The way a fish swims reveals a lot about its personality, say scientists
2021-02-23
(Press-News.org) The way a fish swims reveals a lot about its personality, say scientists
Personality has been described in all sorts of animal species, from ants to apes. Some individuals are shy and sedentary, while others are bold and active. Now a new study published in Ecology and Evolution has revealed that the way a fish swims tells us a lot about its personality.
This new research suggests experts can reliably measure animal personality simply from the way individual animals move, a type of micropersonality trait, and that the method could be used to help scientists understand about personality differences in wild animals.
A team of biologists and mathematicians from Swansea University and the University of Essex filmed the movements of 15 three-spined stickleback fish swimming in a tank which contained two, three, or five plastic plants in fixed positions.
Using the high?resolution tracking data from video recordings, the team took measurements of how much and how often the fish turned, and how much they stopped and started moving.
The data revealed that each fish's movements were very different, and that these differences were highly repeatable - so much so that the researchers could identify a fish just from its movement data.
Dr Ines Fürtbauer, a co-author of the study from Swansea University, said: "These micropersonalities in fish are like signatures - different and unique to an individual. We found the fish's signatures were the same when we made simple changes to the fish tanks, such as adding additional plants. However, it is possible these signatures change gradually over an animal's lifetime, or abruptly if an animal encounters something new or unexpected in its environment. Tracking animals' motion over longer periods and in the wild will give us this sort of insight and help us better understand not only personality but also how flexible an animal's behaviour is."
The authors of the study say that further work with other species and contexts is needed to see how general the phenomenon is, and if the same patterns are seen with land animals or flying species.
Dr Andrew King, lead author from Swansea University, said: "Our work suggests that simple movement parameters can be viewed as micropersonality traits that give rise to extensive consistent individual differences in behaviours. This is significant because it suggests we might be able to quantify personality differences in wild animals as long as we can get fine-scale information on how they are moving; and these types of data are becoming more common with advances in animal tracking technologies."
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-23
A new analysis of B cells and more than 1,000 different monoclonal antibodies from 8 patients with COVID-19 shows that, contrary to previous hypotheses, protective B cell responses to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein remain stable and continue to evolve over a 5-month period, many months after the initial period of active viral replication. However, a large proportion of the neutralizing antibodies generated from these long-lasting B cells did not efficiently recognize various emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants from Brazil and South Africa. These results - from an academia-industry collaboration - will help inform the design of future COVID-19 vaccines that work to constrain viral evolution and stimulate ...
2021-02-23
Researchers have pinpointed a helper T cell population in the lungs of patients with severe COVID-19 that may be central to the development of hyperinflammation, lung injury, and subsequent acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) during disease. Their data support the ongoing investigation of anti-cytokine therapies that target this cell subset, called tissue-resident memory-like Th17 cells (Trm17). To date, the bulk of research on immune responses to COVID-19 has mainly focused on T cells in the blood, while the role of tissue-specific immune cells in the inflamed lung has remained unclear. Accumulating evidence suggests that one of the causes of ...
2021-02-23
WHAT:
Using viruses instead of antibiotics to tame troublesome drug-resistant bacteria is a promising strategy, known as bacteriophage or "phage therapy." Scientists at the National Institutes of Health have used two different bacteriophage viruses individually and then together to successfully treat research mice infected with multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 258 (ST258). The bacterium K. pneumoniae ST258 is included on a CDC list of biggest antibiotic resistance threats in the United States. High rates of morbidity and mortality are associated with untreated K. pneumoniae infections.
Phage therapy has been pursued for about a century, though conclusive research studies are rare and clinical results--from ...
2021-02-23
Imagine if surgeons could transplant healthy neurons into patients living with neurodegenerative diseases or brain and spinal cord injuries. And imagine if they could "grow" these neurons in the laboratory from a patient's own cells using a synthetic, highly bioactive material that is suitable for 3D printing.
By discovering a new printable biomaterial that can mimic properties of brain tissue, Northwestern University researchers are now closer to developing a platform capable of treating these conditions using regenerative medicine.
A key ingredient to the discovery is the ability to control the self-assembly processes of molecules within the ...
2021-02-23
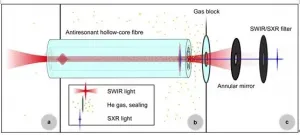
Bright, coherent soft X-ray radiation (SXR) is used in many scientific applications such as advanced absorption spectroscopy or lens-less imaging, and in fundamental research e.g. to produce extremely short isolated optical pulses. Therefore, the generation, control, and detection of this type of short-wavelength light is highly important in fields like fundamental atomic physics, solid-state physics, the semiconductor industry, material science and biology.
To date, high photon flux in the soft X-ray spectral region is mostly delivered by large-scale facilities like synchrotrons or free electron lasers. An alternative is to use high-order harmonic generation (HHG) sources, which are currently driven by pulsed laser systems with ...
2021-02-23
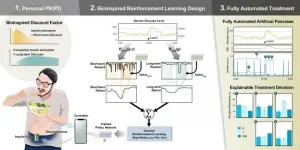
Diabetes is on the rise worldwide. It is a permanent condition that requires care over a life time. To help manage it, an artificial pancreas system, which automatically measures blood sugar levels to infuse the appropriate amount of insulin into the blood, has now become smarter thanks to AI learning.
A research team, led by Professor Sung-Min Park and Ph.D. candidate Seunghyun Lee and M.S. candidate Jiwon Kim of POSTECH's Department of Convergence IT Engineering and Electrical Engineering, has newly developed a reinforcement learning (RL) based AI algorithm that calculates the ...
2021-02-23
Luxembourg, 23 February 2021 - At an online European Parliament workshop hosted by Deirdre Clune MEP (Ireland), Alzheimer Europe launched a new report "Data Sharing in Dementia Research", which reviews recent changes in EU research policy and sets out recommendations to improve data sharing in dementia research.
In this report, Alzheimer Europe evaluates the legal and policy landscapes that dementia researchers have had to navigate since the launch of Horizon 2020 in 2013. The report identifies key barriers and enablers for data sharing. It maps the Horizon 2020 dementia research portfolio, assessing the scale of EU investment in dementia research and the use of clinical ...
2021-02-23
Helsinki, Finland--Technology helps humans maintain connections, get work done, and relax after a long day. How it can best improve the lives of animals, particularly those in captivity, however, has remained an open question.
Scientists from Aalto University, in collaboration with Korkeasaari Zoo, have designed and built an on-demand video device for white-faced saki monkeys to activate as and when they like. While enrichment systems for zoo animals have been around for some time, very few offer animals the ability to choose when and how they use the device, even though choice and control are known to promote animal welfare.
'We were very much interested in how we can give animals control over their ...
2021-02-23
U.S. policies in the Middle East are built on outdated "legacy" aid packages, massive arms sales and a disproportionate focus on the Iranian threat that fail to advance American interests - or help the region's people - and need to be rethought, according to a new RAND Corporation report.
The United States devotes an overwhelming share of foreign military financing to just three countries - Israel, Egypt and Jordan, which received 81% of the $6 billion spent globally in 2019. If policymakers were to pursue an alternative strategy outlined by RAND researchers, ...
2021-02-23
Graphene, a two-dimensional material composed exclusively of carbon, has revealed extraordinary properties, including thermal and electrical conductivity, transparency, and flexibility. When combined, these properties become particularly interesting in the age of touch screens and flexible electronics! 'Unlike 3D materials, graphene has a height reduced to the ultimate dimension of the atom. It's therefore a carbon atom plane,' explains Prof. Jean-Christophe Charlier, a specialist in nanoscopic physics at the Institute of Condensed Matter and Nanosciences of UCLouvain.
In a study published in Nature, the scientist and his team dissected the behaviour of electrons when two layers of graphene superimposed at an ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] The way a fish swims reveals a lot about its personality, say scientists