INFORMATION:
Article Title: "Ultra-rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 in public workspace environments"
Funding: This project was made possible through the support of a grant from Dynamic Combinatorial Chemistry, LLC, The funder provided support in the form of salaries and supplies for authors OY, ZY, JM, and BO, but did not have any additional role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. The specific roles of these authors are articulated in the 'author contributions' section. The opinions expressed in this publication are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of DCC. Firebird Biomolecular Sciences, LLC, GenePath Diagnostics, Inc., and GenePath Diagnostics India Pvt. Ltd. employ the indicated authors and the specific roles of these authors are articulated in the 'author contributions' section.
Competing Interests: Firebird Biomolecular Sciences, LLC, GenePath Diagnostics, Inc., and GenePath Diagnostics India Pvt. Ltd. employ the indicated authors and the specific roles of these authors are articulated in the 'author contributions' section. OY, ZY, SAB and their institutions own intellectual property associated with the assay. Some of the items mentioned here are sold by Firebird Biomolecular Sciences, LLC, which employs the indicated authors and is owned by SAB. This does not alter the authors' and institutions' adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0240524
Ultra-rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 in public workspace environments
2021-02-24
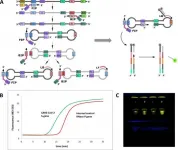
(Press-News.org) Ultra-fast, cheap LAMP-based COVID tests could be performed by non-experts at work and in public spaces, giving results in under an hour
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Improving road safety to tackle crime
2021-02-24
Improving road safety in cities could result in a lower rate of violent crime, according to research from UCL.
Experts analysing crime and car accident data in Mexico City found a surprisingly high level of synchronicity between the two on a weekly cycle, suggesting that applying more resources to prevent road accidents would improve crime rates by enabling more efficient policing.
For the paper, published today in Cities as Complex Systems special issue in PLOS ONE, experts plotted the time and locations of nearly one million car accidents and 200,000 ...
New research at UH Rainbow studies the impact of face masks on heart ra
2021-02-24
CLEVELAND, Ohio - Researchers at University Hospitals Rainbow Babies & Children's Hospital (UH Rainbow) published new findings today that wearing a face mask - either a cloth mask or a surgical mask - did not impair the ability of subjects to get air in and out of their bodies.
The study measured heart rate, transcutaneous carbon dioxide tension, and oxygen levels in 50 adult volunteers at the conclusion of six 10-minute phases: Sitting quietly and then walking briskly without a mask; sitting quietly and then walking briskly while wearing a cloth mask; and sitting quietly and then walking ...
New technology shows potential to improve potency and durability benefits in gene therapy
2021-02-24
WATERTOWN, Mass. - Gene therapy has traditionally been conceptualized as a one-time, curative treatment option; however, research shows that there may be a need for subsequent doses years after initial treatment. While adeno-associated viral (AAV) vectors are a core part of this powerful therapeutic approach, they present two key challenges in gene therapy.
The first challenge is their immunogenicity. In gene therapy, the formation of neutralizing antibodies (Nabs) in response to AAV vector administration precludes retreatment of a patient due to the potentially dangerous immune response that would occur after a second or third administration of the therapy.
The second obstacle relates to their durability. AAV vectors ...
Scientists describe earliest primate fossils
2021-02-24
A new study published Feb. 24 in the journal Royal Society Open Science documents the earliest-known fossil evidence of primates.
A team of 10 researchers from across the U.S. analyzed several fossils of Purgatorius, the oldest genus in a group of the earliest-known primates called plesiadapiforms. These ancient mammals were small-bodied and ate specialized diets of insects and fruits that varied by species. These newly described specimens are central to understanding primate ancestry and paint a picture of how life on land recovered after the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event 66 million years ago that wiped out all dinosaurs -- except for birds -- and led to the rise of mammals.
Gregory Wilson Mantilla, a University of Washington professor of biology and curator of vertebrate ...
Revive the map: 4D building reconstruction with machine learning
2021-02-24
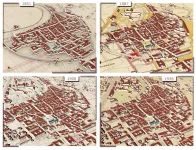
A research team from Skoltech and FBK (Italy) presented a methodology to derive 4D building models using historical maps and machine learning. The implemented method relies on the geometric, neighbourhood, and categorical attributes to predict building heights. The method is useful for understanding urban phenomena and changes contributing to defining our cities' actual shapes. The results were published in the MDPI Applied Sciences journal.
Historical maps are the most powerful source used to analyze changes in urban development. Nevertheless, maps represent the 3D world ...
Record-high Arctic freshwater will flow to Labrador Sea, affecting local and global oceans
2021-02-24
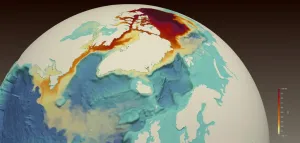
Freshwater is accumulating in the Arctic Ocean. The Beaufort Sea, which is the largest Arctic Ocean freshwater reservoir, has increased its freshwater content by 40% over the past two decades. How and where this water will flow into the Atlantic Ocean is important for local and global ocean conditions.
A study from the University of Washington, Los Alamos National Laboratory and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration shows that this freshwater travels through the Canadian Archipelago to reach the Labrador Sea, rather than through the wider marine passageways that connect to seas in Northern Europe. The open-access study was published Feb. 23 ...
Diabetes patients use of mobile health app found to improve health outcomes, lower medical costs
2021-02-24
Emerging smart mobile health (or mHealth) technologies are changing the way patients track information related to diagnosed conditions. A new study examined the health and economic impacts of mHealth technologies on the outcomes of diabetes patients in Asia. The study concluded that compared to patients who did not use mHealth applications, patients who used the apps had better health outcomes and were able to regulate their health behavior more effectively. They also had fewer hospital visits and lower medical costs.
The study was conducted by researchers at Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) and New York University ...
Study identifies strengths and challenges of responding to dual disasters
2021-02-24
New Orleans, LA -- A new study of how the 2020 major hurricanes and the COVID-19 pandemic affected each other as well as disaster response found that although prior experience enabled community-based organizations to respond to the pandemic, the pandemic is also creating new challenges to preparing for and responding to natural disasters. The research is published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, available here.
"Two major crises hit Louisiana and coastal communities in the Southeastern United States in 2020 - a significant increase in the frequency and severity of hurricanes, and the COVID-19 pandemic," says Benjamin Springgate, MD, MPH, Chief of Community & Population Medicine at ...
A combination therapy for treating severe neurological childhood disorders
2021-02-24
A study aiming to develop a new therapeutic technique could bring a revolution in our approach to treating rare, fatal Sanfilippo syndrome, a disorder that affects children as young as 2 years old and leads to childhood dementia and premature death.
"We are using a combination of gene therapy, stem cells and small molecules to restore metabolic defects in the patient's brain cells" says Dr. Alexey Pshezhetsky, Professor at CHU Ste-Justine and lead GlycoNet Investigator on this project. "First results in the mouse models of the disease are very encouraging."
Sanfilippo syndrome belongs to a group of rare diseases known as lysosomal storage disorders.
The syndrome occurs in ...
Bearded seals are loud - but not loud enough
2021-02-24
ITHACA, N.Y. - During mating season, male bearded seals make loud calls to attract a mate. How loud? Well, even their "quiet" call can still be as ear-rattling as a chainsaw.
These elaborate vocalizations are essential for bearded seal reproduction, and have to be loud enough to be heard over the cacophony of their equally loud brethren.
But in the rapidly changing Arctic soundscape, where noise from industrial activities is predicted to dramatically increase in the next 15 years, bearded seals may need to adjust their calling behavior if they are ...