How wildfires may have larger effects on cloud formation than previously thought
2021-02-25
(Press-News.org) As the frequency and size of wildfires continues to increase worldwide, new research from Carnegie Mellon University scientists shows how the chemical aging of the particles emitted by these fires can lead to more extensive cloud formation and intense storm development in the atmosphere. The research was published online today in the journal Science Advances.
"The introduction of large amounts of ice-nucleating particles from these fires can cause substantial impacts on the microphysics of clouds, whether supercooled cloud droplets freeze or remain liquid, and the propensity of the clouds to precipitate," said Ryan Sullivan, associate professor of chemistry and mechanical engineering. Understanding these impacts is a key factor in accurately modeling Earth's climate and how it could continue to change.
Building on research Sullivan's team in the Center for Atmospheric Particle Studies published last year, the authors collected a variety of different plant materials, burned them and analyzed the particles emitted in the smoke. In particular, the team was interested in ice nucleating particles, rare types of particles that can catalyze ice crystal formation in the atmosphere at higher than usual temperatures and thus greatly affect climatic processes, including cloud formation and whether a cloud precipitates or not. In fact, most precipitation over land starts from ice-containing clouds.
While it was already widely known that particles freshly emitted by the burning of biomass - like tall grasses, shrubs, and trees - can impact ice nucleation greatly, Sullivan's team was interested in finding out the effects of these particles as they traveled for days and weeks in the atmosphere and experienced chemical aging. With a specialized chamber reactor, mass spectrometers, electron microscopy, and an innovative microfluidic droplet freezing technique, the researchers analyzed the particles emitted by the burning of various types of plant material as occurs in wildfires and prescribed burns, and simulated the aging processes these particles would undergo in the atmosphere.
A diagram showing the various aging processes of biomass-burning aerosol in the atmosphere.
Typically, ice nucleating particles lose their potency as they age in the atmosphere, but in this study, the researchers found that the ice nucleating ability of particles emitted by burning biomass actually increased as they experienced simulated atmospheric aging. This represents a very different framework for considering how the climate-forcing properties of a major episodic source of particles evolve in the atmosphere.
"This is because atmospheric aging drives the loss of particle coatings initially present on the smoke particles that conceal the ice-active surface sites," Sullivan explained. "Those sites are the mineral particles produced by the biomass fuel combustion itself that we reported last year in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences."
The data from this study could have a major impact on future research into wildfires and climate change, said Lydia Jahl, who recently received her Ph.D. in chemistry from Carnegie Mellon in Sullivan's group.
"We estimated that burning just one square meter of grassland could influence the concentration of ice nucleating particles in hundreds of thousands of cubic kilometers of the atmosphere," Jahl said. "Climate modelers could use our data further to determine how wildfire emissions influence the balance of incoming solar radiation and outgoing terrestrial radiation, among other cloud properties."
INFORMATION:
Other authors on this study were Thomas A. Brubaker, Bailey B. Bowers and William D. Fahy of Carnegie Mellon; Micahel J. Polen, now of McDaniel College; Leif G. Jahn, now of the University of Texas at Austin; Kerrigan P. Cain, now of NASA Glenn Research Center; and Sara Graves, now of the University of California, Los Angeles.
Funding for this study was provided by grants from the National Science Foundation (CHE-1554941, AGS-1552608, and CBET-1804737).
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-25
Caught between climate change and multi-year droughts, California communities are tapping groundwater and siphoning surface water at unsustainable rates.
As this year's below-average rainfall accentuates the problem, a public-private partnership in the Monterey/Salinas region has created a novel water recycling program that could serve as a model for parched communities everywhere.
As Stanford civil engineers report in the journal Water, this now urbanized region, still known for farming and fishing, has used water from four sources -- urban stormwater runoff, irrigation drainage, food processing water and traditional municipal wastewater ...
2021-02-25
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- When healthcare workers become ill during a disease outbreak, overall case counts and mortality rates may significantly increase, according to a new model created by researchers at Penn State. The findings may help to improve interventions that aim to mitigate the effects of outbreaks such as COVID-19.
"Each year dozens of potentially lethal outbreaks affect populations around the world. For example, Ebola ravaged western Africa in 2014; Zika damaged lives in the Americas in 2015; and now we are in the midst of a worldwide pandemic -- COVID-19," said Katriona Shea, professor of biology and Alumni Professor in the Biological Sciences, Penn State. "Healthcare ...
2021-02-25
New York, NY (February 25, 2021) -- Early detection could reduce the number of African Americans dying from liver cancer, but current screening guidelines may not find cancer soon enough in this community, according to a study published in Cancer in February.
Black patients with liver cancer often have a worse prognosis than those of other racial and ethnic groups. Mount Sinai researchers sought to understand the reasons for this disparity by studying patients with hepatitis C, the leading driver of liver cancer in the United States.
Hepatitis C virus infection can result in cirrhosis, ...
2021-02-25
Feb. 25, 2021 - A new paper published online in the Annals of the American Thoracic Society provides a roadmap that critical care clinicians' professional societies can use to address burnout. While strongly needed prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, the roadmap has taken on even greater urgency due to reports of increasing pandemic-related burnout.
In "Professional Societies' Role in Addressing Member Burnout and Promoting Well-Being," Seppo T. Rinne, MD, PhD, of The Pulmonary Center, Boston University School of Medicine, and co-authors from a task force created by the Critical Care Societies Collaborative (CCSC) describe a rigorous process they used to document 17 major professional ...
2021-02-25
The Clalit Research Institute, in collaboration with researchers from Harvard University, analyzed one of the world's largest integrated health record databases to examine the effectiveness of the Pfizer vaccine against COVID-19. The study provides the first large-scale peer-reviewed evaluation of the effectiveness of a COVID-19 vaccine in a nationwide mass-vaccination setting. The study was conducted in Israel, which currently leads the world in COVID-19 vaccination rates.
The results of this study validate and complement the previously reported findings of the Pfizer/BioNTech ...
2021-02-25
Boston, MA - A new approach to pooled COVID-19 testing can be a highly effective tool for curbing the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, even if infections are widespread in a community, according to researchers at Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard. Simple pooled testing schemes could be implemented with minimal changes to current testing infrastructures in clinical and public health laboratories.
"Our research adds another tool to the testing and public health toolbox," said Michael Mina, assistant professor of epidemiology at Harvard Chan School and associate member of the Broad. "For public health agencies and clinical laboratories ...
2021-02-25
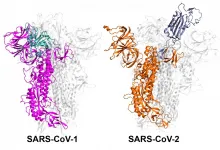
ROCKVILLE, MD - Coronavirus outbreaks have occurred periodically, but none have been as devastating as the COVID-19 pandemic. Vivek Govind Kumar, a graduate student, and colleagues in the lab of Mahmoud Moradi at the University of Arkansas, have discovered one reason that likely makes SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, so much more infectious than SARS-CoV-1, which caused the 2003 SARS outbreak. Moradi will present the research on Thursday, February 25 at the 65th Annual Meeting of the Biophysical Society
The first step in coronavirus infection is for the virus to enter cells. For this entry, the spike proteins on the outside of ...
2021-02-25
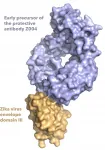
ROCKVILLE, MD - The Zika outbreak of 2015 and 2016 is having lasting impacts on children whose mothers became infected with the virus while they were pregnant. Though the numbers of Zika virus infections have dropped, which scientists speculate may be due to herd immunity in some areas, there is still potential for future outbreaks. To prevent such outbreaks, scientists want to understand how the immune system recognizes Zika virus, in hopes of developing vaccines against it. Shannon Esswein, a graduate student, and Pamela Bjorkman, a professor, at the California Institute of Technology, have new insights on how the body's antibodies attach to Zika virus. Esswein will present the work, which was published in PNAS, on Thursday, February ...
2021-02-25
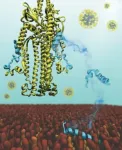
ROCKVILLE, MD - If the coronavirus were a cargo ship, it would need to deliver its contents to a dock in order to infect the host island. The first step of infection would be anchoring by the dock, and step two would be tethering to the dock to bring the ship close enough that it could set up a gangplank and unload. Most treatments and vaccines have focused on blocking the ability of the ship to anchor, but the next step is another potential target. New research by Defne Gorgun, a graduate student, and colleagues in the lab of Emad Tajkhorshid at the University of Illinois addresses the molecular details of this second step, which could inform the design of drugs that block it. Gorgun will present her research on Thursday, February 25 at the ...
2021-02-25
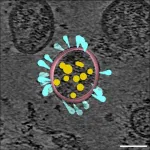
ROCKVILLE, MD - The virus that causes COVID-19 belongs to the family of coronaviruses, "corona" referring to the spikes on the viral surface. These spikes are not static--to infect cells, they change shapes. Maolin Lu, an associate research scientist at Yale University, directly visualized the changing shapes of those spike proteins and monitored how the shapes change when COVID-19 patient antibodies attach. Her work, which was published in Cell Host & Microbe in December 2020 and will be presented on Thursday, February 25 at the 65th Annual Meeting of the Biophysical Society informs the development of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] How wildfires may have larger effects on cloud formation than previously thought