Platelets may play key role in development of lupus
2021-02-17
(Press-News.org) Québec City, February 17, 2021 - Platelets may play a key role in the development of lupus, according to a study published today by researchers at Université Laval and CHU de Québec-Université Laval Research Centre. Extracellular DNA circulating in the blood of patients with lupus causes the inflammatory reaction associated with the disease. The researchers have shown that this DNA comes in part from the platelets, better known for their role in coagulating blood. The details of the breakthrough have been published today in Science Translational Medicine and could lead to a better understanding of the disease and more effective treatment.
"Lupus is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of various body parts, particularly the joints, skin, brain, and kidneys," explained lead author Éric Boilard, professor at the Université Laval Faculty of Medicine and researcher at CHU de Québec-Université Laval Research Centre. "It strikes 40 people per 100,000, frequently between the ages of 20 and 40, and is nine times more prevalent in women than in men. Lupus presents in a variety of ways and can be difficult to diagnose."
One common denominator of severe forms of the disease is the presence of anti-DNA antibodies in the blood. "When DNA circulates freely in the blood, antigen-antibody complexes form and accumulate in the tissues where the lupus presents. Until now, we didn't know exactly where this genetic material was coming from," said Professor Boilard, who is also a researcher at the ARThrite research centre.
In collaboration with fellow professor and clinical researcher Paul R. Fortin, Boilard's team analyzed blood samples from 74 patients with lupus and discovered that the platelets were the source of the extracellular DNA. "To be precise, the DNA is present in the platelet mitochondria. Most of the DNA was actually still inside the mitochondria in the blood we studied. The body produces antibodies against the mitochondria and the mitochondrial DNA because it considers them foreign bodies," explained Professor Boilard.
When the platelets are activated, the mitochondria and their DNA are released. "But this activation does not seem involved in normal platelet functions such as preventing bleeding," said Boilard. "If we can figure out how to interrupt this activation process, we can prevent the mitochondria and the mitochondrial DNA from being released, which will reduce the autoimmune reaction we see with this disease."
INFORMATION:
The article published in Science Translational Medicine is coauthored by Imene Melki, Isabelle Allaeys, Nicolas Tessandier, Tania Lévesque, Nathalie Cloutier, Audrée Laroche, Nathalie Vernoux, Yann Becker, Hadrien Benk-Fortin, Anne Zufferey, Emmanuelle Rollet-Labelle, Marc Pouliot, Guy Poirier, Natacha Patey, Clemence Belleannee, Denis Soulet, Steven E. McKenzie, Alain Brisson, Marie-Eve Tremblay, Christian Lood, Paul R. Fortin, and Éric Boilard.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-17
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- In a new study, Penn State researchers demonstrated that facilitating researcher-policymaker interactions in rapid response processes can influence both how legislators think about policy issues and how they draft legislation.
Penn State professors Max Crowley, associate professor of human development and family studies, and public policy, and Taylor Scott, assistant research professor in the Edna Bennett Pierce Prevention Research Center, co-direct the Research-to-Policy Collaboration, which connects members of Congress with researchers who synthesize evidence about family and child policy in a timely and digestible ...
2021-02-17
Scientists from the Stanley Manne Children's Research Institute at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago demonstrated that a nanotherapy reduces intestinal inflammation and shrinks lesions in a rodent model of severe Crohn's disease. This approach could become an alternative to biologic antibody therapies that carry many side effects, including increased risk of certain cancers. It might also prevent the need for surgery in the future. Findings were published in the journal Advanced Therapeutics.
Crohn's disease is an inflammatory bowel disease characterized by chronic inflammation of the digestive tract, most often in the small intestine. ...
2021-02-17
In response to the increase in opioid overdose deaths in the United States, many states have implemented supply-controlling and harm-reduction policy measures aimed at reducing those deaths. But a recent study from Indiana University found the policies may have had the unintended consequence of motivating those with opioid use disorders to switch to alternative illicit substances, leading to higher overdose mortality.
"Literature from public health to social sciences has presented mixed and contradictory findings on the impact of opioid policies on various opioid ...
2021-02-17
INFORMS Journal on Applied Analytics Key Takeaways:
Although waiting times in walk-up clinics are shorter, people preferred the convenience of drive-through clinics.
People believe drive-through clinics are safer, more convenient and less contagious.
You can vaccinate a large number of people without a lot of waiting and confusion using a drive-through clinic.
CATONSVILLE, MD, February 17, 2021 - Policymakers at all levels of government are racing to vaccinate hundreds of millions of people to save lives and blunt the deadly COVID-19 pandemic. New research published ...
2021-02-17
Researchers have developed a new tool for addressing disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) - a blood disorder that proves fatal in many patients. The technology has not yet entered clinical trials, but in vivo studies using rat models and in vitro models using blood from DIC patients highlight the tech's potential.
"DIC basically causes too much clotting and too much bleeding at the same time," says Ashley Brown, corresponding author of a paper on the work. "Small blood clots can form throughout the circulatory system, often causing organ damage. And because this taxes the body's supply of clotting factors, patients also experience excess bleeding. Depending on ...
2021-02-17
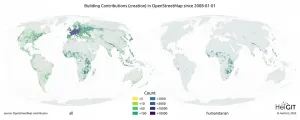
In recent years, free digital world maps like OpenStreetMap (OSM) have become a vital instrument to support humanitarian missions over the entire world. In disaster management as well as the implementation of the United Nations Sustainability Development Goals (SDGs), geodata compiled by the volunteer mapper community open up new possibilities to coordinate aid interventions and carry out sustainability projects. The mapping data are collected either locally using a smartphone and GPS device or on the basis of satellite images. An international team of researchers led by geoinformation ...
2021-02-17
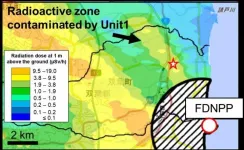
The 10 year anniversary of the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident occurs in March. Work just published in the Journal 'Science of the Total Environment' documents new, large (> 300 micrometers), highly radioactive particles that were released from one of the damaged Fukushima reactors.
Particles containing radioactive cesium (134+137Cs) were released from the damaged reactors at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) during the 2011 nuclear disaster. Small (micrometer-sized) particles (known as CsMPs) were widely distributed, reaching as far as Tokyo. CsMPs have been the subject of many studies in recent years. However, it recently became apparent that larger (>300 micrometers) Cs-containing particles, with much higher levels of activity (~ 105 Bq), were also ...
2021-02-17
The brain's neural activity is irregular, changing from one moment to the next. To date, this apparent "noise" has been thought to be due to random natural variations or measurement error. However, researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Human Development have shown that this neural variability may provide a unique window into brain function. In a new Perspective article out now in the journal Neuron, the authors argue that researchers need to focus more on neural variability to fully understand how behavior emerges from the brain.
When neuroscientists investigate the brain, its activity seems to vary all the time. Sometimes activity is higher or lower, rhythmic or irregular. Whereas averaging brain activity ...
2021-02-17
The researchers analysed how Spanish children and adolescents get to school, based on studies examining the commuting patterns of 36,781 individuals over a 7-year period (2010-2017)
Researchers from the University of Granada (UGR) have conducted the most comprehensive study to date on how Spanish children and young people get to school each day, to determine the active commuting rate.
The results showed that, between 2010 and 2017, in the region of 60% of Spanish children and adolescents actively commuted to school, with no significant variations being observed during this period.
The study, which was recently ...
2021-02-17
Our brains are complicated webs of billions of neurons, constantly transmitting information across synapses, and this communication underlies our every thought and movement.
But what happens to the circuit when a neuron dies? Can other neurons around it pick up the slack to maintain the same level of function?
Indeed they can, but not all neurons have this capacity, according to new research from the University of Chicago. By studying several neuron pairs that innervate distinct muscles in a fruit fly model, researchers found that some neurons compensate for ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Platelets may play key role in development of lupus