(Press-News.org) Canadian researchers are the first to study how different patterns in the way older adults walk could more accurately diagnose different types of dementia and identify Alzheimer's disease.
A new study by a Canadian research team, led by London researchers from Lawson Health Research Institute and Western University, evaluated the walking patterns and brain function of 500 participants currently enrolled in clinical trials. Their findings are published today in Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association.
"We have longstanding evidence showing that cognitive problems, such as poor memory and executive dysfunction, can be predictors of dementia. Now, we're seeing that motor performance, specifically the way you walk, can help diagnose different types of neurodegenerative conditions," says Dr. Manuel Montero-Odasso, Scientist at Lawson and Professor at Western's Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry.
Dr. Montero-Odasso is world renowned for his research on the relationship between mobility and cognitive decline in aging. Leading the Mobility, Exercise and Cognition (MEC) team in London, he is pioneering novel diagnostic approaches and treatments to prevent and combat early dementia.
This study compared gait impairments across the cognitive spectrum, including people with Subjective Cognitive Impairment, Parkinson's Disease, Mild Cognitive Impairment, Alzheimer's disease, Lewy body dementia and Frontotemporal dementia, as well as cognitively healthy controls.
Four independent gait patterns were identified: rhythm, pace, variability and postural control. Only high gait variability was associated with lower cognitive performance and it identified Alzheimer's disease with 70 per cent accuracy. Gait variability means the stride-to-stride fluctuations in distance and timing that happen when we walk.
"This is the first strong evidence showing that gait variability is an important marker for processes happening in areas of the brain that are linked to both cognitive impairment and motor control," notes Dr. Frederico Perruccini-Faria, Research Assistant at Lawson and Postdoctoral Associate at Western's Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry, who is first author on the paper. "We've shown that high gait variability as a marker of this cognitive-cortical dysfunction can reliably identify Alzheimer's disease compared to other neurodegenerative disorders."
When cognitive-cortical dysfunction is happening, the person's ability to perform multiple tasks at the same time is impacted, such as talking while walking or chopping vegetables while chatting with family.
Having gait variability as a motor marker for cognitive decline and different types of conditions could allow for gait assessment to be used as a clinical test, for example having patients use wearable technology. "We see gait variability being similar to an arrhythmia. Health care providers could measure it with patients in the clinic, similar to how we assess heart rhythm with electrocardiograms," adds Dr. Montero-Odasso.
INFORMATION:
This study was primarily funded by the Canadian Consortium on Neurodegeneration in Aging (CCNA), a collaborative research program tackling the challenge of dementia and other neurodegenerative illnesses. The CCNA was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
MEDIA CONTACT: Laura Goncalves, Communications and External Relations, Lawson Health Research Institute, t. 519.685.8500 ext. 64059, c. 226-448-1525, laura.goncalves@lawsonresearch.com
ABOUT LAWSON HEALTH RESEARCH INSTITUTE
Lawson Health Research Institute is one of Canada's top hospital-based research institutes, tackling the most pressing challenges in health care. As the research institute of London Health Sciences Centre and St. Joseph's Health Care London, our innovation happens where care is delivered. Lawson research teams are at the leading-edge of science with the goal of improving health and the delivery of care for patients. Working in partnership with Western University, our researchers are encouraged to pursue their curiosity, collaborate often and share their discoveries widely. Research conducted through Lawson makes a difference in the lives of patients, families and communities around the world.
ABOUT WESTERN
Western delivers an academic experience second to none. Since 1878, The Western Experience has combined academic excellence with life-long opportunities for intellectual, social and cultural growth in order to better serve our communities. Our research excellence expands knowledge and drives discovery with real-world application. Western attracts individuals with a broad worldview, seeking to study, influence and lead in the international community.
ABOUT THE SCHULICH SCHOOL OF MEDICINE & DENTISTRY
The Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry at Western University is one of Canada's preeminent medical and dental schools. Established in 1881, it was one of the founding schools of Western University and is known for being the birthplace of family medicine in Canada. For more than 130 years, the School has demonstrated a commitment to academic excellence and a passion for scientific discovery.
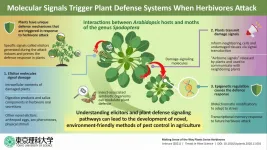
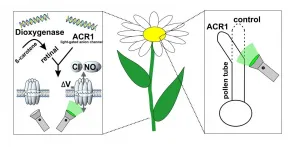
Nature has its way of maintaining balance. This statement rightly holds true for plants that are eaten by herbivores--insects or even mammals. Interestingly, these plants do not just silently allow themselves to be consumed and destroyed; in fact, they have evolved a defense system to warn them of predator attacks and potentially even ward them off. The defense systems arise as a result of inner and outer cellular signaling in the plants, as well as ecological cues. Plants have developed several ways of sensing damage; a lot of these involve the sensing of various "elicitor" molecules produced by either the predator ...
It is almost ten years since the scientific journal Science called optogenetics the "breakthrough of the decade". Put simply, the technique makes it possible to control the electrical activity of cells with pulses of light. With its help, scientists can gain new insights into the functioning of nerve cells, for example, and thus better understand neurological and psychiatric diseases such as depression and schizophrenia.
Established procedure on animal cells
In research on animal cells, optogenetics is now an established technique used in many fields. The picture is different in plant research: transferring the principle to plant cells and applying it widely has not been possible until now.
However, this has now changed: Scientists ...
Individual variation in the shape and structure of the Achilles tendon may influence our susceptibility to injury later in life, says a study published today in eLife.
The findings suggest that studying individual Achilles tendon shape (or 'morphology') could help with identifying patients at risk of injury and designing new, potentially personalised approaches for treating and preventing Achilles tendinopathy and similar conditions.
The Achilles tendon is the tissue that links the calf muscles to the heel bone. It is fundamental to our movement and athletic ability. Its unique structure, which combines three smaller sub-tendons, increases the efficiency of our movement by allowing individual control from connected muscles. For this control to occur, the ...
A drug that helps us to eat less could help the more than 650 million people around the world who live with obesity. One of the emerging drug candidates that interest researchers is the hormone GDF15 that, when given to rodents, lowers their appetite and body weight. New research from the University of Copenhagen finds that the body produces large amounts GDF15 during extended bouts of vigorous exercise, presumably as a physiological stress signal.
This finding highlights central differences between GDF15 given as a drug (pharmacology), and GDF15 released naturally in response to vigorous exercise (physiology). This is an important distinction ...
From 2015 to 2019, public school districts in the United States invested nearly $5 billion to upgrade their Wi-Fi networks, according to EducationSuperHighway. However, in the age of COVID-19-mandated virtual learning, millions of K-12 students still lack the minimal connectivity at home for digital learning.
In a new study from the University of Notre Dame, researchers quantify how school district connectivity increases test scores, but underscore the dark side of technology -- increased behavior problems.
A $600,000 increase in annual internet access spending produces a financial gain of approximately $820,000 to $1.8 million, alongside losses from disciplinary problems totaling $25,800 to $53,440, according to new research from Yixing Chen, an ...
Researchers at the University of Chicago, the University of Birmingham, and Bournemouth University have uncovered evidence that physical embodiment can occur without the sense of touch, thanks to a study involving two participants who lack the ability to feel touch. The research was published on Feb. 12 in END ...
Coral reefs have thrived for millions of years in their shallow ocean water environments due to their unique partnerships with the algae that live in their tissues. Corals provide a safe haven and carbon dioxide while their algal symbionts provide them with food and oxygen produced from photosynthesis. Using the corals Orbicella annularis and Orbicella faveolate in the southern Caribbean, researchers at the Carl R. Woese Institute for Genomic Biology (IGB) have improved our ability to visualize and track these symbiotic interactions in the face of globally warming sea surface temperatures and ...
In coming decades as coastal communities around the world are expected to encounter sea-level rise, the general expectation has been that people's migration toward the coast will slow or reverse in many places.
However, new research co-authored by Princeton University shows that migration to the coast could actually accelerate in some places despite sea-level change, contradicting current assumptions.
The research, published in Environmental Research Letters, uses a more complex behavioral decision-making model to look at Bangladesh, whose coastal zone is at high risk. They found job opportunities are most abundant in coastal cities across Bangladesh, attracting more ...
It's no secret that the risk related to the coronavirus (COVID-19) increases with age, making older adults more vulnerable than younger people.
Less examined has been effects on pregnancy and birthing. According to a new study led by Sarah DeYoung, assistant professor in the Department of Sociology and Criminal Justice, and Michaela Mangum, a master's student in disaster science and management, the pandemic causes additional stress for people who were pregnant or gave birth during the pandemic. The stress was especially prevalent if the person ...
A new study from the Smidt Heart Institute at Cedars-Sinai shows that women have a lower “normal” blood pressure range compared to men. The findings were published today in the peer-reviewed journal Circulation.Currently, established blood pressure guidelines state that women and men have the same normal healthy range of blood pressure. But the new research shows there are differences in normal blood pressure between the sexes.“Our latest findings suggest that this one-size-fits-all approach to considering blood pressure may be detrimental to a woman’s health,” ...