Mimicking a chronic immune response changes the brain
Researchers at the University of Tsukuba in Japan show that simulating an overactive autoimmune response in mice leads to changes in the hippocampal region of the brain
2021-02-17
(Press-News.org) Tsukuba, Japan -- As March comes around, many people experience hay fever. As excessive immune responses go, most would admit that hay fever really isn't that bad. At the other end of the spectrum are severely debilitating autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis. A common thread in all these conditions are cytokines, molecules that cause inflammation. Recent research by the University of Tsukuba sheds light on the effect of excessive cytokines on neuronal and glial cells in the brain.
Researchers led by Professor Yosuke Takei and Assistant Professor Tetsuya Sasaki at the University of Tsukuba in Japan have been studying an important cytokine called interleukin (IL)-17A. Their recent study shows that chronic increases in the levels of IL-17A circulating in mouse blood can reduce the microglia activity in one part of the brain's hippocampus. This might explain why it's related to several neurological diseases.
The researchers focused on IL-17A because it is known to be involved in neurological autoimmune disorders as well as disorders of the mind. "In addition to being linked to multiple sclerosis," explains Sasaki, "recent reports show that IL-17A is also a factor in Alzheimer's disease, schizophrenia, and autism spectrum disorder." To study how chronically high levels of IL-17A can affect the brain, the team used their knowledge of how IL-17A is made naturally in the body.
The researchers focused on immune cells called helper T-cells. Helper T-cells come in many varieties, each one making its own cytokine, and each one created from a generic helper T-cell. "Our strategy," says Sasaki, "was to induce more generic helper T-cells to become the kind that produce IL-17A." With more of these helper T-cells, called Th17, the mutant mice did indeed produce more IL-17A in the gut, which spread throughout the body in the blood.
IL-17A is known to interact with two kinds of glial cells in the nervous system, astrocytes and microglia. The researchers found that chronically high IL-17A led to reduced activity and density of microglia in one region of the hippocampus, a part of the brain that is needed for learning and forming memories. In contrast, astrocytes in the brain did not differ between the mutant and control mice. Thus, there was reason to believe that chronic IL-17A inflammation would affect cognition, specifically memory. Surprisingly, spatial memory seemed to be just as good in the mutant mice as in the control mice.
"These mutant mice can be used in future studies as a model for chronic IL-17A-related inflammation," says Takei. "Further neuronal and behavioral testing will help us begin to understand IL-17A's role in a range of debilitating neurological disorders."
INFORMATION:
The article, Effects of RORγt overexpression on the murine central nervous system," was published in Neuropsychopharmacology Reports at DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/npr2.12162.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-17
Meteorologists frequently study precipitation events using radar imagery generated at both ground level and from satellite data. Radar sends out electromagnetic waves that "bounce" off ice or water droplets suspended in the air. These waves quickly return to the radar site in a process named "backscattering." Scientists have observed that backscattering reaches its peak during the melting process as water falls through the atmosphere. High backscattering typically results in warm color returns on a radar displays, indicating heavy precipitation.
However, recent case studies noted that partially frozen droplets seem ...
2021-02-17
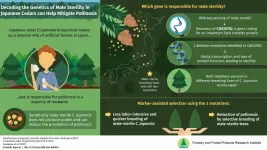
Cryptomeria japonica, or the Japanese cedar, is highly revered as the national tree of Japan. Locally known as "sugi," it covers over 4.5 million hectares of land, accounting for nearly half of Japan's artificial forests. However, it is also notorious for causing hay fever, with a good 26.5% of Japan's population reporting cedar pollen allergies in 2008. Over the past years, pollen allergy caused by this conifer has become a widespread social issue among Japanese residents, with many having to avoid going outdoors during pollen season.
As sterile trees cannot produce and release functional pollen, it is believed that breeding of male-sterile cedar trees could be crucial in reducing the pollen released ...
2021-02-17
A team of MedUni Vienna researchers led by Johannes A. Schmid at the Center for Physiology and Pharmacology, Institute of Vascular Biology and Thrombosis Research, has managed to identify a previously unknown molecular connection between an inflammatory signalling molecule and one of the main oncogenes. The study has been published in the leading journal "Molecular Cancer".
Johannes A. Schmid's working group at the Center for Physiology and Pharmacology, Institute of Vascular Biology and Thrombosis Research, already has many years' experience in the molecular ...
2021-02-17
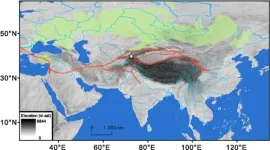
The Silk Road was the most elaborate network of trade routes in the ancient world, linking ancient populations in East Asia to those in southwest Asia, via Central Asia. These trade routes fostered the spread of ideas, religions, and technologies over the past 2,000 years. Before the establishment of organized exchange, starting around the time of the Chinese Han Dynasty (2,223 years ago), a process of trans-Eurasian exchange was already underway through the river valleys and oases of Central Asia. The establishment of populations in the oases of the Taklimakan Desert ...
2021-02-17
Cardiovascular system can be regarded as a mechanical system centered on the heart. Blood flow in the vascular system, hemodynamics factors within the vasculature contain wall shear stress, circumferential wall tensile stress and hydrostatic pressure. Mechanical forces play an important role in vasculature and circulation, such as rapid regulation of vascular wall elasticity, administration of vascular remodeling, and the formation of arteriosclerotic lesions. Stress stimulation within the physiological range enables cells in dynamic balance to maintain homeostasis of vascular morphology, structure and function. Inversely, abnormal stresses stimulation, such as low shear stress, disturbed shear stress and high tensile strain, can break this balance ...
2021-02-17
More people than expected ended their own lives in 2020 in Japan, overturning a decadelong slow decline in the nation's annual number of suicides, according to a new analysis by public health experts at the University of Tokyo. The increase in suicides was especially pronounced among women younger than 30, potentially due to the COVID-19 pandemic's disproportionate effect on part-time and travel industry employees.
"This trend of increased suicides among young women and university and high school students is very different from before COVID-19. Before COVID-19, if suicides increased, we would expect more deaths of middle-aged men," said Dr. Haruka Sakamoto, an expert in public health at the University of Tokyo and first author of the research publication in the Journal of the ...
2021-02-17
After seven years of intense research, a research group from Aarhus University has succeeded - through an interdisciplinary collaboration - in understanding why a very extended structure is important for an essential protein from the human immune system. The new results offer new opportunities for adjusting the activity of the immune system both up and down. Stimulation is interesting in relation to cancer treatment, while inhibition of the immune system is used in treatment of autoimmune diseases.
In our bloodstream and tissues, the complement system acts as one of the very first defense mechanisms against pathogenic organisms. When these are ...
2021-02-17
People with asthma in the most deprived areas are 50% more likely to be admitted to hospital and to die from asthma compared with those in the least deprived areas, a new five-year study of over 100,000 people in Wales has revealed.
Those from more deprived backgrounds were also found to have a poor balance of essential asthma medications that help prevent asthma attacks.
The new research, published in the journal PLOS Medicine, was conducted by Swansea University's Wales Asthma Observatory in collaboration with Asthma UK Centre for Applied Research and Liverpool University, and found ...
2021-02-17
SAN FRANCISCO, CA--February 16, 2021--In people with central nervous system (CNS) lymphoma, cancerous B cells--a type of white blood cell--accumulate to form tumors in the brain or spinal cord, often in close proximity to blood vessels. This disease is quite rare, but individuals who are affected have limited treatment options and often experience recurrence.
Previous research has linked the severity of CNS lymphoma to abnormal leaks in the blood-brain barrier, a protective system that allows some substances to pass from the bloodstream to the brain, while blocking others. However, the specific molecular details of this link have been murky.
Now, Gladstone researchers have ...
2021-02-17
Tsukuba, Japan - It's tough out there in the sea, as the widespread loss of complex marine communities is testament to. Researchers from Japan have discovered that ocean acidification favors degraded turf algal systems over corals and other algae, thanks to the help of feedback loops.
In a study published this month in Communications Biology, researchers from the University of Tsukuba have revealed that ocean acidification and feedback loops stabilize degraded turf algal systems, limiting the recruitment of coral and other algae.
Oceans are undergoing widespread changes as a result of human activities. These changes take the form of regime shifts - major, sudden and persistent changes in ecosystem structure and function. An example is the replacement of coral reefs and kelp ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Mimicking a chronic immune response changes the brain
Researchers at the University of Tsukuba in Japan show that simulating an overactive autoimmune response in mice leads to changes in the hippocampal region of the brain