(Press-News.org) A survey by a Boston University researcher of nearly 33,000 college students across the country reveals the prevalence of depression and anxiety in young people continues to increase, now reaching its highest levels, a sign of the mounting stress factors due to the coronavirus pandemic, political unrest, and systemic racism and inequality.
"Half of students in fall 2020 screened positive for depression and/or anxiety," says END
Depression, anxiety, loneliness are peaking in college students
Nationwide study, co-led by BU researcher Sarah Ketchen Lipson, reveals a majority of students say mental health has impacted their academic performance
2021-02-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Direct cloning method CAPTUREs novel microbial natural products
2021-02-19
Microorganisms possess natural product biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) that may harbor unique bioactivities for use in drug development and agricultural applications. However, many uncharacterized microbial BGCs remain inaccessible. Researchers at University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign previously demonstrated a technique using transcription factor decoys to activate large, silent BGCs in bacteria to aid in natural product discovery.
Now, they have developed a direct cloning method that aims to accelerate large-scale discovery of novel natural products. Their findings are reported in the journal Nature Communications.
Named Cas12a assisted precise targeted cloning using in vivo Cre-lox recombination (CAPTURE), ...
Time-lapse reveals the hidden dance of roots
2021-02-19
DURHAM, N.C. -- Duke researchers have been studying something that happens too slowly for our eyes to see. A team in biologist Philip Benfey's lab wanted to see how plant roots burrow into the soil. So they set up a camera on rice seeds sprouting in clear gel, taking a new picture every 15 minutes for several days after germination.
When they played their footage back at 15 frames per second, compressing 100 hours of growth into less than a minute, they saw that rice roots use a trick to gain their first foothold in the soil: their growing tips make ...
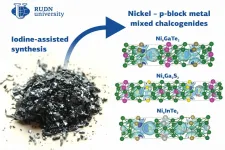
RUDN University chemist used iodine to synthesize new chalcogenides
2021-02-19
A chemist from RUDN University, working with a group of colleagues, synthesized three new chalcogenides (compounds that contain metals and elements from group 16 of the periodic table). The team suggested an unusual approach to synthesis that was based on iodine. An article about the work was published in the Dalton Transactions journal.
Chalcogens are elements of group 16 of the periodic table that include oxygen, sulfur, selenium, tellurium, polonium, and livermorium--an artificial radioactive element. Chalcogenides are compounds of chalcogens with metals that are used as photosensitive ...
Call to action for research ethics in the time of COVID-19 and BLM
2021-02-19
Several University of Illinois Chicago faculty members have addressed the issue of how to ethically conduct research with Black populations.
In their paper "Ethics of Research at the Intersection of COVID-19 and Black Lives Matter: A Call to Action," authors Natasha Crooks, an assistant professor, Phoenix Matthews, a professor, both of the UIC College of Nursing, and Geri Donenberg, director of the Center for Dissemination and Implementation Science at the UIC College of Medicine, highlight the historical issues that impact research involving Black populations. They also provide recommendations for researchers to ethically engage Black populations in research. ...
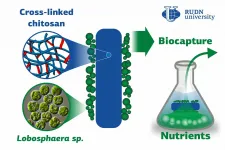
Biotechnologists developed an effective technology for nutrient biocapture from wastewater
2021-02-19
Biotechnologists from RUDN University in collaboration with Lomonosov MSU and Kurchatov institute made an important contribution to the technology of phosphate and nitrate biocapture from wastewater using Lobosphaera algae fixed on the filters.The biomass obtained in the course of this process can be used as a fertilizer. The results of the study were published in the Journal of Water Process Engineering.
Phosphates and nitrates get to the wastewater together with industrial and household waste, especially detergents. Both substances are parts of phosphorus and nitrogen chemical cycles. However, these cycles are disturbed by human activity, as the growing amounts of phosphates and nitrates cannot be processed by water ecosystems. As a result, these substances turn from useful nutrients ...
LSU Health study finds psychosocial factors may drive peritoneal dialysis patient dropout
2021-02-19
New Orleans, LA - A retrospective study conducted by LSU Health New Orleans reports that contrary to previous research, most patients who drop out of peritoneal dialysis may do so for psychosocial reasons. The findings are published in The American Journal of the Medical Sciences, available here. The paper inspired a companion editorial, available here.
The research team evaluated the reasons that 27 of the 83 patients enrolled in the peritoneal dialysis program withdrew between 2016 and 2018. Twenty-four or 86% were African American. They found that psychosocial factors, including mental health illness such as anxiety and depression, loss of support networks, or inability to tolerate ...
Study reveals energy sources supporting coral reef predators
2021-02-19
Since Charles Darwin's day, the abundance of life on coral reefs has been puzzling, given that most oceanic surface waters in the tropics are low in nutrients and unproductive.
But now research, led by Newcastle University and published in in the journal Science Advances, has confirmed that the food web of a coral reef in the Maldives relies heavily on what comes in from the open ocean.
The team found that these offshore resources contribute to more than 70% of reef predator diets, the rest being derived from reef associated sources.
Led by Dr Christina Skinner, now based at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, the researchers included collaborators from Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (USA), Banyan Tree Marine ...
Sounding rocket CLASP2 elucidates solar magnetic field
2021-02-19
Cooperative operations between a solar observation satellite and a sounding-rocket telescope have measured the magnetic field strength in the photosphere and chromosphere above an active solar plage region. This is the first time that the magnetic field in the chromosphere has been charted all the way up to its top. This finding brings us closer to understanding how energy is transferred between layers of the Sun.
Despite being the brightest object in the sky, the Sun still holds many mysteries for astronomers. It is generally believed that magnetic fields play an important role in heating the solar corona, but the details of the process are still unclear. To solve this mystery it is important to understand the magnetic field in the chromosphere, which is sandwiched ...
New technology enables predictive design of engineered human cells
2021-02-19
Northwestern University synthetic biologist Joshua Leonard used to build devices when he was a child using electronic kits. Now he and his team have developed a design-driven process that uses parts from a very different kind of toolkit to build complex genetic circuits for cellular engineering.
One of the most exciting frontiers in medicine is the use of living cells as therapies. Using this approach to treat cancer, for example, many patients have been cured of previously untreatable disease. These advances employ the approaches of synthetic biology, a growing ...
The CLASP2 space experiment achieves an unprecedented map of the Sun's magnetic field
2021-02-19
Every day space telescopes provide spectacular images of the solar activity. However, their instruments are blind to its main driver: the magnetic field in the outer layers of the solar atmosphere, where the explosive events that occasionally affect the Earth occur. The extraordinary observations of the polarization of the Sun's ultraviolet light achieved by the CLASP2 mission have made it possible to map the magnetic field throughout the entire solar atmosphere, from the photosphere until the base of the extremely hot corona. This investigation, published today in the journal Science Advances, has been carried out by the international team responsible for this suborbital experiment, which includes several scientists of the POLMAG group of the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New tool reveals the secrets of HIV-infected cells
HMH scientists calculate breathing-brain wave rhythms in deepest sleep
Electron microscopy shows ‘mouse bite’ defects in semiconductors
Ochsner Children's CEO joins Make-A-Wish Board
Research spotlight: Exploring the neural basis of visual imagination
Wildlife imaging shows that AI models aren’t as smart as we think
Prolonged drought linked to instability in key nitrogen-cycling microbes in Connecticut salt marsh
Self-cleaning fuel cells? Researchers reveal steam-powered fix for ‘sulfur poisoning’
Bacteria found in mouth and gut may help protect against severe peanut allergic reactions
Ultra-processed foods in preschool years associated with behavioural difficulties in childhood
A fanged frog long thought to be one species is revealing itself to be several
Weill Cornell Medicine selected for Prostate Cancer Foundation Challenge Award
Largest high-precision 3D facial database built in China, enabling more lifelike digital humans
SwRI upgrades facilities to expand subsurface safety valve testing to new application
Iron deficiency blocks the growth of young pancreatic cells
Selective forest thinning in the eastern Cascades supports both snowpack and wildfire resilience
A sea of light: HETDEX astronomers reveal hidden structures in the young universe
Some young gamers may be at higher risk of mental health problems, but family and school support can help
Reduce rust by dumping your wok twice, and other kitchen tips
High-fat diet accelerates breast cancer tumor growth and invasion
Leveraging AI models, neuroscientists parse canary songs to better understand human speech
Ultraprocessed food consumption and behavioral outcomes in Canadian children
The ISSCR honors Dr. Kyle M. Loh with the 2026 Early Career Impact Award for Transformative Advances in Stem Cell Biology
The ISSCR honors Alexander Meissner with the 2026 ISSCR Momentum Award for exceptional work in developmental and stem cell epigenetics
The ISSCR honors stem cell COREdinates and CorEUstem with the 2026 ISSCR Public Service Award
Minimally invasive procedure effectively treats small kidney cancers
SwRI earns CMMC Level 2 cybersecurity certification
Doctors and nurses believe their own substance use affects patients
Life forms can planet hop on asteroid debris – and survive
Sylvia Hurtado voted AERA President-Elect; key members elected to AERA Council
[Press-News.org] Depression, anxiety, loneliness are peaking in college studentsNationwide study, co-led by BU researcher Sarah Ketchen Lipson, reveals a majority of students say mental health has impacted their academic performance