Artificial pancreas system upgraded with AI algorithm
2021-02-23
(Press-News.org) Diabetes is on the rise worldwide. It is a permanent condition that requires care over a life time. To help manage it, an artificial pancreas system, which automatically measures blood sugar levels to infuse the appropriate amount of insulin into the blood, has now become smarter thanks to AI learning.
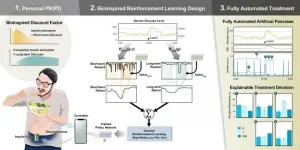
A research team, led by Professor Sung-Min Park and Ph.D. candidate Seunghyun Lee and M.S. candidate Jiwon Kim of POSTECH's Department of Convergence IT Engineering and Electrical Engineering, has newly developed a reinforcement learning (RL) based AI algorithm that calculates the amount of insulin needed for a diabetic patient and injects it automatically. These findings were published as a feature article in the latest issue of IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, an international journal on medical information science.
Patients with type 1 diabetes must inject insulin daily. One must check the amount of carbohydrates in the food ingested each time, calculate the proper amount of insulin, then inject the correct dosage before each meal. Though artificial pancreas systems on the market help with this process, there is still the hassle of having to input the meal intake in advance each time.
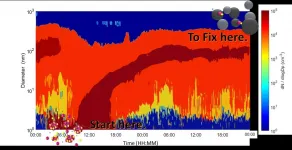
To eliminate this inconvenience, the research team added a pharmacological concept to reinforcement learning, widely known as the algorithm of AlphaGo. This method of AI algorithm achieved a mean glucose of 124.72 mg/dL and percentage time in the normal range of 89.56%. Even without inputting the meal intake, the policy showed performance comparable to that of conventional artificial pancreas.
"The fully automated artificial pancreas is like autonomous driving for the medical industry," explained Professor Sung-Min Park. "The newly developed AI algorithm enables fully automated blood sugar control without the hassle of inputting meal or exercise information." He added, "We expect this algorithm to be extended to other drug-based treatments."
INFORMATION:
This study was conducted with the support from the Mid-career Researcher Program in Basic Research in Science and Engineering of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-23
Luxembourg, 23 February 2021 - At an online European Parliament workshop hosted by Deirdre Clune MEP (Ireland), Alzheimer Europe launched a new report "Data Sharing in Dementia Research", which reviews recent changes in EU research policy and sets out recommendations to improve data sharing in dementia research.
In this report, Alzheimer Europe evaluates the legal and policy landscapes that dementia researchers have had to navigate since the launch of Horizon 2020 in 2013. The report identifies key barriers and enablers for data sharing. It maps the Horizon 2020 dementia research portfolio, assessing the scale of EU investment in dementia research and the use of clinical ...
2021-02-23
Helsinki, Finland--Technology helps humans maintain connections, get work done, and relax after a long day. How it can best improve the lives of animals, particularly those in captivity, however, has remained an open question.
Scientists from Aalto University, in collaboration with Korkeasaari Zoo, have designed and built an on-demand video device for white-faced saki monkeys to activate as and when they like. While enrichment systems for zoo animals have been around for some time, very few offer animals the ability to choose when and how they use the device, even though choice and control are known to promote animal welfare.
'We were very much interested in how we can give animals control over their ...
2021-02-23
U.S. policies in the Middle East are built on outdated "legacy" aid packages, massive arms sales and a disproportionate focus on the Iranian threat that fail to advance American interests - or help the region's people - and need to be rethought, according to a new RAND Corporation report.
The United States devotes an overwhelming share of foreign military financing to just three countries - Israel, Egypt and Jordan, which received 81% of the $6 billion spent globally in 2019. If policymakers were to pursue an alternative strategy outlined by RAND researchers, ...
2021-02-23
Graphene, a two-dimensional material composed exclusively of carbon, has revealed extraordinary properties, including thermal and electrical conductivity, transparency, and flexibility. When combined, these properties become particularly interesting in the age of touch screens and flexible electronics! 'Unlike 3D materials, graphene has a height reduced to the ultimate dimension of the atom. It's therefore a carbon atom plane,' explains Prof. Jean-Christophe Charlier, a specialist in nanoscopic physics at the Institute of Condensed Matter and Nanosciences of UCLouvain.
In a study published in Nature, the scientist and his team dissected the behaviour of electrons when two layers of graphene superimposed at an ...
2021-02-23
Its muscular body shape and large pectoral fins are perfect for long-distance travel, yet movement patterns of the whitespotted eagle ray (Aetobatus narinari) remain a mystery. Researchers from Florida Atlantic University's Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institute in collaboration with Mote Marine Laboratory & Aquarium, the University of Florida and the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission, are the first to conduct a multiyear study examining large-scale movements of whitespotted eagle rays in United States waters.
Between 2016 and 2018, scientists fitted 54 rays with acoustic transmitters ...
2021-02-23
Doha, Qatar - (February 23, 2021) - A group of researchers at Qatar Foundation have reported the first and largest genetic association study in the Middle East, that has been published online in Nature Communications - a leading a peer-reviewed, open access, scientific journal published by Nature Research.
The study titled "Whole genome sequencing in the Middle Eastern Qatari population identifies genetic associations with 45 clinically relevant traits" highlights a vital piece of information wherein now there is a better understanding of the genetic risk factors that are specific to the Arab population, including those that are shared with other ethnicities.
Qatar was among the first countries to launch its own large-scale, national genome project. Qatar Genome ...
2021-02-23
A recent genetic study at the University of Helsinki provides new information on the occurrence of a DVL2 gene defect associated with a screw tail and its relevance to canine constitution and health. The variant was found in several Bulldog and Pit Bull type breeds, and it was shown to result in caudal vertebral anomalies and shortening of the muzzle. The DLV2 variant may also affect the development of the heart.
Dog breeding is often focused on appearance. In some breeds, the ideal body shape is bulky, with a broad head and short muzzle, short legs and a very short and kinked tail, also known as a "screw tail". In a previous study in the United States, screw tail was linked to a variant in the DVL2 gene. The variant has become enriched ...
2021-02-23
According to recent estimates, there will be roughly 10 billion people to feed in 2050. Agricultural production will need to increase by almost 56% to guarantee food security globally, without converting more land for agriculture (in line with environmental and climate targets). This unprecedented challenge has ushered in the era of "smart agriculture," which promises to revolutionize food production by combining agricultural techniques with information technology, automation, and artificial intelligence. This new era, called "Agriculture 4.0," could ensure sustainable food production for the entire world. However, as communities gradually embrace smart agriculture, it is important to understand how to manage the security and privacy risks associated with the integration of ...
2021-02-23
Washington, DC / New Delhi, India - Researchers at CDDEP, in collaboration with leading experts in the field, have produced the "Infectious Diseases in the South-East Asia Region" report, which examines cross-boundary challenges in communicable disease control in countries in the South-and South-East Asia region. The report emphasizes infectious diseases related to other sources of disease burden in the region and communicates overall trends in the health and economic burden they impose.
Despite substantial progress in recent years, which has seen reductions in deaths from HIV and malaria and an increase ...
2021-02-23
Researchers of the University of Helsinki have resolved for the first time, how the ultrafine particles of atmosphere effect on the climate and health.
Atmospheric air pollution kills more than 10,000 people every day. The biggest threat to human health has been assumed to be the mass accumulation of atmospheric particles with diameter smaller 2.5 μm: the higher the mass and loss of visibility, the bigger the threat.
The researchers of the Institute for Atmospheric and Earth System Research (INAR) at the University of Helsinki together with collaborators in China discovered that if we want to solve the accumulation of the biggest particles, we need to start with the smallest.
Until recent ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Artificial pancreas system upgraded with AI algorithm