Optical frequency combs found a new dimension
2021-02-20
(Press-News.org) Periodic pulses of light forming a comb in the frequency domain are
widely used for sensing and ranging. The key to the miniaturisation of
this technology towards chip-integrated solutions is the generation of
dissipative solitons in ring-shaped microresonators. Dissipative solitons
are stable pulses circulating around the circumference of a nonlinear
resonator.
Since their first demonstration, the process of dissipative soliton
formation has been extensively studied and today it is rather
considered as textbook knowledge. Several directions of further
development are actively investigated by different research groups
worldwide. One of these directions is the generation of solitons in
coupled resonators. The collective effect of many resonators promises
better performance and control over the frequency combs, exploiting
another (spatial) dimension.
But how does the coupling of additional resonators change the soliton
generation process? Identical oscillators of any kind, affecting each
other, can no longer be considered as a set of distinct elements. Due to
the hybridisation phenomenon, the excitation of such a system
influences all its elements, and the system has to be treated as a whole.
The simplest case when the hybridisation takes place is two coupled
oscillators or, in molecular terminology, a dimer. As well as coupled
pendulums and atoms forming a molecule, modes of coupled optical
microresonators experience hybridisation but, in contrast to other
systems, the number of involved modes is large (typically from tens to
hundreds). Therefore, solitons in a photonic dimer are generated in
hybridised modes involving both resonators, which adds another
degree of control if one has access to hybridisation parameters.
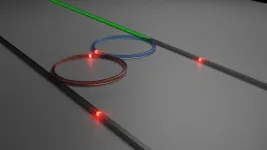
In a paper published at Nature Physics, researchers from the laboratory of Tobias J. Kippenberg at EPFL, and IBM Research Europe led by Paul Seidler, demonstrated the generation of dissipative solitons and, therefore, coherent frequency combs in a photonic molecule made of two microresonators. The generation of a soliton in the dimer implies two counter-propagating solitons in both resonator rings. The
underlying electric field behind every mode of the dimer resembles two
gears turning in opposite directions, which is why solitons in the
photonic dimer are called Gear Solitons. Imprinting heaters on both
resonators, and thereby controlling the hybridisation, authors
demonstrated the real-time tuning of the soliton-based frequency
comb.
Even the simple dimer arrangement, besides the hybridised (gear)
soliton generation, has demonstrated a variety of emergent
phenomena, i.e. phenomena not present at the single-particle
(resonator) level. For instance, researchers predicted the effect of
soliton hopping: periodic energy exchange between the resonators forming the dimer while maintaining the solitonic state. This phenomenon is the result of simultaneous generation of solitons in both hybridised mode families whose interaction leads to energy oscillation. Soliton hopping, for example, can be used for the generation of configurable combs in the radio-frequency domain.
"The physics of soliton generation in a single resonator is relatively wellunderstood today," says Alexey Tikan a researcher at the Laboratory of Photonics and Quantum Measurements, EPFL. "The field is probing other directions of development and improvement. Coupled resonators are one of a few such perspectives. This approach will allow for the employment of concepts from adjacent fields of Physics. For example, one can form a topological insulator (known in solid state physics) by coupling resonators in a lattice, which will lead to the generation of robust frequency combs immune to the defects of the lattice, and at the same time profiting from the enhanced efficiency and additional degrees of control. Our work makes a step towards these fascinating ideas!"
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-20
A survey by a Boston University researcher of nearly 33,000 college students across the country reveals the prevalence of depression and anxiety in young people continues to increase, now reaching its highest levels, a sign of the mounting stress factors due to the coronavirus pandemic, political unrest, and systemic racism and inequality.
"Half of students in fall 2020 screened positive for depression and/or anxiety," says END ...
2021-02-19
Microorganisms possess natural product biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) that may harbor unique bioactivities for use in drug development and agricultural applications. However, many uncharacterized microbial BGCs remain inaccessible. Researchers at University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign previously demonstrated a technique using transcription factor decoys to activate large, silent BGCs in bacteria to aid in natural product discovery.
Now, they have developed a direct cloning method that aims to accelerate large-scale discovery of novel natural products. Their findings are reported in the journal Nature Communications.
Named Cas12a assisted precise targeted cloning using in vivo Cre-lox recombination (CAPTURE), ...
2021-02-19
DURHAM, N.C. -- Duke researchers have been studying something that happens too slowly for our eyes to see. A team in biologist Philip Benfey's lab wanted to see how plant roots burrow into the soil. So they set up a camera on rice seeds sprouting in clear gel, taking a new picture every 15 minutes for several days after germination.
When they played their footage back at 15 frames per second, compressing 100 hours of growth into less than a minute, they saw that rice roots use a trick to gain their first foothold in the soil: their growing tips make ...
2021-02-19
A chemist from RUDN University, working with a group of colleagues, synthesized three new chalcogenides (compounds that contain metals and elements from group 16 of the periodic table). The team suggested an unusual approach to synthesis that was based on iodine. An article about the work was published in the Dalton Transactions journal.
Chalcogens are elements of group 16 of the periodic table that include oxygen, sulfur, selenium, tellurium, polonium, and livermorium--an artificial radioactive element. Chalcogenides are compounds of chalcogens with metals that are used as photosensitive ...
2021-02-19
Several University of Illinois Chicago faculty members have addressed the issue of how to ethically conduct research with Black populations.
In their paper "Ethics of Research at the Intersection of COVID-19 and Black Lives Matter: A Call to Action," authors Natasha Crooks, an assistant professor, Phoenix Matthews, a professor, both of the UIC College of Nursing, and Geri Donenberg, director of the Center for Dissemination and Implementation Science at the UIC College of Medicine, highlight the historical issues that impact research involving Black populations. They also provide recommendations for researchers to ethically engage Black populations in research. ...
2021-02-19
Biotechnologists from RUDN University in collaboration with Lomonosov MSU and Kurchatov institute made an important contribution to the technology of phosphate and nitrate biocapture from wastewater using Lobosphaera algae fixed on the filters.The biomass obtained in the course of this process can be used as a fertilizer. The results of the study were published in the Journal of Water Process Engineering.
Phosphates and nitrates get to the wastewater together with industrial and household waste, especially detergents. Both substances are parts of phosphorus and nitrogen chemical cycles. However, these cycles are disturbed by human activity, as the growing amounts of phosphates and nitrates cannot be processed by water ecosystems. As a result, these substances turn from useful nutrients ...
2021-02-19
New Orleans, LA - A retrospective study conducted by LSU Health New Orleans reports that contrary to previous research, most patients who drop out of peritoneal dialysis may do so for psychosocial reasons. The findings are published in The American Journal of the Medical Sciences, available here. The paper inspired a companion editorial, available here.
The research team evaluated the reasons that 27 of the 83 patients enrolled in the peritoneal dialysis program withdrew between 2016 and 2018. Twenty-four or 86% were African American. They found that psychosocial factors, including mental health illness such as anxiety and depression, loss of support networks, or inability to tolerate ...
2021-02-19
Since Charles Darwin's day, the abundance of life on coral reefs has been puzzling, given that most oceanic surface waters in the tropics are low in nutrients and unproductive.
But now research, led by Newcastle University and published in in the journal Science Advances, has confirmed that the food web of a coral reef in the Maldives relies heavily on what comes in from the open ocean.
The team found that these offshore resources contribute to more than 70% of reef predator diets, the rest being derived from reef associated sources.
Led by Dr Christina Skinner, now based at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, the researchers included collaborators from Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (USA), Banyan Tree Marine ...
2021-02-19
Cooperative operations between a solar observation satellite and a sounding-rocket telescope have measured the magnetic field strength in the photosphere and chromosphere above an active solar plage region. This is the first time that the magnetic field in the chromosphere has been charted all the way up to its top. This finding brings us closer to understanding how energy is transferred between layers of the Sun.
Despite being the brightest object in the sky, the Sun still holds many mysteries for astronomers. It is generally believed that magnetic fields play an important role in heating the solar corona, but the details of the process are still unclear. To solve this mystery it is important to understand the magnetic field in the chromosphere, which is sandwiched ...
2021-02-19
Northwestern University synthetic biologist Joshua Leonard used to build devices when he was a child using electronic kits. Now he and his team have developed a design-driven process that uses parts from a very different kind of toolkit to build complex genetic circuits for cellular engineering.
One of the most exciting frontiers in medicine is the use of living cells as therapies. Using this approach to treat cancer, for example, many patients have been cured of previously untreatable disease. These advances employ the approaches of synthetic biology, a growing ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Optical frequency combs found a new dimension