Researchers identify mechanism by which exercise strengthens bones and immunity
2021-02-24
(Press-News.org) Scientists at the Children's Medical Center Research Institute at UT Southwestern (CRI) have identified the specialized environment, known as a niche, in the bone marrow where new bone and immune cells are produced. The study, published in Nature, also shows that movement-induced stimulation is required for the maintenance of this niche, as well as the bone and immune-forming cells that it contains. Together, these findings identify a new way that exercise strengthens bones and immune function.
Researchers from the Morrison laboratory discovered that forces created from walking or running are transmitted from bone surfaces along arteriolar blood vessels into the marrow inside bones. Bone-forming cells that line the outside of the arterioles sense these forces and are induced to proliferate. This not only allows the formation of new bone cells, which helps to thicken bones, but the bone-forming cells also secrete a growth factor that increases the frequency of cells that form lymphocytes around the arterioles. Lymphocytes are the B and T cells that allow the immune system to fight infections.
When the ability of the bone-forming cells to sense pressure caused by movement, also known as mechanical forces, was inactivated, it reduced the formation of new bone cells and lymphocytes, causing bones to become thinner and reducing the ability of mice to clear a bacterial infection.
"As we age, the environment in our bone marrow changes and the cells responsible for maintaining skeletal bone mass and immune function become depleted. We know very little about how this environment changes or why these cells decrease with age," says Sean Morrison, Ph.D., the director of CRI and a Howard Hughes Medical Institute Investigator. "Past research has shown exercise can improve bone strength and immune function, and our study discovered a new mechanism by which this occurs."
Previous work from the Morrison laboratory discovered the skeletal stem cells that give rise to most of the new bone cells that form during adulthood in the bone marrow. They are Leptin Receptor+ (LepR+) cells. They line the outside of blood vessels in the bone marrow and form critical growth factors for the maintenance of blood-forming cells. The Morrison lab also found that a subset of LepR+ cells synthesize a previously undiscovered bone-forming growth factor called Osteolectin. Osteolectin promotes the maintenance of the adult skeleton by causing LepR+ to form new bone cells.
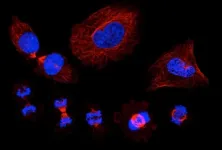
In the current study, Bo Shen, Ph.D., a postdoctoral fellow in the Morrison laboratory, looked more carefully at the subset of LepR+ cells that make Osteolectin. He discovered that these cells reside exclusively around arteriolar blood vessels in the bone marrow and that they maintain nearby lymphoid progenitors by synthesizing stem cell factor (SCF) - a growth factor on which those cells depend. Deleting SCF from Osteolectin-positive cells depleted lymphoid progenitors and undermined the ability of mice to mount an immune response to bacterial infection.
"Together with our previous work, the findings in this study show Osteolectin-positive cells create a specialized niche for bone-forming and lymphoid progenitors around the arterioles. Therapeutic interventions that expand the number of Osteolectin-positive cells could increase bone formation and immune responses, particularly in the elderly," says Shen.
Shen found that the number of Osteolectin-positive cells and lymphoid progenitors decreased with age. Curious if he could reverse this trend, Shen put running wheels in the cages so that the mice could exercise. He found the bones of these mice became stronger with exercise, while the number of Osteolectin-positive cells and lymphoid progenitors around the arterioles increased. This was the first indication that mechanical stimulation regulates a niche in the bone marrow.
Shen found that Osteolectin-positive cells expressed a receptor on their surfaces - known as Piezo1 - that signals inside the cell in response to mechanical forces. When Piezo1 was deleted from Osteolectin-positive cells of mice, these cells and the lymphoid progenitors they support became depleted, weakening bones and impairing immune responses.
"We think we've found an important mechanism by which exercise promotes immunity and strengthens bones, on top of other mechanisms previously identified by others," says Morrison.
INFORMATION:
Morrison is a professor of pediatrics at UT Southwestern, a Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT) Scholar in Cancer Research, and a member of the National Academies of Science and Medicine. He also holds the Kathryne and Gene Bishop Distinguished Chair in Pediatric Research at Children's Research Institute at UT Southwestern and the Mary McDermott Cook Chair in Pediatric Genetics. Shen is a Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award Fellow.
National Institutes of Health (DK11875), National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (F32 HL139016-01); the Leopoldina Fellowship Program (LPDS 2016-16) of the German National Academy of Sciences and the Fritz Thyssen Foundation, and donors to the Children's Medical Center Foundation supported this work.
About CRI
Children's Medical Center Research Institute at UT Southwestern (CRI) is a joint venture of UT Southwestern Medical Center and Children's Medical Center Dallas, the flagship hospital of Children's Health. CRI's mission is to perform transformative biomedical research to better understand the biological basis of disease. Located in Dallas, Texas, CRI is home to interdisciplinary groups of scientists and physicians pursuing research at the interface of regenerative medicine, cancer biology and metabolism. For more information, visit: cri.utsw.edu. To support CRI, visit: give.childrens.com/about-us/why-help/cri/.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-24
A study of spatial learning in mice shows that exposure to new experiences dampens established representations in the brain's hippocampus and prefrontal cortex, allowing the mice to learn new navigation strategies. The study, published in Nature, was supported by the National Institutes of Health.
"The ability to flexibly learn in new situations makes it possible to adapt to an ever-changing world," noted Joshua A. Gordon, M.D., Ph.D., a senior author on the study and director of the National Institute of Mental Health, part of NIH. "Understanding the neural basis of this flexible learning in animals gives us insight into ...
2021-02-24
Asymmetry in the proton confounds physicists, but a new discovery may bring back old theories to explain it.
Symmetry -- displayed in areas ranging from mathematics and art, to living organisms and galaxies -- is an important underlying structure in nature. It characterizes our universe and enables it to be studied and understood.
Because symmetry is such a pervasive theme in nature, physicists are especially intrigued when an object seems like it should be symmetric, but it isn't. When scientists are confronted with these broken symmetries, it's as if they've found an object with a strange reflection in the mirror.
"Nature is leading the way for concepts in older models of the proton to get a second look." -- ...
2021-02-24
UCLA materials scientists and their colleagues have developed a new method to make synthetic biomaterials that mimic the internal structure, stretchiness, strength and durability of tendons and other biological tissues.
The researchers developed a two-pronged process to enhance the strength of existing hydrogels that could be used to create artificial tendons, ligaments, cartilage that are 10 times tougher than the natural tissues. Although the hydrogels contain mostly water with little solid content (about 10% polymer), they are more durable than Kevlar and rubber, which are both 100% polymer. This kind of breakthrough has never been achieved in water-laden polymers until this study, which was recently published in Nature. ...
2021-02-24
With the hope of contributing to the fight against cancer, researchers in Sweden have published a new molecular mapping of proteins that regulate the cell division process - identifying 300 such proteins.
The release of the data, which was published today in the scientific journal, Nature, is significant because it helps bring medical research closer to the point of being able to target specific proteins to treat cancer.
Identifying and understanding what characterizes these proteins is important, says co-author Emma Lundberg, a professor at KTH Royal Institute of Technology whose research group at Science ...
2021-02-24
What The Study Did: National COVID-19 registry data are used in this study to describe the epidemiology, clinical characteristics, complications, and hospital and postdischarge outcomes of pediatric patients with multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) and to compare each in patients with severe COVID-19.
Authors: Adrienne G. Randolph, M.D., of Boston Children's Hospital, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2021.2091)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of ...
2021-02-24
What The Study Did: This randomized clinical trial compares the effects of once-weekly subcutaneous semaglutide versussplacebo for weight management as an adjunct to intensive behavioral therapy with initial low-calorie diet in adults with overweight or obesity.
Authors: Thomas A. Wadden, Ph.D., of the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2021.1831)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
2021-02-24
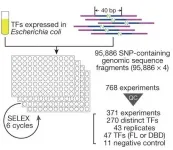
Many genetic variants have been found to have a linkage with genetic diseases, but the understanding of their functional roles in causing diseases are still limited. An international research team, including a biomedical scientist from City University of Hong Kong (CityU), has developed a high-throughput biological assay technique which enabled them to conduct a systematic analysis on the impact of nearly 100,000 genetic variants on the binding of transcription factors to DNA. Their findings provided valuable data for finding key biomarkers of type 2 diabetes for diagnostics and treatments. And they ...
2021-02-24
Long-term use of a medication used to treat kidney transplant patients may not be necessary in individuals with low-to-moderate risk of organ rejection, according to the results of a study led by a University of Cincinnati transplant researcher.
The randomized clinical trial of 385 patients on immunosuppressive drugs tacrolimus and mycophenolate examined whether use of these medicines called corticosteroids could be eliminated at seven days after kidney transplantation. The study shows that 15 years after transplantation no difference in kidney transplant survival or patient survival rates were found between patients who received long-term corticosteroids versus those who had corticosteroid eliminated early, explains E. Steve Woodle, MD, the William ...
2021-02-24
MEMPHIS, TN, FEBRUARY 24, 2021:- Early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease has been shown to reduce cost and improve patient outcomes, but current diagnostic approaches can be invasive and costly. A recent study, published in the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, has found a novel way to identify a high potential for developing Alzheimer's disease before symptoms occur. Ray Romano, Ph.D., RN, completed the research as part of his Ph.D. in the Nursing Science Program at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center (UTHSC) College of Graduate Health Sciences. Dr. Romano conducted the research through the joint laboratory ...
2021-02-24
Plants and animals can rapidly respond to changes in their environment, such as a Venus flytrap snapping shut when a fly touches it. However, replicating similar actions in soft robots requires complex mechanics and sensors. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces have printed liquid metal circuits onto a single piece of soft polymer, creating an intelligent material that curls under pressure or mechanical strain. Watch a video of the smart material here.
Ideally, soft robots could mimic intelligent and autonomous behaviors ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers identify mechanism by which exercise strengthens bones and immunity