missing or Rituximab binds to it, the organization of the B cell surface changes. The resting B cell is activated in the process. The team has published the research in the journal PNAS as part of contributions by new members of the National Academy of Science.
B cells are white blood cells and part of the immune system. When they recognize ...
2021-02-10
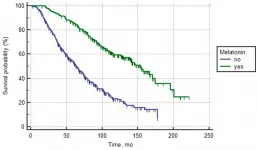
Oncotarget recently published "Melatonin increases overall survival of prostate cancer patients with poor prognosis after combined hormone radiation treatment" which reported that a retrospective study included 955 patients of various stages of prostate cancer who received combined hormone radiation treatment from 2000 to 2019. Comprehensive statistical methods were used to analyze the overall survival rate of PCa patients treated with melatonin in various prognosis groups.
The overall survival rate of PCa patients with favorable and intermediate prognoses treated or not treated ...
2021-02-10
JACKSONVILLE, Fla. (February 10, 2021) - Brain volume, verbal IQ, and overall IQ are lower in children with Type 1 diabetes (T1D) than in children without diabetes, according to a new longitudinal study published in Diabetes Care, a journal of the American Diabetes Association. The nearly eight-year study, led by Nelly Mauras, MD, a clinical research scientist at Nemours Children's Health System in Jacksonville, Florida, and Allan Reiss MD, a Professor at the Stanford University School of Medicine in California, compared brain scans of young children who have T1D with those of non-diabetic children to assess the extent to which glycemic exposure may adversely affect the ...
2021-02-10
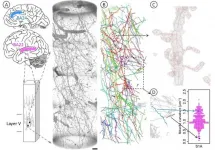
It was reported that volume of the brain areas such as superior temporal gyrus and anterior cingulate cortex reduces in schizophrenia but precise change of three-dimensional structure of neuron has remains unclear.
Dr. Itokawa and colleague performed Nanotomography experiments using Fresnel zone plate optics at the BL37XU beamline of the SPring-8 synchrotron radiation facility and at the 32-ID beamline of the Advanced Photon Source (APS) of Argonne National Laboratory.
A total of 34 three-dimensional image datasets of layer V of the BA22 cortex were blinded ...
2021-02-10
The recent review, published in Environment International and led by the University of Tartu, summarises the effect of aquatic pollution on cancer prevalence in wild animals with the help of more than 300 reviewed studies. Authors shed light on understudied yet important fields in cancer research in wild animals - summarising the key effects and pointing to future research avenues to crack the puzzle of why cancer develops in polluted environments.
„What was immediately evident was the bias towards fish in current research into aquatic wildlife cancer. However, given this bias it is especially interesting ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Endovascular aneurysm repair linked to higher readmission rates
Chances of readmission were 1.5 times higher with less-invasive technique