(Press-News.org) Every day, people die from simple infections even though they have been treated with antibiotics. This is because more and more bacteria have become resistant to the types of antibiotics that doctors can prescribe.
- It's a huge societal problem and a crisis that we must solve. For example, by developing new antibiotics that can defeat the resistant bacteria, says professor of chemistry at the Department of Physics, Chemistry and Pharmacy, University of Southern Denmark, Poul Nielsen.
Resistant bacteria are not only known from pig farms, where it is becoming increasingly difficult to keep the pigsties disease-free. Hospitals are also experiencing with increasing regularity that, for example, infectious diseases cannot be controlled in patients. Thus, an infection in a surgical wound can become life-threatening even if the operation went well.
According to Poul Nielsen, it is important to be at the forefront of the development because the list of resistant bacteria will only grow, which means that the treatment options will be reduced. It is therefore important to develop alternatives that can be used when the current antibiotics no longer work.
- Resistance can occur very quickly, and then it's essential that we're ready, he says.
Together with his research assistant Christoffer Heidtmann and associate professor Janne Kudsk Klitgaard from the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology as well as Clinical Microbiology, he has developed a substance that has the potential to become a new effective antibiotic, and SDU has now taken out a patent for it.
Unlike traditional antibiotics such as penicillin, sulfonamides and tetracyclines, this antibiotic is from the pleuromutilin class.
The substance is developed in a medicinal chemistry project and recently published in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.
The substance fights both resistant enterococcus, streptococcus and staphylococcus bacteria. The substance and the pleuromutilin class do this via a unique mechanism of action, which also causes resistance to develop at a very slow pace.
So far, the substance has been tested on bacteria and human cells. The next step towards becoming an approved drug is animal studies and then clinical studies in humans.
- If this substance is to reach doctors and patients as a drug, comprehensive and cost-intensive further development efforts are needed, which we can only initiate under the auspices of the university.
- The big pharmaceutical companies have that kind of money, but they are traditionally not interested in this kind of tasks, because they are not financially attractive, says Poul Nielsen.
According to Poul Nielsen, there are several reasons why it is not financially attractive to develop new antibiotics:
Antibiotics are only taken for days or weeks. There is more money in drugs for chronically ill people, such as antidepressants or blood pressure medicine.
Newly developed antibiotics will be backups and not used until the current antibiotics no longer work. So earnings are not just around the corner.
The bacteria can also become resistant to a new antibiotic, and then it has to be taken off the market again.
- However, this doesn't change the fact that the world community is in dire need of new effective drugs against antibiotic resistance. Maybe we should consider this a societal task, rather than a task that will only be solved if it's financially attractive, says Poul Nielsen.
He and his colleagues hope that the work of further developing their new antibiotic can continue. Whether it will happen, and whether it will be in a public or private context, only time will tell.
INFORMATION:
Resistant bacteria in Denmark
MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) comes from pigs, among others. May cause wound infection, abscesses, impetigo, infection of bones and joints as well as blood poisoning.
ESBL (Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase) is an enzyme that causes resistant intestinal bacteria from especially poultry, which can cause inflammation of the bladder, inflammation of the renal pelvis and blood poisoning.
Clostridium difficile is an intestinal bacterium that causes diarrhoea and is transmitted through faeces. It forms spores, which means that water, soap and alcohol have no effect.
VRE (Vancomycin-resistant enterococci) are bacteria that are born resistant to a wide range of antibiotics. VRE typically causes inflammation of the bladder but can also cause inflammation of the heart valves (endocarditis).
The WHO has presented an action plan to stop the spread of resistance. According to the organisation, we are heading towards a 'post-antibiotic era, in which common infections and minor injuries can once again kill'.
(Source: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antibiotic-resistance)
Can long-term stress lead to heart attacks? Most people would probably answer in the affirmative, but the scientific evidence of this is scarce. A new study by researchers from Linköping University in Sweden reveals that the levels of the stress hormone cortisol were increased in the months preceding a heart attack. The results, published in Scientific Reports, suggest that long-term stress is a risk factor for heart attacks.
"The levels of the stress hormone cortisol differed between people who have had a heart attack and those not affected. This suggests that cortisol in hair may be a new risk marker for heart attacks. We must take stress seriously", says Professor Tomas Faresjö from the Department of Health, ...
Ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms (rAAA) are responsible for nearly 2% of all deaths in U.S. men over the age of 65. Endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) has emerged as a newer and less invasive alternative to open repair for rAAA, and current guidelines recommend EVAR as a first-line option for treatment of rAAA when certain criteria are met. But researchers from the University of Missouri School of Medicine have discovered that while EVAR is more commonly utilized for rAA, shortens hospital stay and has a lower initial mortality rate, the odds of ...
Researchers at the RIKEN Center for Biosystems Dynamics Research in Japan have discovered a recipe for continuous cyclical regeneration of cultured hair follicles from hair follicle stem cells.
Scientists have been making waves in recent years by developing ways to grow a variety of useful items in laboratories, from meat and diamonds to retinas and other organoids. At the RIKEN Center for Biosystems Dynamics Research in Japan, a team led by Takashi Tsuji has been working on ways to regenerate lost hair from stem cells. In an important step, a new study identifies a population of hair follicle stem cells in the skin and a recipe for normal cyclical regeneration in the lab.
The researchers took fur and whisker cells ...
Experts from the Natural History Museum, The Francis Crick Institute and the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History Jena have joined together to untangle the different meanings of ancestry in the evolution of our species Homo sapiens.
Most of us are fascinated by our ancestry, and by extension the ancestry of the human species. We regularly see headlines like 'New human ancestor discovered' or 'New fossil changes everything we thought about our ancestry', and yet the meanings of words like ancestor and ancestry are rarely discussed in detail. In the new paper, published in Nature, experts review our current understanding of how modern human ancestry around the globe can be traced into the distant ...
MINNEAPOLIS/ST.PAUL (02/10/2021) -- University of Minnesota Medical School researchers studied SARS-CoV-2 infections at individual cellular levels and made four major discoveries about the virus, including one that validates the effectiveness of remdesivir - an FDA-approved antiviral drug - as a form of treatment for severe COVID-19 disease.
"Since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, the way that each individual responds differently to the infection has been closely studied. In our new study, we examined variations in the way individual cells reacted differently to the coronavirus and responded to antiviral treatment," said Ryan Langlois, PhD, senior author of the study, associate professor in the Department ...
PHILADELPHIA -- Past exposure to seasonal coronaviruses (CoVs), which cause the common cold, does not result in the production of antibodies that protect against the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, according to a study led by Scott Hensley, PhD, an associate professor of Microbiology at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.
Prior studies have suggested that recent exposure to seasonal CoVs protects against SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. However, research from Hensley's team, published in Cell, suggests that if there is such protection, it does not come from antibodies.
"We found that many people possessed antibodies that could bind to SARS-CoV-2 before the pandemic, but these antibodies could not prevent infections," Hensley said. ...
Researchers from the University of Basel have developed a virtual reality app for smartphones to reduce fear of heights. Now, they have conducted a clinical trial to study its efficacy. Trial participants who spent a total of four hours training with the app at home showed an improvement in their ability to handle real height situations.
Fear of heights is a widespread phenomenon. Approximately 5% of the general population experiences a debilitating level of discomfort in height situations. However, the people affected rarely take advantage of the available treatment options, such as exposure therapy, which involves putting the person in the anxiety-causing situation under the guidance of a professional. On the one hand, people ...
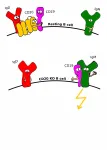
Rituximab, an anti-cancer drug targeting the membrane protein CD20, was the first approved therapeutic antibody against B tumor cells. Immunologists at the University of Freiburg have now solved a mystery about how it works. A team headed by Professor Dr. Michael Reth used cell cultures, healthy cells, and cells from cancer patients to investigate how CD20 organizes the nanostructures on the B cell membrane. If the protein is missing or Rituximab binds to it, the organization of the B cell surface changes. The resting B cell is activated in the process. The team has published the research in the journal PNAS as part of contributions by new members of the National Academy of Science.
B cells are white blood cells and part of the immune system. When they recognize ...
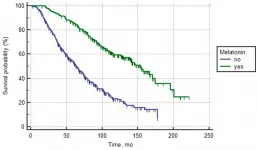
Oncotarget recently published "Melatonin increases overall survival of prostate cancer patients with poor prognosis after combined hormone radiation treatment" which reported that a retrospective study included 955 patients of various stages of prostate cancer who received combined hormone radiation treatment from 2000 to 2019. Comprehensive statistical methods were used to analyze the overall survival rate of PCa patients treated with melatonin in various prognosis groups.
The overall survival rate of PCa patients with favorable and intermediate prognoses treated or not treated ...
JACKSONVILLE, Fla. (February 10, 2021) - Brain volume, verbal IQ, and overall IQ are lower in children with Type 1 diabetes (T1D) than in children without diabetes, according to a new longitudinal study published in Diabetes Care, a journal of the American Diabetes Association. The nearly eight-year study, led by Nelly Mauras, MD, a clinical research scientist at Nemours Children's Health System in Jacksonville, Florida, and Allan Reiss MD, a Professor at the Stanford University School of Medicine in California, compared brain scans of young children who have T1D with those of non-diabetic children to assess the extent to which glycemic exposure may adversely affect the ...