Abnormal sodium levels in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 predict death or respiratory failure
Study findings can directly affect patient care, researchers say
2021-02-25
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON--Hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and abnormal sodium levels in the blood have an increased risk of experiencing respiratory failure or dying, according to a study published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
"This study shows for the first time that patients presenting at the hospital with COVID-19 and low sodium are twice as likely to need intubation or other means of advanced breathing support as those with normal sodium," said lead investigator Ploutarchos Tzoulis, M.D., Ph.D., M.Sc., Honorary Associate Professor in Endocrinology at University College London (UCL) Medical School in London, U.K.
Additionally, the researchers found that patients who develop high sodium levels during the hospital stay were three times more likely to die than those who have normal sodium levels throughout hospitalization.
"Sodium measurements can inform doctors about which COVID-19 patients are at high risk of deterioration and death," Tzoulis said. "Sodium levels can guide decision making about whether a COVID-19 patient needs hospital admission or monitoring in the intensive care unit."
Sodium is routinely measured as part of bloodwork done for all patients coming to the hospital, and its measurement is inexpensive, Tzoulis noted. Sodium is an essential mineral and helps regulate fluid volume in the body and blood pressure.
The study was conducted in 488 adults with COVID-19 admitted to two London hospitals, UCL Hospital and Whittington Hospital, over an eight-week period last year. The 277 men and 211 women had a median age of 68 years. They had a median hospital stay of eight days.
Nearly 32 percent of COVID-19 patients with low sodium levels at admission needed a breathing tube and ventilator or oxygen through a face mask compared with only 17.5 percent of patients whose sodium values were normal, the investigators reported. Unlike excess sodium in the blood, low sodium levels had no association with an increased risk of dying in the hospital, Tzoulis said.
Among patients with high sodium levels at any time during their hospital stay, nearly 56 percent died versus about 21 percent of patients whose sodium remained normal, the data showed.
Doctors usually treat high sodium levels with intravenous fluids, and low sodium may require intravenous fluids, fluid restriction or medications. However, both conditions are often underestimated and undertreated, Tzoulis said.
Fluid losses due to diarrhea, vomiting, sweating, and not drinking enough water can lead to high sodium levels. Therefore, Tzoulis stressed the importance of avoiding dehydration during a hospital admission for COVID-19.
INFORMATION:
Other authors of the study include: Julian A. Waung (co-first author), Aiyappa Biddanda, John Cousins, Alice Dewsnip, Kanoyin Falayi, Will McCaughran, Chloe Mullins, Ammara Naeem and Muna Nwokolo of Whittington Health NHS Trust, London, U.K.; Emmanouil Bagkeris of Imperial College London in London, U.K.; Eithar Deyab, Syed Bitat and Swarupini Ponnampalam of University College London Hospital NHS Foundation Trust in London, U.K.; PierreMarc Bouloux of University College London; Hugh Montgomery of Whittington Health NHS Trust and University College London; and Ziad Hussein and Stephanie E. Baldeweg of both University College London Hospital NHS Foundation Trust and University College London.
The manuscript, "Dysnatremia is a Predictor for Morbidity and Mortality in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19," was published online, ahead of print.
The research also will be presented at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society's annual meeting, which runs from March 20-23.
Endocrinologists are at the core of solving the most pressing health problems of our time, from diabetes and obesity to infertility, bone health, and hormone-related cancers. The Endocrine Society is the world's oldest and largest organization of scientists devoted to hormone research and physicians who care for people with hormone-related conditions.
The Society has more than 18,000 members, including scientists, physicians, educators, nurses and students in 122 countries. To learn more about the Society and the field of endocrinology, visit our site at http://www.endocrine.org. Follow us on Twitter at @TheEndoSociety and @EndoMedia.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-25
An improved high-tech fluorescence microscopy technique is allowing researchers to film cells inside the breast as never seen before.
This new protocol provides detailed instructions on how to capture hi-res movies of cell movement, division and cooperation, in hard-to-reach regions of breast tissue.
The technology - called multiphoton microscopy - uses infrared lasers to illuminate fluorescently labelled breast cells without harming them, so that elusive cell behaviours can be observed within living tissue.
With the new method, WEHI researchers have revealed how breast cells rearrange, interact and sense their environment as the breast grows during development and recedes after lactation.
Cell imaging within living tissue has been ...
2021-02-25
As the frequency and size of wildfires continues to increase worldwide, new research from Carnegie Mellon University scientists shows how the chemical aging of the particles emitted by these fires can lead to more extensive cloud formation and intense storm development in the atmosphere. The research was published online today in the journal Science Advances.
"The introduction of large amounts of ice-nucleating particles from these fires can cause substantial impacts on the microphysics of clouds, whether supercooled cloud droplets freeze or remain liquid, and the propensity of the clouds to precipitate," said Ryan Sullivan, associate ...
2021-02-25
Caught between climate change and multi-year droughts, California communities are tapping groundwater and siphoning surface water at unsustainable rates.
As this year's below-average rainfall accentuates the problem, a public-private partnership in the Monterey/Salinas region has created a novel water recycling program that could serve as a model for parched communities everywhere.
As Stanford civil engineers report in the journal Water, this now urbanized region, still known for farming and fishing, has used water from four sources -- urban stormwater runoff, irrigation drainage, food processing water and traditional municipal wastewater ...
2021-02-25
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- When healthcare workers become ill during a disease outbreak, overall case counts and mortality rates may significantly increase, according to a new model created by researchers at Penn State. The findings may help to improve interventions that aim to mitigate the effects of outbreaks such as COVID-19.
"Each year dozens of potentially lethal outbreaks affect populations around the world. For example, Ebola ravaged western Africa in 2014; Zika damaged lives in the Americas in 2015; and now we are in the midst of a worldwide pandemic -- COVID-19," said Katriona Shea, professor of biology and Alumni Professor in the Biological Sciences, Penn State. "Healthcare ...
2021-02-25
New York, NY (February 25, 2021) -- Early detection could reduce the number of African Americans dying from liver cancer, but current screening guidelines may not find cancer soon enough in this community, according to a study published in Cancer in February.
Black patients with liver cancer often have a worse prognosis than those of other racial and ethnic groups. Mount Sinai researchers sought to understand the reasons for this disparity by studying patients with hepatitis C, the leading driver of liver cancer in the United States.
Hepatitis C virus infection can result in cirrhosis, ...
2021-02-25
Feb. 25, 2021 - A new paper published online in the Annals of the American Thoracic Society provides a roadmap that critical care clinicians' professional societies can use to address burnout. While strongly needed prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, the roadmap has taken on even greater urgency due to reports of increasing pandemic-related burnout.
In "Professional Societies' Role in Addressing Member Burnout and Promoting Well-Being," Seppo T. Rinne, MD, PhD, of The Pulmonary Center, Boston University School of Medicine, and co-authors from a task force created by the Critical Care Societies Collaborative (CCSC) describe a rigorous process they used to document 17 major professional ...
2021-02-25
The Clalit Research Institute, in collaboration with researchers from Harvard University, analyzed one of the world's largest integrated health record databases to examine the effectiveness of the Pfizer vaccine against COVID-19. The study provides the first large-scale peer-reviewed evaluation of the effectiveness of a COVID-19 vaccine in a nationwide mass-vaccination setting. The study was conducted in Israel, which currently leads the world in COVID-19 vaccination rates.
The results of this study validate and complement the previously reported findings of the Pfizer/BioNTech ...
2021-02-25
Boston, MA - A new approach to pooled COVID-19 testing can be a highly effective tool for curbing the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, even if infections are widespread in a community, according to researchers at Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard. Simple pooled testing schemes could be implemented with minimal changes to current testing infrastructures in clinical and public health laboratories.
"Our research adds another tool to the testing and public health toolbox," said Michael Mina, assistant professor of epidemiology at Harvard Chan School and associate member of the Broad. "For public health agencies and clinical laboratories ...
2021-02-25
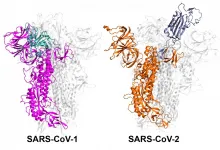
ROCKVILLE, MD - Coronavirus outbreaks have occurred periodically, but none have been as devastating as the COVID-19 pandemic. Vivek Govind Kumar, a graduate student, and colleagues in the lab of Mahmoud Moradi at the University of Arkansas, have discovered one reason that likely makes SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, so much more infectious than SARS-CoV-1, which caused the 2003 SARS outbreak. Moradi will present the research on Thursday, February 25 at the 65th Annual Meeting of the Biophysical Society
The first step in coronavirus infection is for the virus to enter cells. For this entry, the spike proteins on the outside of ...
2021-02-25
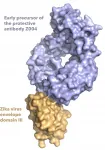
ROCKVILLE, MD - The Zika outbreak of 2015 and 2016 is having lasting impacts on children whose mothers became infected with the virus while they were pregnant. Though the numbers of Zika virus infections have dropped, which scientists speculate may be due to herd immunity in some areas, there is still potential for future outbreaks. To prevent such outbreaks, scientists want to understand how the immune system recognizes Zika virus, in hopes of developing vaccines against it. Shannon Esswein, a graduate student, and Pamela Bjorkman, a professor, at the California Institute of Technology, have new insights on how the body's antibodies attach to Zika virus. Esswein will present the work, which was published in PNAS, on Thursday, February ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Abnormal sodium levels in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 predict death or respiratory failure
Study findings can directly affect patient care, researchers say