INFORMATION:
Title: Discrimination between Invasive and In situ Melanomas Using a Convolutional Neural Network,
https://www.jaad.org/article/S0190-9622(21)00336-4/fulltext
Title (supplementary text about the ML algorithm): Supplemental material -- Discrimination between Invasive and In situ Melanomas Using a Convolutional Neural Network,
http://dx.doi.org/10.17632/y883xdgw86.1
Algorithm that performs as accurately as dermatologists
2021-02-12
(Press-News.org) A study has now been presented that boosts the evidence for using AI solutions in skin cancer diagnostics. With an algorithm they devised themselves, scientists at the University of Gothenburg show the capacity of technology to perform at the same level as dermatologists in assessing the severity of skin melanoma.
The study, published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, and its results are the work of a research group at the Department of Dermatology and Venereology at Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg.
The study was conducted at Sahlgrenska University Hospital in Gothenburg. Its purpose was, through machine learning (ML), to train an algorithm to determine whether skin melanoma is invasive and there is a risk of it spreading (metastatizing), or whether it remains at a growth stage in which it is confined to the epidermis, with no risk of metastasis.
The algorithm was trained and validated on 937 dermatoscopic images of melanoma, and subsequently tested on 200 cases. All the cases included were diagnosed by a dermatopathologist.
The majority of melanomas are found by patients rather than doctors. This suggests that, in most cases, diagnosis is relatively easy. Before surgery, however, it is often much more difficult to determine the stage the melanoma has reached.
To make the classifications more accurate, dermatologists use dermatoscopes -- instruments that combine a type of magnifying glass with bright illumination. In recent years, interest in using ML for skin tumor classifications has increased, and several publications have shown that ML algorithms can perform on par with, or even better than, experienced dermatologists.
The current study is now giving a further boost to research in this field. When the same classification task was performed by the algorithm on the one hand and seven independent dermatologists on the other, the result was a draw.
"None of the dermatologists significantly outperformed the ML algorithm," states Sam Polesie, a researcher at the University of Gothenburg and specialist doctor at Sahlgrenska University Hospital, who is the corresponding author of the study.
In a developed form, the algorithm could serve as support in the task of assessing the severity of skin melanoma before surgery. The classification affects how extensive an operation needs to be, and is therefore important for both the patient and the surgeon.
"The results of the study are interesting, and the hope is that the algorithm can be used as clinical decision support in the future. But it needs refining further, and prospective studies that monitor patients over time are necessary, too," Polesie concludes.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New study identifies the main genetic causes of autoimmune Addison's disease
2021-02-12
Novel genetic associations could pave the way for early interventions and personalized treatment of an incurable condition.
Scientists from the University of Bergen (Norway) and Karolinska Institutet (Sweden) have discovered the genes involved in autoimmune Addison's disease, a condition where the body's immune systems destroys the adrenal cortex leading to a life-threatening hormonal deficiency of cortisol and aldosterone.
Groundbreaking study
The rarity of Addison's disease has until now made scanning of the whole genome for clues to the disease's genetic origins difficult, as this method normally requires many thousands of study participants. However, by combining the world's two largest ...
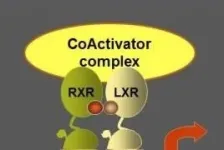
Antitumoral effects of LXR activation
2021-02-12
Tumor cells are able to avoid the attack of the immune system through several mechanisms. For instance, these can secrete factors that turn macrophages -cells in the immune system- into dual action agents that contribute to the tumor progress and will protect it from immune body defences: these become, thus, the tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs).
An article published in the journal Cancer Research describes a new molecular mechanism that counteracts the immunosupressive action of these macrophaes to boost tumor growth, and brings knowledge of potential interest for the design of future therapeutical options against cancer. The preclinical study is led by the tenure-track 2 lecturer Annabel Valledor, from the Faculty ...
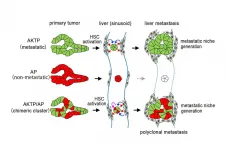
Going the distance--insights into how cancer cells spread
2021-02-12
Most tumors consist of a heterogenous mix of cells. Genetic mutations found only in some of these cells are known to aid with the spread and progression of cancer. However, oncologists often find that when tumors metastasize to distant organs, they retain this heterogenous nature--a phenomenon termed "polyclonal metastasis". The mechanism by which non-metastatic cells accompany the metastatic cells is ambiguous. Now, Masanobu Oshima and his research team have used mouse models to explain how non-metastatic cells begin their long commute.
The team has previously developed various cancerous mutants of mice and analyzed ...
Increasing hurricane intensity around Bermuda linked to rising ocean temperatures
2021-02-12
New research shows that hurricane maximum wind speeds in the subtropical Atlantic around Bermuda have more than doubled on average over the last 60 years due to rising ocean temperatures in the region.
Hurricanes intensify by extracting energy from the warm ocean surface via air-sea heat fluxes, so a warmer ocean can lead to more intense hurricanes.
Improving predictions of wind speeds from hurricanes will help determine the right level of response in advance of the storm and potentially limit the resulting damage in Bermuda.
Between 1955 and ...
Producing more sustainable hydrogen with composite polymer dots
2021-02-12
Hydrogen for energy use can be extracted in an environmentally friendly way from water and sunlight, using photocatalytic composite polymer nanoparticles developed by researchers at Uppsala University. In laboratory tests, these "polymer dots" showed promising performance and stability alike. The study has been published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
How we are to meet future demand for sustainable energy is a much-debated question. One feasible way to go is hydrogen, which can be produced from renewable resources: water and solar energy. But the process ...
Chemotherapy and hearing loss: Until now, an unquantified risk
2021-02-12
Cisplatin is one of the most effective chemotherapy agents, used in just under half of pediatric cancer cases. Permanent hearing loss is a common side effect of this medication, but until now, studies have been too small and too varied to accurately characterize this risk. Today in The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health, investigators at Children's Hospital Los Angeles published results of the largest study of cisplatin-induced hearing loss to date. The study establishes the first benchmarks for the prevalence of hearing loss, and reveals that the risk of hearing loss is affected not only by how much drug is given, but by how that drug is delivered--dosing schedules, complementary treatments, and more. These findings will allow oncologists to deliver more information ...
Mexico's poor have little luck obtaining opioids intended for palliative care
2021-02-12
If you're poor and terminally ill in southern Mexico, there's far less chance you'll get the painkillers you need for palliative care than your cousins in more prosperous regions, particularly those pharmacy-rich areas along Mexico-U.S. border, say UCLA researchers and colleagues who studied opioid dispensing levels across the country.
What's more, the researchers' paper in the journal The Lancet Public Health suggests it's likely that some of the opioids intended for Mexican citizens are ending up in American pockets.
Despite a Mexican government initiative launched in 2015 to improve access to prescription opioids among palliative care patients, the country has seen only a marginal increase in dispensing levels, and inequities in dispensing ...
New machine learning theory raises questions about nature of science
2021-02-12
A novel computer algorithm, or set of rules, that accurately predicts the orbits of planets in the solar system could be adapted to better predict and control the behavior of the plasma that fuels fusion facilities designed to harvest on Earth the fusion energy that powers the sun and stars.
The algorithm, devised by a scientist at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL), applies machine learning, the form of artificial intelligence (AI) that learns from experience, to develop the predictions. "Usually in physics, you make observations, create a theory based on those observations, and then use that theory to predict new observations," said PPPL physicist Hong Qin, author of a paper detailing ...
New discovery could pave the way for improved treatments for diabetes
2021-02-12
Monash University researchers have uncovered the barrier to β-cell (beta cell) regeneration that could pave the way for improved treatments for diabetes and diseases that involve organ and tissue damage.
The human body doesn't repair itself very well, with our liver the only organ that can regenerate efficiently. We have limited capacity to regenerate new cells or tissue after birth as the genes involved in development are switched off.
This process happens through DNA methylation, a biological process where chemicals (methyl groups) are written on DNA and modify the way the gene functions. ...
Applying quantum computing to a particle process
2021-02-12
A team of researchers at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) used a quantum computer to successfully simulate an aspect of particle collisions that is typically neglected in high-energy physics experiments, such as those that occur at CERN's Large Hadron Collider.
The quantum algorithm they developed accounts for the complexity of parton showers, which are complicated bursts of particles produced in the collisions that involve particle production and decay processes.
Classical algorithms typically used to model parton showers, such ...