INFORMATION:
Self-healing concrete for regions with high moisture and seismic activity
2021-02-17
(Press-News.org) Preparing regular concrete scientists replaced ordinary water with water concentrate of bacteria Bacillus cohnii, which survived in the pores of cement stone. The cured concrete was tested for compression until it cracked, then researchers observed how the bacteria fixed the gaps restoring the strength of the concrete. The engineers of the Polytechnic Institute of Far Eastern Federal University (FEFU), together with colleagues from Russia, India, and Saudi Arabia, reported the results in Sustainability journal.
During the experiment, bacteria activated when gained access to oxygen and moisture, which occurred after the concrete cracked under the pressure of the setup. The "awakened" bacteria completely repaired fissures with a width of 0.2 to 0.6 mm within 28 days. That is due to microorganisms released a calcium carbonate (CaCO3), a product of their life that crystallized under the influence of moisture. After 28 days of self-healing experimental concrete slabs retrieved their original compressive strength. In the renewed concrete, the bacteria "fell asleep" again.
"Concrete remains the world's number one construction material because it is cheap, durable, and versatile. However, any concrete gets cracked over time because of various external factors, including moisture and repetitive freezing/thawing cycles, the quantity of which in the Far East of Russia, for example, is more than a hundred per year. Concrete fissuring is almost irreversible process that can jeopardize the entire structure." Says engineer Roman Fediuk, FEFU professor. "What we have accomplished in our experiment aligns with international trends in construction. There is pressing demand for such "living" materials with the ability to self-diagnose and self-repair. It's very important that bacteria healed small fissures-forerunners of serious deep cracks that would be impossible to recover. Thanks to bacteria working in the concrete, one can reduce or avoid at all technically complex and expensive repair procedures."
Spores of Bacillus cohnii capable of staying alive in concrete for up to two hundred years and, theoretically, can extend the lifespan of the structure for the same period. This is almost 4 times more than the 50-70 years of conventional concrete service life.
Self-healing concrete is most relevant for construction in seismically risky areas, where small fissures appear in buildings after earthquakes of a modest magnitude, and in areas with high humidity and high rainfall where a lot of oblique rain falls on the vertical surfaces of buildings. Bacteria in concrete also fill the pores of the cement stone making them smaller and less water gets inside the concrete structure.
Scientists have cultivated the bacteria Bacillus cohnii in the laboratory using a simple agar pad and culture medium, forcing them to survive in the conditions of the pores of the cement stone and to release the desired "repair" composition. Fissures healing was assessed using a microscope. The chemical composition of the bacteria repairing life product was studied via electron microscopy and X-ray images.
Next, the scientists plan to develop reinforced concrete, further enhancing its properties with the help of different types of bacteria. That should speed up the processes of material self-recovery.
A scientific school of the scientific school of geomimetics run at FEFU. Engineers follow the principle of nature mimicking in the development of composites for special structures and civil engineering. Concrete, as conceived by the developers, should have the strength and properties of natural stone. The foundations of geomimetics were laid by Professor Valery Lesovik from V.G. Shukhov BSTU, Corresponding Member of the Russian Academy of Architecture and Construction Sciences.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Vets' depression, social support & psychological resilience play role in later well being
2021-02-17
(Boston)--Veterans who experienced the combination of low depression, high social support and high psychological resilience as they left military service were most likely to report high well-being a year later.
Neither demographic and military characteristics nor trauma history emerged as strong predictors of veterans' well-being when considered in the context of other factors. Although most predictors were similar for women and men, depression was a stronger predictor of women's well-being.
Every year, more than 200,000 U.S. service members transition out of the military. Although most military veterans can be expected ...
Platelets may play key role in development of lupus
2021-02-17
Québec City, February 17, 2021 - Platelets may play a key role in the development of lupus, according to a study published today by researchers at Université Laval and CHU de Québec-Université Laval Research Centre. Extracellular DNA circulating in the blood of patients with lupus causes the inflammatory reaction associated with the disease. The researchers have shown that this DNA comes in part from the platelets, better known for their role in coagulating blood. The details of the breakthrough have been published today in Science ...
Helping Congress get the most from research
2021-02-17
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- In a new study, Penn State researchers demonstrated that facilitating researcher-policymaker interactions in rapid response processes can influence both how legislators think about policy issues and how they draft legislation.
Penn State professors Max Crowley, associate professor of human development and family studies, and public policy, and Taylor Scott, assistant research professor in the Edna Bennett Pierce Prevention Research Center, co-direct the Research-to-Policy Collaboration, which connects members of Congress with researchers who synthesize evidence about family and child policy in a timely and digestible ...
New potential therapy for Crohn's disease in children
2021-02-17
Scientists from the Stanley Manne Children's Research Institute at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago demonstrated that a nanotherapy reduces intestinal inflammation and shrinks lesions in a rodent model of severe Crohn's disease. This approach could become an alternative to biologic antibody therapies that carry many side effects, including increased risk of certain cancers. It might also prevent the need for surgery in the future. Findings were published in the journal Advanced Therapeutics.
Crohn's disease is an inflammatory bowel disease characterized by chronic inflammation of the digestive tract, most often in the small intestine. ...
IU study finds unintended consequences of state, opioid policies
2021-02-17
In response to the increase in opioid overdose deaths in the United States, many states have implemented supply-controlling and harm-reduction policy measures aimed at reducing those deaths. But a recent study from Indiana University found the policies may have had the unintended consequence of motivating those with opioid use disorders to switch to alternative illicit substances, leading to higher overdose mortality.
"Literature from public health to social sciences has presented mixed and contradictory findings on the impact of opioid policies on various opioid ...
New research finds drive-through mass-vaccination clinics could alter COVID-19 trajectory
2021-02-17
INFORMS Journal on Applied Analytics Key Takeaways:
Although waiting times in walk-up clinics are shorter, people preferred the convenience of drive-through clinics.
People believe drive-through clinics are safer, more convenient and less contagious.
You can vaccinate a large number of people without a lot of waiting and confusion using a drive-through clinic.
CATONSVILLE, MD, February 17, 2021 - Policymakers at all levels of government are racing to vaccinate hundreds of millions of people to save lives and blunt the deadly COVID-19 pandemic. New research published ...
New tech aims to tackle 'disseminated intravascular coagulation' blood disorder
2021-02-17
Researchers have developed a new tool for addressing disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) - a blood disorder that proves fatal in many patients. The technology has not yet entered clinical trials, but in vivo studies using rat models and in vitro models using blood from DIC patients highlight the tech's potential.
"DIC basically causes too much clotting and too much bleeding at the same time," says Ashley Brown, corresponding author of a paper on the work. "Small blood clots can form throughout the circulatory system, often causing organ damage. And because this taxes the body's supply of clotting factors, patients also experience excess bleeding. Depending on ...
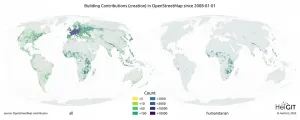
Global mapping projects aid humanitarian organisations
2021-02-17
In recent years, free digital world maps like OpenStreetMap (OSM) have become a vital instrument to support humanitarian missions over the entire world. In disaster management as well as the implementation of the United Nations Sustainability Development Goals (SDGs), geodata compiled by the volunteer mapper community open up new possibilities to coordinate aid interventions and carry out sustainability projects. The mapping data are collected either locally using a smartphone and GPS device or on the basis of satellite images. An international team of researchers led by geoinformation ...
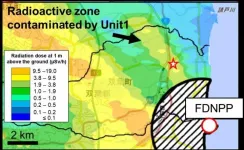
New highly radioactive particles found in Fukushima
2021-02-17
The 10 year anniversary of the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident occurs in March. Work just published in the Journal 'Science of the Total Environment' documents new, large (> 300 micrometers), highly radioactive particles that were released from one of the damaged Fukushima reactors.
Particles containing radioactive cesium (134+137Cs) were released from the damaged reactors at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) during the 2011 nuclear disaster. Small (micrometer-sized) particles (known as CsMPs) were widely distributed, reaching as far as Tokyo. CsMPs have been the subject of many studies in recent years. However, it recently became apparent that larger (>300 micrometers) Cs-containing particles, with much higher levels of activity (~ 105 Bq), were also ...
How the 'noise' in our brain influences our behavior
2021-02-17
The brain's neural activity is irregular, changing from one moment to the next. To date, this apparent "noise" has been thought to be due to random natural variations or measurement error. However, researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Human Development have shown that this neural variability may provide a unique window into brain function. In a new Perspective article out now in the journal Neuron, the authors argue that researchers need to focus more on neural variability to fully understand how behavior emerges from the brain.
When neuroscientists investigate the brain, its activity seems to vary all the time. Sometimes activity is higher or lower, rhythmic or irregular. Whereas averaging brain activity ...