INFORMATION:
B cells continue to work against SARS-CoV-2 months after infection, but do not recognize mutant
Variants from Brazil and South Africa
2021-02-23
(Press-News.org) A new analysis of B cells and more than 1,000 different monoclonal antibodies from 8 patients with COVID-19 shows that, contrary to previous hypotheses, protective B cell responses to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein remain stable and continue to evolve over a 5-month period, many months after the initial period of active viral replication. However, a large proportion of the neutralizing antibodies generated from these long-lasting B cells did not efficiently recognize various emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants from Brazil and South Africa. These results - from an academia-industry collaboration - will help inform the design of future COVID-19 vaccines that work to constrain viral evolution and stimulate better neutralizing antibody and B cell responses against emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants. Mrunal Sakharkar and colleagues profiled spike protein-specific B cell and antibody responses in 8 patients with mild and severe COVID-19 over five months. Consistent with previous findings, they observed a significant decline in neutralizing antibody levels in the blood over time; however, levels of spike protein-specific memory B cells remained stable or even increased during the same time frame. As well, over the course of 120 days, monoclonal antibodies isolated from these B cells underwent increased somatic hypermutation, binding affinity, and neutralization potency - all signs of persistent B cell activity. The researchers also observed cross-neutralizing B cell populations, but these comprised just a small fraction of the B cell repertoire and were not prominent in the neutralizing response to SARS-CoV-2. Rather, a large proportion of the neutralizing antibody response only targeted conserved epitopes shared between SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV and did not efficiently recognize emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants from Brazil and South Africa that harbor mutations at amino acid positions 417 and 484 of the spike protein. Thus, the authors suggest careful monitoring of circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants for variability in these protein sites to determine how these mutations impact vaccine-induced immunity.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists identify potential contributor to hyper immune responses in patients with severe COVID-19
2021-02-23
Researchers have pinpointed a helper T cell population in the lungs of patients with severe COVID-19 that may be central to the development of hyperinflammation, lung injury, and subsequent acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) during disease. Their data support the ongoing investigation of anti-cytokine therapies that target this cell subset, called tissue-resident memory-like Th17 cells (Trm17). To date, the bulk of research on immune responses to COVID-19 has mainly focused on T cells in the blood, while the role of tissue-specific immune cells in the inflamed lung has remained unclear. Accumulating evidence suggests that one of the causes of ...
Mouse study shows bacteriophage therapy could fight drug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae
2021-02-23
WHAT:
Using viruses instead of antibiotics to tame troublesome drug-resistant bacteria is a promising strategy, known as bacteriophage or "phage therapy." Scientists at the National Institutes of Health have used two different bacteriophage viruses individually and then together to successfully treat research mice infected with multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 258 (ST258). The bacterium K. pneumoniae ST258 is included on a CDC list of biggest antibiotic resistance threats in the United States. High rates of morbidity and mortality are associated with untreated K. pneumoniae infections.
Phage therapy has been pursued for about a century, though conclusive research studies are rare and clinical results--from ...
'Walking' molecule superstructures could help create neurons for regenerative medicine
2021-02-23
Imagine if surgeons could transplant healthy neurons into patients living with neurodegenerative diseases or brain and spinal cord injuries. And imagine if they could "grow" these neurons in the laboratory from a patient's own cells using a synthetic, highly bioactive material that is suitable for 3D printing.
By discovering a new printable biomaterial that can mimic properties of brain tissue, Northwestern University researchers are now closer to developing a platform capable of treating these conditions using regenerative medicine.
A key ingredient to the discovery is the ability to control the self-assembly processes of molecules within the ...
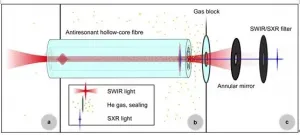
Fibre-integrated, high-repetition-rate water window soft X-ray source
2021-02-23
Bright, coherent soft X-ray radiation (SXR) is used in many scientific applications such as advanced absorption spectroscopy or lens-less imaging, and in fundamental research e.g. to produce extremely short isolated optical pulses. Therefore, the generation, control, and detection of this type of short-wavelength light is highly important in fields like fundamental atomic physics, solid-state physics, the semiconductor industry, material science and biology.
To date, high photon flux in the soft X-ray spectral region is mostly delivered by large-scale facilities like synchrotrons or free electron lasers. An alternative is to use high-order harmonic generation (HHG) sources, which are currently driven by pulsed laser systems with ...
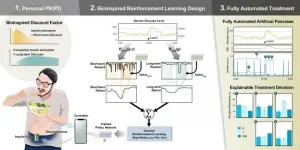
Artificial pancreas system upgraded with AI algorithm
2021-02-23
Diabetes is on the rise worldwide. It is a permanent condition that requires care over a life time. To help manage it, an artificial pancreas system, which automatically measures blood sugar levels to infuse the appropriate amount of insulin into the blood, has now become smarter thanks to AI learning.
A research team, led by Professor Sung-Min Park and Ph.D. candidate Seunghyun Lee and M.S. candidate Jiwon Kim of POSTECH's Department of Convergence IT Engineering and Electrical Engineering, has newly developed a reinforcement learning (RL) based AI algorithm that calculates the ...
Alzheimer Europe sets out recommendations to improve data sharing in dementia research
2021-02-23
Luxembourg, 23 February 2021 - At an online European Parliament workshop hosted by Deirdre Clune MEP (Ireland), Alzheimer Europe launched a new report "Data Sharing in Dementia Research", which reviews recent changes in EU research policy and sets out recommendations to improve data sharing in dementia research.
In this report, Alzheimer Europe evaluates the legal and policy landscapes that dementia researchers have had to navigate since the launch of Horizon 2020 in 2013. The report identifies key barriers and enablers for data sharing. It maps the Horizon 2020 dementia research portfolio, assessing the scale of EU investment in dementia research and the use of clinical ...
Saki monkeys get screen time for more control over their lives in captivity
2021-02-23
Helsinki, Finland--Technology helps humans maintain connections, get work done, and relax after a long day. How it can best improve the lives of animals, particularly those in captivity, however, has remained an open question.
Scientists from Aalto University, in collaboration with Korkeasaari Zoo, have designed and built an on-demand video device for white-faced saki monkeys to activate as and when they like. While enrichment systems for zoo animals have been around for some time, very few offer animals the ability to choose when and how they use the device, even though choice and control are known to promote animal welfare.
'We were very much interested in how we can give animals control over their ...
Reimagined US-Middle East strategy would lean less on arms sales, more on dev't/governance
2021-02-23
U.S. policies in the Middle East are built on outdated "legacy" aid packages, massive arms sales and a disproportionate focus on the Iranian threat that fail to advance American interests - or help the region's people - and need to be rethought, according to a new RAND Corporation report.
The United States devotes an overwhelming share of foreign military financing to just three countries - Israel, Egypt and Jordan, which received 81% of the $6 billion spent globally in 2019. If policymakers were to pursue an alternative strategy outlined by RAND researchers, ...
The magic angle of twisted graphene
2021-02-23
Graphene, a two-dimensional material composed exclusively of carbon, has revealed extraordinary properties, including thermal and electrical conductivity, transparency, and flexibility. When combined, these properties become particularly interesting in the age of touch screens and flexible electronics! 'Unlike 3D materials, graphene has a height reduced to the ultimate dimension of the atom. It's therefore a carbon atom plane,' explains Prof. Jean-Christophe Charlier, a specialist in nanoscopic physics at the Institute of Condensed Matter and Nanosciences of UCLouvain.
In a study published in Nature, the scientist and his team dissected the behaviour of electrons when two layers of graphene superimposed at an ...
Drifter or homebody? Study first to show where whitespotted eagle rays roam
2021-02-23
Its muscular body shape and large pectoral fins are perfect for long-distance travel, yet movement patterns of the whitespotted eagle ray (Aetobatus narinari) remain a mystery. Researchers from Florida Atlantic University's Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institute in collaboration with Mote Marine Laboratory & Aquarium, the University of Florida and the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission, are the first to conduct a multiyear study examining large-scale movements of whitespotted eagle rays in United States waters.
Between 2016 and 2018, scientists fitted 54 rays with acoustic transmitters ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] B cells continue to work against SARS-CoV-2 months after infection, but do not recognize mutantVariants from Brazil and South Africa